* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter5
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual control theory wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Counterproductive work behavior wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
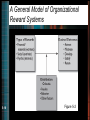
Organizational Behavior 5 core concepts Motivation in Practice: How to Bring Out the Best in People 5-2 McGraw-Hill/Irwin Organizational Behavior, Core Concepts Copyright © 2008 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives • Explain how goals contribute to performance management • Describe how feedback can provide information for improved performance • Define types of rewards, and summarize their relationship to performance • Describe how the effects and consequences of behaviors can influence future behaviors 5-3 Improving Individual Job Performance: A Continuous Process Situational Factors 5-4 Performance Improvement Cycle Desired Outcomes Figure 5-1 Motivation in Practice • Performance management – an organization-wide system for improving performance by setting, monitoring, and evaluating goals; providing feedback and coaching; and rewarding employees on a continuous basis 5-5 Types of Goals • Performance outcome goal – what an individual is trying to accomplish • Learning goal – defines the particular skills, knowledge, and abilities the employee will acquire 5-6 Management by Objectives • Management by objectives – management system incorporating participation in decision making, goal setting, and feedback 5-7 Goal Setting Process Step 1: Set goals Step 2: Promote goal commitment Step 3: Provide support and feedback 5-8 Setting Goals • • • • • 5-9 Specific Measurable Attainable Results-oriented Time-bound Feedback • Feedback – objective information about performance 5-10 Functions of Feedback • Instructional – instructs employees by clarifying roles or teaching new behavior • Motivational – serves or promises a reward 5-11 Recipients of Feedback • Characteristics of the recipient • Perception of feedback • Cognitive evaluation of feedback 5-12 Characteristics of the recipient • Employees with low self-esteem and low self-efficacy tend not to actively seek feedback • Employees who are high in the need for achievement respond more favorably to feedback 5-13 Nontraditional Feedback • Upward feedback – employees evaluate their boss • 360-degree feedback – comparison of anonymous feedback from one’s superior, subordinates, and peers with self-perceptions 5-14 Organizational Reward Systems • Extrinsic rewards – financial, material, or social rewards from the environment • Intrinsic rewards – self-granted, psychic rewards 5-15 A General Model of Organizational Reward Systems 5-16 Figure 5-2 Building Blocks of Intrinsic Motivation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5-17 Leading for meaningfulness Leading for choice Leading for competence Leading for progress Organizational Reward Systems • Pay for Performance – monetary incentives tied to one’s results or accomplishments – Also known as incentive pay or variable pay 5-18 Organizational Reward Systems • Team-based pay – incentive compensation that rewards individuals for teamwork, rewards teams for collective results, or both 5-19 Positive Reinforcement • Law of effect – behavior with favorable consequences is repeated; behavior with unfavorable consequences disappears • Respondent behavior – Skinner’s term for unlearned stimulus – response reflexes • Operant behavior – Skinner’s term for learned consequenceshaped behavior 5-20 Contingent Consequences in Operant Conditioning Figure 5-3 5-21 Contingent Consequences • Positive reinforcement – making behavior occur more often by contingently presenting something positive • Negative reinforcement – making behavior occur more often by contingently withdrawing something negative 5-22 Contingent Consequences • Punishment – making behavior occur less often by contingently presenting something negative or withdrawing something positive • Extinction – making behavior occur less often by ignoring or not reinforcing it 5-23 Schedules of Reinforcement • Continuous reinforcement – reinforcing every instance of a behavior • Intermittent reinforcement – reinforcing some but not all instances of a behavior 5-24 Intermittent Reinforcement 1. 2. 3. 4. 5-25 Fixed ratio Variable ratio Fixed interval Variable interval Schedules of Reinforcement 5-26 Behavior Shaping • Shaping – reinforcing closer and closer approximations to a target behavior 5-27