* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bioinformatics
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
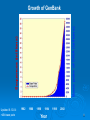
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
BIOINFORMATICS مدرس :جناب آقای دکتر توحید خواه تنظیم :رضا صفری()85233515 1 DEFINITION Any use of computer to handle biological information. (Tk ATTWOD,…,intrud to bioinf.99) با این تعریف موضوعاتی چون med imaging-image analysis-AI وneural network جزو .بیوانفورماتیک هستند در عمل این اصطالح به معنی استفاده از کامپیوتر جهت تعیین محتویات .)computational molecular biology( مولکولی عناصر زنده Fredj Takaya –Institute Pasteur: The mathematical ,statistical & computing methods that aim to solve biological problems using DNA and amino acid sequences and related information. 2 Definition… . وارد منابع گردید91 اصطالح بیوانفورماتیک نسبتا جدید واز سال و توسعه الگوریتم ها وdatabase حرکتهایی در زمینه ساخت60 در دهه انجام شد کهsequence analysis کشف بیولوژیکی با کمک . گفته میشدmolecular evolution : bioinformatics عناصر تشکیل دهنده Biology Computerscience(computational biology) Mathematics(biomathematics) Informatics Statistics 3 Bioinformatics vs computational biology. Bioinformatics is concerned with the information. Comp.biology is concerned with the hypothesis. Bioinformatics is also often specified as an applied subfield of the more general discipline of biomedical informatics. 4 bioinformatics medical informatics Tool-users public health informatics Tool-makers algorithms databases infrastructure 5 6 ?Why does bioinformatics appear انجام تحقیقات در آزمایشگاه وقت گیر و هزینه بر رشد انفجاری داده های بیولوژیکی طی چند دهه حجم دادها هر 15ماه دو برابر می شود. حجم دادها در یک آزمایشگاه ژنتیک روزانه 100گیگا بایت است. داده های حجیم نیاز به وجود databaseهای کامپیوتری تا ذخیره –دسته بندی وایندکس گذاری شده و ابزارهایی بوجود آید تا این داده ها قابل دسترسی آسان و آنالیز باشند. در ابتدای انقالب ژنی توجه ویژه معطوف به تولید و حفظ داده ها بمنظور ذخیره اطالعات بیو لوژیکی (توالی اسید آمینه و نوکلئوتیدها). پسشرفت های قابل مالحظه در تکنولوژی کامپیوتر: ()CPU,disk storage,internet 7 Sequences (millions) Base pairs of DNA (billions) Growth of GenBank Updated 8-12-04: >40b base pairs 1982 1986 1990 1994 Year 1998 2002 8 Central dogma of molecular biology DNA genome RNA transcriptome protein proteome Central dogma of bioinformatics and genomics 9 Aims of Bioinformatics 1.Biological database: A large ,organized body of persistent data , usually associated with computerized software designed to update,query,and retrieve components of the data stored within the system. Simple database:simple file,some records,same sets of informations. Additional requrements: easy access a method for extractingonly needed information to answer a specific qeustion. 10 There are three major public DNA databases EMBL Housed at EBI European Bioinformatics Institute GenBank DDBJ Housed at NCBI National Center for Biotechnology Information Housed in Japan 11 List of URL 12 NCBI (natioal center for biotechnology information) www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov Entrez: a unique search and retrieval system access to many databases for exam: Entrez protein DB crosslink to Entrez Taxonomy DB(finding tax. Inf for the species from which a prot seq was derived. 13 Entrez integrates… • the scientific literature; • DNA and protein sequence databases; • 3D protein structure data; • population study data sets; • assemblies of complete genomes 14 Entrez is a search and retrieval system that integrates NCBI databases 15 Four ways to access DNA and protein sequences [1] Entrez Gene with RefSeq [2] UniGene [3] European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) and Ensembl (separate from NCBI) [4] ExPASy Sequence Retrieval System (separate from NCBI) 16 27 Page 2.Data Analysis: The information in these DBs is useless until analysed . Bioinf. Tools can be used to obtain seq. of genes or proteins. Seq canbe analysed in many ways: Assembling: Mapping: Compare:a comparison of genes within a species or between diff.spp. can show similarities between protein function or relation between spp.(use to construct phylogenic trees) Phylogenetics: understanding the relatioships between diff. kinds of life 17 Analysis of: Gene expression: (measuring mRNA level by EST,SAGE,..tech) noise-prone (developing statistical tools to separate signal from noise).applies in tumor cells. Identification of genes that are expressed differentialy in a affected cell provide a basis for explaining the cause of illness and highlights potential drug targets. 18 Analysis of: Regulation: complex events starting with extracellular signal such as a hormone and leading to increase or decrease in the activity of one or more proteins. bioinformatics tech.have been applied to explore various steps in this process. Protein expression: protein microarrays,HT MS Mutations in cancer:point mutation,detction methods measure several hundred thousand sites throughout the genom,generate tetrabyte of data per experiment. 19 Prediction of protein structure : Amino acid seq.(primary structure) can be determined from the seq of gene that codes for it. Prediction of secondary,tertiary ,….. Protein structures. Using of homology to predict gene function: similar function with similar seq. Which part of prot. Is important in structure formation& Interaction with other prot. Homology modeling Hemoglobin & leghemoglobin(same structure &functiondiff. a.a) 20 Comparative Genomics: Establishment of the correspondence between gene(orthology analysis) or other genomic features. Gene(pointmutation), chromosom(duplication,lateraltransfer,inversion,delet….), whole genome (hybridization,polypeptidasion,…) RAPID SPECIATION 21 3.Evolutionary Biology: The study of the origin & descent of spp.and their change over time. New insight to molecular basis of disease. Investigating the function of homologs of a disease gene. Homology:two genes sharing a common evolut.history. Finding evolut.relationships between diff.forms of life. Closely related orgnisms have similar seq. Protein Family:proteins that show a significant seq. Protein Folds:distinct protein building block. Reconstruct the evolut. Rlationship between two species. Estimate time of divergence. 22 Bioinformatics&evolutionary biology Trace the evolution of a large number of organism by measuring changing in their DNA Compare entire genomes and the prediction of important factors Build complex computational models of populations to predict the outcome of the system overtime Track and share information on an increasingly large number of spp. 23 Measuring Biodiversity of an Ecosystem: Total genomic complement of a particular environment,from all of the spp. Present. Collect the spp.names,descriptions,genetic information,status and size of population,habitant needs,….. Genetic health of a breeding pool(agriculture) Endangered population(in silico) 24 4.Modeling biological systems: Computer simulations of cellular subsystems to analyze & visualize the complex connection of cellular processes. Artificial life(virtual evolution)attemps to understand evolutionary processes via comp. simulation of simple (artificial) life forms. Protein-protein docking: protein structure by XRC&NMR Predict p-p interaction only by these 3D shapes. The most straightforward application of the database is to predict the function of uncharacterised protein through their homology to characterised proteins. 25 Protein Modeling: DNA seq encode proteins with specific functions. In the absence of a protein structure ,by using protein or molecular modeling researchers try to predict 3D structure. By using Templates predict Target Helpful in proposing and testing biological hypothesis. Starting point to confirm a structure through XRC & NMR Increasingly important tool for scientists working to understand normal and disease-related process in living organisms. Changig of undesired action of an enzyme. 26 5.Genom Mapping: Serve a scaffold for orienting seq. information. Past: Manually mapping the genomic region time-consuming and painstaking process. Now: by new tec. A number of high quality genom-wide maps are available. comp.maps gene hunting: faster,cheaper,more practical By these advances,researcher‘s burden has shifted from mapping a genom to navigate a vast number of web sites and DBs 27 6.Map Viewer: A tool for visualizing whole genome or single chromosomes. Whole genom view:display a schematic for all of an organism‘s chromosomes. Map view: show one or more detailed maps for a single ch. Using Map viewer ,researchers can find answers to question such as: Where does a particular gene exist within an organism`s genome? Which gene are located on a particular chromosome& in what order? What is the corresponding seq. data for a gene that exist in a particular chromosome region? What is the distance between two gene/ 28 An important aspects of complete genom is distinguish between coding & non-coding region. The biggest excitement : availability of complete genom seq. for diff. organism. 29 >100,000 species are represented in GenBank all species 128,a941 viruses 6,137 bacteria 31,262 archaea 2,100 eukaryota 87,147 30 Human Genome project The greatest achievment of bioinformatics methods. 31 A typical scenario Post-natal genotyping Assess susceptibility or immunity From specific disease&pathogens Early detection of illness Unique combination of vaccines Minimising healthcare costs 32 Rapid progress of bioinformatics Advances in the diagnosis,treatment,and prevention of many genetic disease Bioinformatics has transformed the biology from purely lab-based science to an information science 33 34 35 36