* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Inheritance patterns... Two categories of traits : Any trait
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
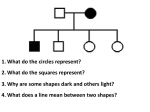
Types of Inheritance patterns... Two categories of traits : Any trait whose gene is found on the X or Y chromosomes is a sex-linked trait. The trait will show up in one gender more than the other. Ex. Male pattern baldness Color blindness Hemophilia Muscular Dystrophy An affected female would have to have inherited two copies, one on each X chromosome. A male would only have to inherit ONE copy on his one and only X chromosome. Any trait whose gene is a part of chromosome pairs 1-22 ( autosomal, or non-sex chromosomes) is an autosomal trait. Affects both genders equally. Autosomal Inheritance Patterns Autosomal Recessive, Autosomal Dominant, Codominant Autosomal Recessive... Classic Mendelian recessive allele. Only pure recessive shows it (ex. Blue eyes). If both parents are hybrids, 25 % of kids will get it. Occurs in only a small part of any normal population. Tay-Sachs disease, PKU, and Albinism Ex. Tay-Sachs disease : Fast PNS and CNS deterioration before age 1, blindness, muscle inactivity, mental disabilities, quick death. Caused by undigested fat collecting in brain cells...no appropriate enzyme to digest it...cells expand....brain dies. Ex. Phenylketonuria (PKU) : Cannot convert the chemical phenylalanine to tyrosine normally, gene making the necessary enzyme is defective. Unusual products of this screwed up process damages the CNS, disabled within months of birth unless diagnosed with routine newborn test. Ex. Albinism : Normal pigment (melanin) for eyes, skin, and hair color cannot be made. White / pink appearance. Sun sensitive. Autosomal Dominant... If you inherit it, you show it. A classic Mendelian dominant allele. ( TT and Tt both show it, tt doesn’t....ex. Stubby fingers)...if one parent shows it, half the kids show it. Very common in a normal population. Sometimes these genes mutate by sheer fluke, and the very rare condition it causes cannot be hidden once inherited. Ex. Progeria : Rapid aging, 1 in 8M births, mutated dominant gene influencing cell division and chromosome condition. Ex. Huntington’s Disease : Another mutated dominant gene, progressive brain deterioration, loss of motor control, memory, speech after age 35. Autosomal Codominant... Hybrids are afflicted with something, but not as bad as the “full blown” pure recessive. Hybrids have a better chance of surviving. ( “heterozygous advantage”) Ex. Sickle Cell Anemia : Blood hemoglobin screwed up, frequent blood clots, swelling, pain, poor circulation. Early death. Trait Patterns in Pedigree Diagrams : Sex linked... hemophilia in the Royal Family of Russia....