* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gametes Have a Single Set of Chromosomes
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
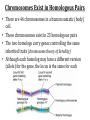
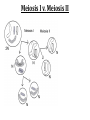
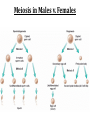
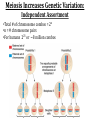
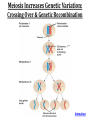
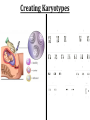
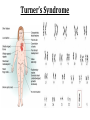
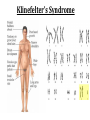
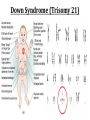
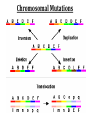
(8.12-8.24) Chromosomes Exist in Homologous Pairs • There are 46 chromosomes in a human somatic (body) cell. • These chromosomes exist in 23 homologous pairs • The two homologs carry genes controlling the same inherited traits (chromosome theory of heredity) • Although each homolog may have a different version (allele) for the gene, the locus is the same for each Autosomes v. Sex Chromosomes • Only the first 22 of the 23 chromosome pairs are definite homologs. (The autosomes) • The 23rd pair contains the sex chromosomes (X/Y). • Females have two Xs; Males have an X and Y • Only small portions of X and Y are homologous Gametes Have a Single Set of Chromosomes • A cell with two homologous chromosomes is diploid (2n) • Gametes (egg & sperm) are haploid (1n) because they only have a single set of chromosomes • Fusion of the haploid cells produces a diploid zygote during fertilization Meiosis Reduces the Chromosome Number from Diploid to Haploid • Often referred to as “reduction division” meiosis is a cell division that forms haploid gametes in diploid organisms • Many stages closely resemble corresponding stages in mitosis • Preceded by duplication of chromosomes, followed by two consecutive divisions, Meiosis I and II Animation Meiosis I v. Meiosis II Meiosis in Males v. Females Meiosis Increases Genetic Variation: Independent Assortment •Total # of chromosome combos = 2n •n = # chromosome pairs •For humans 223 or ~8 million combos Meiosis Increases Genetic Variation: Crossing Over & Genetic Recombination Animation Linkage & Gene-Mapping •Genes that are located close together have a lower frequency of crossing over •By evaluating relative frequencies, geneticists can map the locations of genes on chromosomes Creating Karyotypes Non-Disjunction: Meiosis I v. Meiosis II Turner’s Syndrome Klinefelter’s Syndrome Jacob’s Syndrome/Super Male (XYY) • • • • • Acne Agression Tall stature Superior muscle strength Reduced muscle coordination Triple X/Super female Syndrome (XXX) • No unique physical features apart from tall stature. • It may be asymptomatic and diagnosed incidentally • There is an increased incidence of motor and cognitive impairment, and psychological problems • Fertility of affected females is normal • There is a slight increased risk of offspring with chromosomal abnormalities Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13) •Least common trisomy •More female fetuses survive to birth •Severe heart & kidney defects Edward’s Syndrome (Trisomy 18) • 25% die before within first month, only 10% survive past first year • Growth deficiency • Feeding difficulties • Breathing difficulties • Developmental delays • Kidney malformations • Structural heart defects Chromosomal Mutations