* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOLOGY STANDARD 4
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
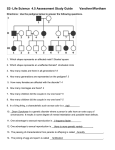
Understanding of the following terms are needed for mastery of the Genetics and Biotechnology Unit BIOLOGY STANDARD 4.0 GLOSSARY Allele - one form of a gene having two or more alternate forms, that occupy corresponding positions on homologous chromosomes Autosome - any chromosome other than the sex chromosome Carrier - an individual who is heterozygous for a recessive trait, and therefore will not express the trait, but may pass the trait on to its offspring. (Example is carrier of Sickle Cell anemia) Chromosomes - long coiled strands of deoxyribonucleic acid and protein that comprise the genetic material Co-dominant - a genetic pattern where the pair of alleles is equally expressed in the offspring for example a black chicken mated with a white chicken produce speckled offspring Cystic fibrosis - a genetic disorder caused by a recessive trait carried on the autosomes that caused mucus build up in the pancreas, lings, digestive tract, and other organs Diploid - referring to a cell having two sets (2N) of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid; the genetic material that contains information to code for proteins within the nucleus of the cell Dominant - the term used to describe the gene that is expressed when a single allele is present. In Mendel's experiments with peas, tallness was a dominant trait. Gamete - a cell that has the potential to combine with another cell for sexual reproduction; this cell contains only half the chromosome number of the organism (In) and has been formed by the process of meiosis Gene - the basic unit of heredity that codes for a particular protein Genotype - the genetic make-up of the organism represented by letters Haploid - cells that contains a single set of chromosomes (N) Heterozygous — the genetic condition of an organism with one dominant and one recessive allele for a particular trait Homologous chromosomes - a matching pair of chromosomes that possess genes for the same traits; one of the pair is inherited from the organism's father, and one comes from the mother Homozygous - the genetic condition of an organism that has two identical alleles for a given trait Hybrid - an organism that receives different genetic information from each parent for a particular trait Hybridization - the crossing of two breeds to obtain an offspring with characteristics of both Inbreeding - the technique of crossing two individuals with similar genotypes Incomplete dominance - the pattern of inheritance the produces offspring with a phenotype showing a blend of both parents for example the pink flowered offspring from red and white flowed phlox Karyotype - a photograph of a cell's chromosomes, arranged in homologous pairs, this picture can be used to detect problems originating in the chromosomes of an individual, even before birth Law of dominance - an inheritance pattern where the offspring will express a particular trait even if only receiving a single allele for that trait. Law of independent assortment — Mendel's second law, stating that each allele pair segregates independently during gamete formation Law of segregation - Mendel's first law, stating that each pair of alleles separate during the formation of gametes. Linkage group — genes that are found close together on the same chromosome Meiosis - the type of cell division that forms cells containing only half the chromosomes of the original cell. This is required to form gametes for sexual reproduction. Mendel - Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) established the basic principles of heredity by breeding garden peas in an Augustinian monastery Multiple alleles - three or more different alleles for a single gene found in a population that control a particular trait, like blood type alleles. Mutation - spontaneous change in a gene or chromosome Pedigree - a chart showing how a trait is inherited in a family Phenotype - the physical appearance of an organism Polygenic - a pattern of inheritance that involves many genes controlling a trait such as eye color, skin color, and height Protein synthesis — the process of putting together amino acids to form proteins; controlled by DNA Punnett square - a chart used to predict all possible genotypes from all the gametes of a given set of parents Recessive - the allele that is not expressed in the phenotype unless the organism in homozygous for that allele Replication - the process of making exact copies of DNA for the production of new cells RNA - ribonucleic acid aids DNA in the production of proteins; there are three forms of RNA, messenger, ribosomal, and transfer Sex chromosome - chromosome containing the genetic information to code for the sex of the organism Sex-linked - genes found on the X or Y chromosomes Sickle cell anemia - genetic disorder caused by recessive autosomal inheritance; the red blood cells are sickle-shaped and unable to transport oxygen efficiently Synapsis - the pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis Tay - Sachs - a genetic disorder that causes complex lipids to collect in the brain, leading to death in early childhood Test cross - breeding of an organism of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the genotype of the unknown individual. The ratio of phenotypes in the offspring determines the unknown genotype. Transcription - the process of copying the DNA code onto a strand of mRNA Translation - the process of synthesizing amino acids into proteins with the aid of RNA