* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell - Belle Vernon Area School District
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
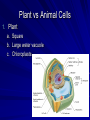
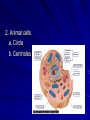
The Cell Basic Unit of Life The Cell I. Introduction to the cell The concept that all living material is made of cells or chemical products of cells is a CENTRAL, unifying theme in modern biology. II. Cell has all the characteristics of Life A. Grow D. Respond to stimuli B. Reproduce E. Homeostasis C. Move F. Organized III. The cell is the fundamental unit of life Cell Time Line of Discovery A. Discovery of the cell 1. 1665 Robert Hooke examine cork and noticed that the material was made up of “little boxes” or cells. (DEAD material only). 2. 1675 Anton van Leeuwenhoek microscopic creatures. Bacteria & protista. (Living material). Leeuwenhoek 3. 1805 Lorenz Oken - first initial statement of the cell theory. 4. 1838 Mathias Schleiden - conclude that plants were composed of cells. 5. 1839 Theodore Schwann - concluded that animals were composed of cells. 6. 1855 Rudolph Virchow - while studying disease, determined that cells only come from other cells. Cell Theory 1. All living material is made up of cells or the products of cells. 2. Cells come from preexisting cells. 3. The cell is the most elementary form of life. 4. Every cell has a cell membrane that separates it from the environment & from other cells. 5. Most cells are small 0.001 cm. Cell Diversity All living things are made of cells, but not all cells are identical. A. Size & Shape 2m long, nerve cells down a giraffe’s neck to 0.2 um. Most are around 10 - 50 um. Many are cuboidal (plants) or spherical (animals). Cells then are limited in size by the ratio of volume to surface area. B Two Types of cells 1. Prokaryote - No nucleus ex. Bacteria 2. Eukaryote – Nucleus ex. Protista, Fungi, Plants, Animals Plant vs Animal Cells 1. Plant a. Square b. Large water vacuole c. Chloroplasts 2. Animal cells a. Circle b. Centrioles Multicellular Organization Organization from very simple to very complex Division of labor occur within a cell. Certain organelles carry out specific functions. Each cell depends on all other cells to perform one or more of the life functions. Inner Life of a Cell Tissues, Organs, & Organ Systems 1. Molecule-group of atom held together by bonds. (water, phosphate). 2. Organelle-cell component that preforms a specific function. (Mitochondria SER, RER, Nucleus). 3. Cell-basic unit of life (Nerve Cell). 4. Tissue-group of similar cells that carry out a common function. (Nervous Tissue). 5. Organ-several type of tissues that together perform a bodily function. (Brain). 6. Organ System -a groups of organs that work together that perform a related task. (Brain, spinal cord, nerves). 7. Organism-a living thing. (Human).