* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the cell
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
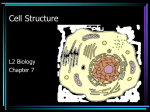
Title: A tour of the cell Intro: Cells are as basic to biology as atoms are to chemistry. ALL organisms are comprised of one or more cells. Most cells cannot be seen without magnification, therefore most peoples understanding of cells and their importance is relatively new. An Egg is the largest type of cell 1- The Cell Theory a- The microscope – 1- 1665 Robert Hooke – 1st person to look at cells (cork) – monk. Looked at non-living things under the microscope. 2- 1700 Anton Van Leeuwenhoek – built his own microscopes – a merchant (not a scientist). Worked with fabrics and used the microscopes he made to determine the “thread count.” 1st person to observe living things under the microscope (took scrapings off his teeth + saw bacteria under the microscope). 3- Cell theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. Development of this theory during the mid 17th century was made possible by advances in microscopy. This theory is one of the foundations of biology. The theory says that new cells are formed from other existing cells, and that the cell is a fundamental unit of structure, function and organization in all living organisms. Cells define our shape and how we work - function (all liver cells look alike, Kidney cells look alike no matter what animal they are from) Germans came up with cell theory: a- Matthias Schleiden – all plants are made of cells b- Theodore Schwann – all animals are made of cells c- Rudolf Virchow – all cells come pre-existing cells 4- Cell Theory – Modern interpretation Cells contain heredity info in the nucleus Proteins for all of life’s functions are produced in the cell Genetic material is past from 1 person to the next 5- Overview of animal and plant cells – differences: a- There are both similarities and differences in plant and animal cells. Animal cells contain centrioles important for cell division and small vacuoles to store food and water. Whereas, plant cells have cells walls (made of cellulose), chloroplasts (photosynthesis) and one large vacuole to store water. However, in general most of the organelles found in both plants and animals have the same function. They are much more alike than different. 6- Two major classes of cells a- Prokaryotic – 1- lack a nucleus and all other membrane bound organelles 2- much more simple in structure w/DNA concentrated in 1 area of the cell 3- appear much earlier in the fossil record – arrived earlier in evolution TWO GROUPS: a- The monera are the most common forms of bacteria and the ones we encounter all the time (causes strep throat) b- The archaea – ancient bacteria – more simple than the monera – arrived before the monera THREE TYPES: 1- halophiles – found in high salt concentrations ( especially in the Dead Sea + Great Salt Lake in Utah) 2- thermophiles – like to live in extreme heat such as in steam vents from volcanoes and geysers. Different bacteria thrive in different temperatures. 3 – Methanogens – bacteria that live in the absence of oxygen ( in methane). Swamp gas reflects this type of bacteria. They live in our digestive system – large intestine – they thrive on the methane produced in our digestive system. They produce vitamin E in our digestive system – goes into our blood and helps w/clotting. b- Eukaryotic 1- Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, which is the largest organelle in the cells. These types of cells have membrane bound organelles 2- larger than prokaryotic cells 3- came after prokaryotic cells in evolution 4- Kingdoms that contain eukaryotic cells are Animals, Plants, Fungus and Protists (1 cell organisms).