* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math Voc. - knomi.net
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
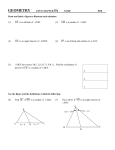
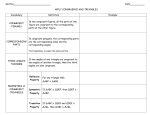
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Math Voc.
By: Reed Carpenter
Integer
• 1. A member of the set of positive whole
numbers {1, 2, 3, . . . }, negative whole
numbers {-1, -2, -3, . . . }, and zero {0}.
• 2. A complete unit or entity.
Rational Number
• A number that can be expressed as an integer
or a quotient of integers. For example, 2, -5,
and 1/2 are rational numbers.
Scientific Notation
• A method of writing or displaying numbers in
terms of a decimal number between 1 and 10
multiplied by a power of 10. The scientific
notation of 10,492, for example, is 1.0492 ×
104
Perfect Square
• An integer that is the square of an integer.
Irrational Number
• A number that cannot be expressed as a ratio
between two integers and is not an imaginary
number. If written in decimal notation, an
irrational number would have an infinite
number of digits to the right of the decimal
point, without repetition. Pi and the square
root of 2 (2) are irrational numbers.
Real Numbers
• A number that can be written as a terminating
or no terminating decimal; a rational or
irrational number. The numbers 2, -12.5, 3/7 ,
and pie are all real numbers.
Density Property
• The commutative property of addition says
that we can add numbers in any order. The
commutative property of multiplication is very
similar. It says that we can multiply numbers in
any order we want without changing the
result.
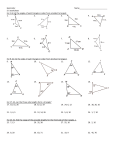
Adjacent Angles
• (Mathematics) two angles that have the same
vertex and a side in common
Coefficient
• 1. A number or symbol multiplied with a
variable or an unknown quantity in an
algebraic term, as 4 in the term 4x, or x in the
term x(a + b).
• 2. A numerical measure of a physical or
chemical property that is constant for a
system under specified conditions such as the
coefficient of friction.
Distance Formula
• Given the points ( 1, -2 ) and ( -3, 5 ), find the
distance between them.
Domain
• 1. Mathematics The set of all values that an independent variable
of a function can have. In the function y = 2x, the set of values that
x (the independent variable) can have is the domain. Compare
range.
• 2. Computer Science A group of networked computers that share a
common communications address.
• 3. Biology A division of organisms that ranks above a kingdom in
systems of classification that are based on shared similarities in
DNA sequences rather than shared structural similarities. In these
systems, there are three domains: the archaea, the bacteria, and
the eukaryotes.
• 4. Physics A region in a ferromagnetic substance in which the
substance is magnetized with the same polarization throughout.
Hypotenuse
• The side of a right triangle opposite the right
angle. It is the longest side, and the square of
its length is equal to the sum of the squares of
the lengths of the other two sides.
Legs Of A Right Triangle
• In a right triangle, the sides opposite to the
acute angles are called the Legs of a Triangle.
Range
• The difference between the lowest and
highest values.
In {4, 6, 9, 3, 7} the lowest value is 3, and the
highest is 9, so the range is 9-3 = 6.
Range can also mean all the output values of a
function.
Slope
• The rate of change of a line. For any two
points, it is the change in the y values divided
by the change in the x values, and is referred
to as the change in the rise over the change in
the run of a line.
Prism
• A solid with two congruent parallel faces,
where any cross section parallel to those faces
is congruent to them.
Scatter Plot
• A graph of plotted points that show the
relationship between two sets of data.
In this example, each dot represents one
person's weight versus their height.
Slope Intercept Form
• Slope Intercept Form is also called as
gradient, y-intercept form. Slope Intercept
Form is used to generate the Equation of a
straight line with a slope m and y - intercept c
of the line.
Absolute Value
• The absolute value of a number may be
thought of as its distance from zero.
Exponent
• An Exponent is a mathematical notation that
implies the number of times a number is to be
multiplied by itself.
Product
• Product simply means 'multiply'.
Pythagorean Theorem
• The theorem that the sum of the squares of
the lengths of the sides of a right triangle is
equal to the square of the length of the
hypotenuse.
Acute Triangle
• A triangle where all three internal angles are
acute (less than 90 degrees).
Probability
• Probability is the likelihood of something
happening in the future. It is expressed as a
number between zero (can never happen) to
1 (will always happen). It can be expressed as
a fraction, a decimal, a percent, or as "odds".
Factor
• To factor a number means to break it up into
numbers that can be multiplied together to
get the original number.
Variable
• Variables are (usually) letters or other symbols
that represent unknown numbers or values.
Evaluate
• 1. to determine or set the value or amount of;
appraise: to evaluate property.
• 2. to judge or determine the significance,
worth, or quality of; assess: to evaluate the
results of an experiment.
• 3. Mathematics . to ascertain the numerical
value of (a function, relation, etc.).
Quotient
• the result of division; the number of times one
quantity is contained in another.
Acute Angle
• An angle whose measure is between 0° and
90°.
Congruent
• 1. agreeing; accordant; congruous.
• 2. Mathematics . of or pertaining to two
numbers related by a congruence.
• 3. Geometry . coinciding at all points when
superimposed: congruent triangles.
Reciprocal
• 1. given or felt by each toward the other; mutual:
reciprocal respect.
• 2. given, performed, felt, etc., in return:
reciprocal aid.
• 3. corresponding; matching; complementary;
equivalent: reciprocal privileges at other health
clubs.
• 4. Grammar . (of a pronoun or verb) expressing
mutual relationship or action: “Each other” and
“one another” are reciprocal pronouns.
• 5. inversely related or proportional; opposite.
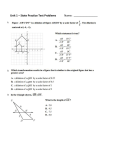
Vertex
• 1. the highest point of something; apex; summit; top: the vertex of
a mountain.
• 2. Anatomy, Zoology . the crown or top of the head.
• 3. Craniometry . the highest point on the midsagittal plane of the
skull or head viewed from the left side when the skull or head is in
the Frankfurt horizontal.
• 4. Astronomy . a point in the celestial sphere toward which or from
which the common motion of a group of stars is directed.
• 5. Geometry . a. the point farthest from the base: the vertex of a
cone or of a pyramid.
• b. a point in a geometrical solid common to three or more sides.
• c. the intersection of two sides of a plane figure.
Polygon
• a figure, especially a closed plane figure,
having three or more, usually straight, sides.
Scalene Triangle
• A triangle where all three sides are different in
length.
Area
• 1. any particular extent of space or surface; part: the
dark areas in the painting; the dusty area of the room.
• 2. a geographical region; tract: the Chicago area; the
unsettled areas along the frontier.
• 3. any section reserved for a specific function: the
business area of a town; the dining area of a house.
• 4. extent, range, or scope: inquiries that embrace the
whole area of science.
• 5. field of study, or a branch of a field of study: Related
areas of inquiry often reflect borrowed notions.
Perimeter
• 1. the border or outer boundary of a twodimensional figure.
• 2. the length of such a boundary.
• 3. a line bounding or marking off an area.
• 4. the outermost limits.
• 5. Military . a fortified boundary that protects
a troop position.
Circumference
• 1. the outer boundary, especially of a circular
area; perimeter: the circumference of a circle.
• 2. the length of such a boundary: a one-mile
circumference.
• 3. the area within a bounding line: the vast
circumference of his mind.
Obtuse Angle
• an angle greater than 90° but less than 180°.
Complementary
• 1. forming a complement; completing.
• 2. complementing each other.
Diameter
• Diameter is a line segment that passes
through the center of a circle with both its
endpoints lying on the circle.
Sum
• The result of adding two or more numbers.
Dividend
• The number that is divided by another
number in a division operation is called a
Dividend.
Divisor
• The quantity by which another quantity, the
dividend, is to be divided.
Median
• The median of a set of numbers is the number in the middle. For
example, in the set of numbers {4,6,25}, the median is 6. However
the numbers must be in order for the median to be in the middle.
If there are an even number of numbers, then the median is the
average of the last 2 middle numbers. There are 2 ways to find the
median of a set of numbers:
1. Rewrite the numbers in order, then find the one in the middle
2. Cross off the highest number, then the lowest, then the highest,
lowest, on and on, until only one number is left. That number will
be the median.
This second method works best when you have a large number of
numbers.
So, here is a problem for you:
What is the median of {9,2,1,6,3}?
Mean
• The mean of a set of numbers is their
average. You find the average of a set of
numbers by adding them up and dividing by
the number of numbers you have. So, the
mean of 3,4,6,9, and 3 is:
Mode
• The mode of a set of data is the value in the
set that occurs most often.
Pyramid
• A pyramid is a polyhedron with a polygonal
base and triangles for sides.
Quadrilateral
• A quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite
sides parallel.
Parallelogram
• A Parallelogram is a quadrilateral whose
opposite sides are parallel and equal and
opposite angles are equal.
Rectangle
• A 4-sided polygon where all interior angles are
90°
Reflection
• A Reflection is a transformation in which the
figure is the mirror image of the other.
Rate
• A rate is a ratio that compares two quantities
having different units of measure.
Trapezoid
• The trapezoid has 2 sides that are parallel
lines.
• Trapezoid is a quadrilateral with only one pair
of parallel sides.
Cylinder
• A Cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric
figure that has two congruent and parallel
bases.
Octagon
• A polygon with eight sides is called an
octagon.
Pentagon
• Pentagon is a polygon with five sides.
Right Triangle
• The longest side of a right triangle. The side
opposite the right angle.
Rhombus
Lowest Terms
X- Axis and Y- Axis