* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Groby Bio Page
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
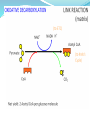
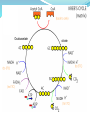
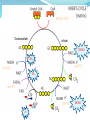
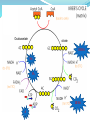
1.4.5. Link reaction and Krebs cycle Starter Complete Glycolysis summary sheet Learning Objectives Describe what the link reaction is Describe what happens during the Krebs cycle Explain the role of Success Criteria Outline the link reaction, with reference to decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetate and the reduction of NAD (Grade D-E) Explain that coenzyme A carries acetate from the link reaction to Krebs cycle (Grade C) hydrogen carrier molecules Outline the Krebs cycle, in the Krebs cycle including the roles of NAD and FAD, and substrate-level phosphorylation (Grade A-B) Respiration The process of respiration can be split into 4 stages. 1. 2. 3. 4. Glycolysis Link reaction Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Products of Glycolysis 2 reduced NAD (NADH + H+) 2 Pyruvate 2 ATP The Fate of Pyruvate? THIS DEPENDS ON THE AVAILABILITY OF OXYGEN!!! The fate of pyruvate 6 of 39 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Aerobic Respiration If O2 is present 3C pyruvate passes into mitochondria. Here it is completely oxidised forming CO2 and H2O. The second stage of aerobic respiration is the link reaction. The Link Reaction Cytoplasm Mitochondria The Link reaction Glycolysis The Krebs Cycle Links Glycolysis to the Krebs Cycle. The end product of the link reaction can enter the Krebs Cycle. NAD+ NADH + H+ Acetate (2C) Pyruvate (3C) Coenzyme A Acetyl coenzyme A (2C) CO2 Coenzyme A now combines with the The Pyruvate is decarboxylated (CO2) to form Start with Pyruvate produced in Acetate Glycolysis This produces Acetate Acetyl coenzyme It is also dehydrogenated (H+Aremoved) The Acetyl coenzyme A now enters Krebs cycle Link Reaction Pyruvate decarboxylase removes a carboxyl group from pyruvate Pyruvate(3C) in the form of CO2. Pyruvate dehydrogenase removes H atoms from pyruvate Decarboxylation NAD+ collects hydrogen ions. CO2 (1C) This forms reduced NAD + (NADH + H+) NAD Oxidation The remaining 2-carbon Reduction molecule combines with NADH + H+ Coenzyme coenzyme A to produce acetylcoenzyme A (acetyl CoA). (CoA) No ATP is produced in this reaction. Acetyl CoA (2C) Task Write down the equation for the link reaction Overall equation for one link reaction and Kreb cycle: Pyruvate + NAD + CoA acetyl CoA + reduced NAD + CO2 The Products of the Link Reaction go to the Krebs Cycle (takes place in matrix) So for each glucose molecule: 2 acetylcoenzyme A (go into the Krebs cycle) 2 Carbon dioxide (released as a waste products) 2 Reduced NAD (go to the electron transport chain) Krebs cycle – metabolic cycle Each step in the cycle requires enzymes to reduce the activation energy. The reactions all take place in the matrix of the mitochondria and are usually represented as a circular diagram. Oxaloacetate citrate DeNa DeNa A Fa... Na This little tune will help you to remember the Krebs Cycle. Remember, respiration is all about releasing energy from your food. Oxidation releases energy. When a carbon compound is oxidised, coenzymes are reduced. The coenzymes involved are: NAD and FAD. Carboxylation is the removal of CO2. DENA DENA A FA... NA DENA: Decarboxylation and production of reduced NAD DENA: Decarboxylation and production of reduced NAD A: Production of ATP FA... : Production of reduced FAD (The ‘...’ means a gap) NA: Production of reduced NAD Oxaloacetate citrate DENA NA FA DENA A Krebs cycle Acetyl CoA joins with the C4(oxaloacetate) group CoA is released to transport more pyruvate into the matrix A C6 fragment is formed (citrate) DENA C6 (citrate) is oxidatively decarboxylated. A C5 group is formed. The carbon is given off as carbon dioxide NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+ Krebs cycle The C5 fragment is oxidised and decarboxylated further to a C4 compound. Again the carbon removed forms carbon dioxide. NAD+ is further reduced to NADH + H+. DENA Krebs cycle The final stage in the cycle has the C4 (oxaloacetate) acceptor regenerated. ADP is reduced to ATP A FAD (Coenzyme)is reduced to FADH2 . FA There is a reduction of NAD+ to NADH + H+. NA Oxaloacetate citrate DENA NA FA DENA A (a) Pyruvate (3C) (b) Link reaction (c) C4 + C2= C6 (d) Recycling of CoA (e) Decarboxylation C6 to C5 and the reduction of NAD (f) Decarboxylation C5 to C4 and the reduction of NAD (g) C4 to C4 with the reduction of coenzymes FAD and NAD. ATP is made directly. This cycle follows one acetyl group. Each glucose that enters glycolysis will produce 2 acetyl groups. (h) C4 to C4 acceptor Krebs Cycle Summary Each Acetyl CoA entering the cycle results in: 1. 2 CO2 molecules 2. 1 ATP molecules (S.L.P) 3. 8 pairs of H atoms (Later used in the E.T.C to produce ATP) Used to reduce NAD and FAD. Three reduced NAD are produced and 1 reduced FAD per cycle. NAD = Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide FAD = Flavine adenine dinucleotide Importance of the Krebs cycle 1) Breaks down macromolecules into smaller ones 2) Produces H atoms that are carried by NAD to ETC for oxidative phosphorylation, to produce ATP. 3) Regenerates 4 –carbon molecule that combines with acetylcoenzyme A, which would otherwise accumulate. 4) Source of intermediate compounds used by cells in the manufactures of other important substances such as fatty acids, amino acids and chlorophyll Counting carbons - Plenary 28 of 39 © Boardworks Ltd 2009 Learning Objectives Describe what the link reaction is Describe what happens during the Krebs cycle Explain the role of hydrogen carrier molecules in the Krebs cycle 29 of 39 Success Criteria • Outline the link reaction, with reference to decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetate and the reduction of NAD (Grade D-E) • Explain that coenzyme A carries acetate from the link reaction to Krebs cycle (Grade C) • Outline the Krebs cycle, including the roles of NAD and FAD, and substrate-level phosphorylation (Grade A-B) © Boardworks Ltd 2009