* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Review - Milan Area Schools
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
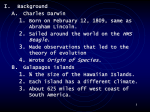
Name:________________ Evolution Review Concepts Chapter 14: Earth’s History A. Earth’s Age – More than _______________ years old B. _______________________Dating – The use of isotope decay to arrive at age of object. C. ________ – the amount of time it takes for a specific isotope to decay by one half D. Carbon _____– the isotope of Carbon 12 used to date _____________ materials i. Carbon 14 has been in the atmosphere at a relatively steady amount throughout time. ii. An organism stops absorbing Carbon 14 when _____________ iii. Carbon 14 has a half-life of 5,715 years; therefore, it is only useful for Organic remains ______________ years or less old. Carbon 14 Decay 120 Ammount of Carbon 14 (g 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 5000 10000 15000 20000 25000 30000 35000 Fossil Age (years) Chap 15. The Fossil Record: Part One A.Types of Fossils 1. _____________ – when an organism (usually flat) is covered by fine silt that then hardens into rock. This leaves a one-dimensional impression within the rock. 2. ___________– When a three dimensional organism dies and is covered with silt which hardens, the organism decays leaving a hollow impression of the exterior of the organism. 3. _________ – When a mold fills with minerals forming a three dimensional shape. B. Law of ________________ – law that states that successive layers of rock or soil deposited one on top of each other over time with the youngest layer on top and oldest on the bottom. C. __________ – name given to individual layers of rock or soil. d. Relative age – determination of fossil age in relation to another fossil based on location (depth) of strata where each was found. (allows you to say tha a fossil that was deeper is _________ that a fossil closer to the surface) E. Absolute age – Estimate of age based on all available tools (radioactive dating, strata location etc. F. Principle of fossil ____________= slight changes in fossils over time, new replacing old G. __________________ – the disappearance of an organism H. _______________ – the disappearance of many organisms at the same time. B. Biogeography – geographical distribution of fossils and related living organisms. Chap 15 Part Two: Theories of Evolution A. Lamarck – _____________ _____________(not determined by genes) passed on to offspring. (Theory replaced by Wallace and Darwin) B. Natural Selection i. Alfred Wallace – contemporary of Darwin, proposed natural selection theory just prior to Darwin. ii. Charles Darwin – credited with theory of natural selection, published “ The Origin of Species” in 1859 Basic events in natural selection: a. you have a population and it _________________ b. there is _______________ in the population (not all are same) c. the conditions in the ______________ change d. this causes a _____________ to survive and those organisms with an _____________ advantage are more likely to survive and reproduce e. over time, the _____________ changes and there are more individuals with the desired trait iii. Darwin 1. _________________ – Charles Lyell - Geological structures resulted from cycles of observable processes operating over large periods of time these are the same as modern day processes. (basically said that earth was much older than previously thought) 2. Visited the ______________Islands – while he was a naturalist aboard the HMS Beagle. While there he especially noticed these kinds of birds __________ 3. 1858 - Published “On The Origin Of Species By Means Of Natural Selection” (Origin of Species) 4. __________ with modification – Newer forms of fossils are modified descendants of older fossils 5. Modification by Natural Selection a. _______________ adapt to environment by changes in genetic makeup b. Individuals that are better able to pass traits on to larger number of offspring are the _______________ Chap 15 Part Three: Evidence for evolution: 1. _____________ Structures – Similar features that originated in a shared ancestor and have similar forms 2. _______________ Structures – Features that serve identical functions in independently evolved species 3. ______________Structures – Apparently useless features that may have had a function in the past 4. Patterns of evolution 1. ______________ – 2 species that evolve together like clownfish and anemones] 2. ______________ evolution – 2 species that are not related but have similar features like sugar gliders and flying squirrels 3. ________________ evolution: 2 species that shared a common ancestor but now have evolved different traits a. _____________ radiation - Darwin’s finches b. ______________ selection – different breeds of dogs Chap 16 Genetic Equilibrium A.Variation of traits in a Population Variation often has this shape: _____________ B. Causes of Variations a.Mutations b.Recombination during meiosis C. Changes in the ___________ __________________ (all of the genetic info in a population) depends on: a.Allele frequency b.Phenotype frequency ______________ drift = when population traits change because of a random event) B. Hardy – Weinberg Genetic Equilibrium 1. 5 Conditions for no evolution to occur a. No net __________ b. No immigration or Emigration c. The population is very _______________ d. Individuals randomly mate e. Selection does not occur C. Changes in population (selection types) A. _____________ selection: favors average individuals B. _____________ selection favors individuals at either extreme C. ______________ selection: favors individuals at 1 end (like all tall organisms) Species Concepts: ____________ Concept: Species defined by looks (similar structures, bones, characteristics) good for fossils ____________ Concept: Species defined as individuals who can successfully reproduce and produce fertile offspring Isolating Mechanisms: _______________ : physical separation by rivers, mountains etc ________________: non-physical separation of groups that live together and are capable of reproducing but don't A. Prezygotic: isolation ______________ reproduction (easier on females) like nocturnal and diurnal B. Postzygotic: isolation _____________ reproduction that produces infertile offspring Rates of Evolution: Theories on how fast evolution (or species formation) occurred: A. ________________ Equilibrium: theory that states that evolution went through long periods with little or no change with brief periods of lots of change B. __________________: This theory states that evolution of new species occurred slowly over a long period of time. * Modern theory suggests a mixture of the 2 and fossil evidence supports this