* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
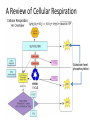
Chapter 6 ACQUIRING ENERGY Energy for Life • All energy comes from the sun – Producers convert light into chemical energy (glucose bonds) – Consumers eat/break bonds to release energy • Energy coupling reactions recycle components – Cellular respiration (break): • 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP – Photosynthesis (make): • ATP + 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Which reaction term applies to each? Redox Reactions • Coupled reactions that move electrons between molecules – Review: electrons form bonds and energy is released when they break (endergonic or exergonic?) • LEO goes GER – Lose an electron = oxidation • Glucose oxidized to CO2 – Gain an electron = reduction • O2 reduced to H20 • NAD+ reduced to NADH – What do all these reactions have in common? Electron Carriers • NADH and NADPH hold e-’s = high energy bonds – Carry 2 e-’s and a H+ – Precursor = NAD + and NADP + • Molecules oxidized e-’s released & captured – Dehydrogenase Cellular Respiration • Aerobic respiration – Requires O2 – High energy (ATP) yield – Glycolysis • Common to all paths • Energy from sugar (glucose) – Citric acid cycle (Kreb’s cycle) • Requires O2 – Oxidative phosphorylation (ETS and Chemiosmosis) • Requires O2 • Anaerobic respiration – Doesn’t require O2 – Organisms w/o mitochondria – Low energy yield Step 1: Glycolysis • Aerobic and anaerobic • In the cytoplasm • Starts with: – Glucose (6C’s) – 2 ATP • Ends with: – 2 pyruvate (3C’s) • Important products of this process: – Net 2 ATP • 4 ATP substrate-level phosphorylation – 2 NADH Intermediate Step: ‘Grooming’ • Starts with: – 2 Pyruvate (3C’s) • High energy product • Ends with: – 2 Acetyl-CoA (2C’s) • Important products of this process: – 2 CO2 • Decarboxylation – 2 NADH Step 2: Citric Acid Cycle • In the mitochondrial matrix • Starts with: – 2 Acetyl CoA • Ends with: – 4 CO2 • Important products of this process: – 2 ATP substrate level phosphorylation – 6 NADH – 2 FADH2 6 C’s 4 C’s 4 C’s Step 3: Electron Transport System (ETS) • In the inner mitochondrial membrane • Starts with: – 10 NADH (previous steps) – 2 FADH2 (citric acid cycle) – O2 • Ends with: – H2O • Important products of this process: – H + gradient Electrons and the Importance of Oxygen • Review – Electron energy determined by arrangement • e-’s further from the nucleus = more PE • e-’s dropping levels release E – Oxygen is highly electronegative • Integral protein complexes use a little less energy to ‘hold’ the electrons • Extra energy transports a H+ across out of the matrix into the intermembrane space • O2 is the last molecule to accept e-’s to become water Electrons from reactions in glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle Step 4: ATP Generation (Chemiosmosis) • In the inner mitochondrial membrane • Starts with: – H + gradient • Ends with: – 32 – 34 ATP • ATP synthase facilitates A Review of Cellular Respiration Substrate level phosphorylation Fermentation • If no O2 available • Starts with: – Glucose • Ends with: – Lactate or – CO2 and ethanol • Important products of this process: – 2 pyruvate – 2 ATP – 2 NADH/NAD+ • Makes yogurt, bread, alcoholic beverages