* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Summary
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
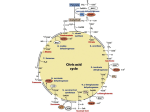
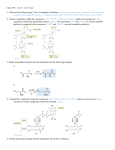
Pyruvate Oxidation: Pyruvate Dehydrogenase and the TCA Cycle Aerobic “respiration” in mitochondria: important for ATP synthesis and a source of intermediates for other biochemical pathways pyruvate (C3H3O3) + 4 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O 3 CO2 + 4 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + GTP First step: pyruvate dehydrogenase Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex Classic multienzyme complex: 3 enzyme proteins 5 cofactors: TPP, CoA-SH, lipoic acid, NAD +, FAD Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex Classic multienzyme complex: 3 enzyme proteins 5 cofactors: TPP, CoA-SH, lipoic acid, NAD +, FAD functional groups Pyruvate dehydrogenase function Animation: http://www. brooksco le.com/chemistry_d/templates/st udent_resources/sha red_resources/ animations/pdc/pdc.html Acetyl-CoA is oxidized in the citric acid (Kreb’s, TCA) cycle QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. TCA Cycle Recap TCA cycle: acetyl-CoA(C2H3O-CoA) + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O CoA-SH + 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + GTP Include pyruvate oxidation: pyruvic acid(C3H4O3) + 4 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O 3 CO2 + 4 NADH + 4 H+ + FADH2 + GTP • • • Complete oxidation of the pyruvate carbons Reduction of 4 NAD+ and one FAD Phosphorylation of one GDP The TCA cycle is a source of biosynthetic precursors But what happens when intermediates are removed from the cycle? Without intermediates, the cycle stops! “Anaplerotic” reactions replenish the intermediates. Pyruvate + CO2 + ATP + H2O OAA + ADP + Pi + 2 H+ A modification of the TCA cycle (glyoxylate cycle) lets plants and bacteria make carbohydrates from fats. to glucose Q uickTim e™ and a TI FF ( Uncom pr essed) decom pr essor ar e needed t o see t his pic t ur e. isocitric lyase malate synthase Summary •The TCA cycle gives complete oxidation of the pyruvate carbons. •And reduction of 4 NAD+ and one FAD. •And phosphorylation of one GDP. •The TCA cycle is a source of biosynthetic precursors. •Pyruvate carboxylase and the glyoxylate cycle replenish precursors •Replenishment of NAD + and FAD are also essential.