* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sustainism is the New Modernism
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
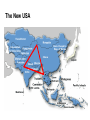
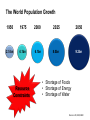
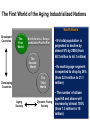
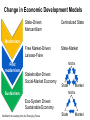
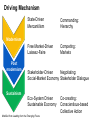
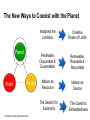
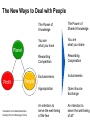
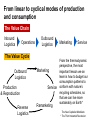
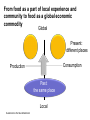
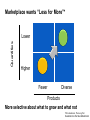
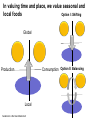
System Transformation New Approach for Achieving Stable Growth, Shared Prosperity, Secured Peace & Sustainable Planet Suvit Maesincee Sasin Institute for Global Affairs (SIGA) • Grand Challenges • Global Dynamics • Thriving in the 21st Century • Food for Culture Grand Challenges The 20th Century Challenges Four terrible global tragedies - Two brutal WWs - A global pandemic - A worldwide depression The 21st Century Challenges • • • • • • • Source: Divided Nations Global Economic Crisis The Eurozone Chaos The Arab Spring Uprisings Consequences of Climate Change Cyber-Attacks Pandemics The Nuclear Worst Case Scenario in Fukushima Interaction Between Nature & Humanity Nature Humanity Entropic Flow From Order to Disorder Negative-Entropic Flow From Disorder to Order Nature The World of Imbalance Humanity Human-Nature Imbalance Human-Human Imbalance Humanity Nature Nature The World of Rebalance Humanity Human-Nature Rebalance Human-Human Rebalance Humanity Nature Global Dynamics Global Dynamics Geo-Political Change Demographic Climate Change Change Global Dynamics Geo-Political Change Demographic Climate Change Change The Transition of Power Global GDP % World Economic Structure 75 Developed Countries 50 The Triad The Rise of the Rest Developing Countries 25 The Rest of the World 1820 70 1913 50 73 2005 Source: The Economist The Rise of Asia The New USA The Rise of the Asian Middle Class Sector In the year 2000, the middle classes in East Asia and the Pacific region were estimated to be around one sixth of the total global middle class (approx 72 million people or 1.4% of the global population) In 2030, the World Bank predicts this proportion will rise to nearly half of the total global middle class , approx 600 million people or 8.9%, accounting for 7.7% of global income Source: Bussolo, Maurizio (2007) World Bank, Australian Government Global Dynamics Geo-Political Change Demographic Climate Change Change The World Population Growth 1950 1975 2000 2025 2050 2.5 bn 4.1bn 6.1bn 8.0bn 9.2bn Resource Constraints • Shortage of Foods • Shortage of Energy • Shortage of Water Source: UN, FAO, BBC The First World of the Aging Industrialized Nations South Korea Developed Countries The First World North America, Europe, and Asia’s Pacific Rim The Second World The Third World Developing Countries Aging Society Dynamic Young Society • It’s total population is projected to decline by almost 9% by 2050 (from 48.3 million to 44.1 million) • Its working-age segment is expected to drop by 36% (from 32.9 million to 21.1 million) • The number of citizen aged 60 and above will increase by almost 150% (from 7.3 million to 18 million) The Third World of fast growing, young, and increasingly urbanized countries with poorer economies and often weak governments Developed Countries • Today, roughly nine out of ten children under the age of 15 live in developing countries The First World The Second World Developing Countries Aging Society • Over 70% of the world’s population growth, between now and 2050, will be concentrated in The 24 countries, all of Third which are classified by World the World Bank as low income or lower-middle Dynamic Young income Society The Second World of fast growing & economically dynamic countries with a healthy mix of young and old inhabitants Thailand’s Potential Supportive Ratio The First World 7 The Second World Brazil, Iran, Mexico, Thailand, Turkey, and Vietnam The Third World 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 2000 2020 Source: Kua Wongboonsin 2050 Global Dynamics Geo-Political Change Demographic Climate Change Change Asean countries are likely to face more severe consequences of the climate change than the global average due to limited adaptive capabilities Level of Complexity and Integration Local Climate Change Action parallel to Global Action Renewed Local Government Warsaw Climate Roadmap to 2015 Local Climate Action Durban Adaptation Charter The Global Cities Covenant on Climate (Mexico Pact) and the carbon Cities Climate Registry Cancun Agreement Copenhagen World Catalogue of Local Climate Commitment Local Government Climate Roadmap World Mayors Council and others Voluntary climate action 1990 Durban Copenhagen Accord Bali action Plan Global Climate Action Kyoto Protocol UNFCC 2005 2007 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Governing for Sustainability, p. 157 Food and Fuel Security • • Food • • • • • Fuel • Focus on climate change mitigation or resilience plan Improve farm productivity through education and other supportive measure i.e. land utilization, irrigation system, infrastructure and technology etc. Offer incentive to attract more investment on food production Form a collaborative network with other countries to do R&D on food security issue Improve energy efficiency Encourage on renewable energy Classify and separate type of food base on purpose i.e. food for hunger and food for energy and formulate plan focusing on the purpose of each type of food Form a collaborative network with other countries to do R&D on energy issue Offshore Farming The 1st Wave Manufacturing The 2nd Wave Services The 3rd Wave Food & Agriculture Resource wars – the world will demand 70 percent more food by 2050, outstripping population growth Cash-rich Arab and Asian governments are buying up arable farmland all over developing world - Chinese businesses are investing in South America and Africa, not only to gain access to commodities, but to get in position to profit from sales to the emerging middle class - China is also buying up large tracks of land throughout Africa to produce biofuels and to produce food - India's companies have formed a consortium to invest in corporate farming of oilseeds in Latin America, most notably Uruguay and Paraguay Thriving in the st 21 Century The Systemic Transformation Framework Technology • Human life is mirrored in nature, and vice versa Nature • Balance the infinite growth imperative & the finite resources of Planet Earth Systemic Transformation • Bridging technology & real needs of society • It is not high-tech or low-tech, but appropriateness and sustainable solutions Humanity Capitalism • Capitalism with social and environmental balance Sustainism is the New Modernism, Leading from the Emerging Future In response to environmental imbalance & social inequality, we see a shift from the current Age of Postmodernism towards a New Age of Sustainism Modernism Postmodernism Sustainism • Make it • Use It • • Machinelike Environment • Socio-Technical Environment • Mirroring Nature in the Digital Environment Revitalize it * Modified from Sustainism is the New Modernism From Neo-Classical Paradigm to Ecological Paradigm Modernism Post-Modernism Planet Society Economy Business Sustainism Business Economy Society Planet Neo-classical Paradigm Ecological Paradigm The Earth as a subsystem of the Human Economy * Human Economy as a subsystem of the Earth’s Ecosystem * * Meme Wars : The Creative Destruction of Neoclassical Economics Change in Economic Development Models State-Driven Mercantilism Centralized State Free Market-Driven Laissez-Faire State-Market Modernism Post modernism NGOs Stakeholder-Driven Social-Market Economy State Market NGOs Sustainism Eco-System Driven Sustainable Economy Modified from Leading from the Emerging Future State Market Primary Societal Challenges State-Driven Mercantilism • Stability • Expansion Free Market-Driven Laissez-Faire • Growth • Distribution Stakeholder-Driven Social-Market Economy • Negative Externalities • Inequality Modernism Post modernism Sustainism • Green Society Eco-System Driven • Inclusive Growth Sustainable Economy Modified from Leading from the Emerging Future Driving Mechanism State-Driven Mercantilism Commanding: Hierarchy Free Market-Driven Laissez-Faire Competing: Markets Modernism Post modernism Stakeholder-Driven Negotiating: Social-Market Economy Stakeholder Dialogue Sustainism Eco-System Driven Sustainable Economy Modified from Leading from the Emerging Future Co-creating: Conscientious-based Collective Action You cannot have well humans on a sick Planet* We are seeking for • New ways to coexist with the planet • New ways to deal with people • New ways to secure profit *Thomas Berry, Cultural Historian The New Ways to Coexist with the Planet Planet Profit People Imagined the Limitless Creative Power of Limits Perishable, Disposable & Expendable Renewable, Reusable & Recyclable Nature as Resource Nature as Source The Search for Autonomy Sustainism is the New Modernism The Quest for Embeddedness The New Ways to Deal with People The Power of Knowledge The Power of Shared Knowledge You are what you have You are what you share Rewarding Competition Rewarding Cooperation Exclusiveness Inclusiveness Appropriation Open-Source Exchange An intention to serve the well-being of the few An intention to serve the well-being of all* Planet Profit People Sustainism is the New Modernism *Leading from the Emerging Future The New Ways to Secure Profit Planet Profit People Scale & Scope Scarcity & Proportionality Control Supply Chain Engaging in the Open Collaborative Network Productivity Generativity Efficiency Sustainability Utility Stewardship The Third Industrial Revolution, P.225 Malthus Vs. Smith • The tension between the bad news and good news today resembles what the world has faced before, at the onset of both the first and second industrial revolutions • That tension boils down to the worldviews of two scholars, Thomas Robert Malthus and Adam Smith, both of whom wrote in the late 1700s • Malthus argued that the growing population would overwhelm the world, leading to widespread famine. Smith argued that businessmen could adapt and innovate rapidly enough that productivity could increase faster than consumption • Where Malthus saw “Disaster,” Smith saw “Opportunity” • While over time there have been eruptions of famine and shortage in different parts of the world, Smith was right. As the first and second industrial revolutions unfolded, opportunity has trumped scarcity • We believe that history is repeating itself and that Smith will be right again Resource Revolution Fundamental Logics of Resource Revolution • Finding opportunities to substitute away from scarce resources • Eliminating waste throughout the system, from production though end use • Increasing “Circularity” –upgrading, reusing, or recycling products • Optimizing efficiency, convenience, safety, and reliability • Moving products, services, and the processes that develop or deliver them out of the physical world and into the virtual realm Resource Revolution Three Strategic Thrusts • Combining information technology, nano-scale materials science, and detailed understanding of biology with industrial technology ad infrastructure yields substantial productivity increase • Embedding high productivity economic growth in the developing world to support the 2.5 million new members of the middle class presents the largest wealth creation opportunity in a century • Capturing this opportunities requires a new approach to management Resource Revolution From Cost Advantage to Loss Advantage • Achieving superior efficiency in 21st century terms—”socio-efficiency”-results not in cost advantage, but in loss advantage • Loss advantage means an advantage in minimizing a business’s own direct cost, while also minimizing the social human, public and environment losses the business imposes on other economic actors • While businesses seeking a cost advantage are often irresponsible , shifting, hiding, and pushing costs onto others, business seeking a loss advantage are radically—indeed, disruptively—responsible: they take responsibility for the full spectrum of the costs and losses production occurs • Loss advantage happens by re-conceptualizing, organizing, and rebuilding production and consumption as a value cycle, instead of a value chain • Today’s innovators are discovering that building cycles instead of chains is the key to renewing resources for tomorrow, instead of merely exploiting them today The New Capitalist Manifesto The Missing Factor • GDP is a measure of the wealth that a country generates each year, but from a thermodynamic point of view, it is more a measure of the temporary energy value embedded in the goods or services produced at the expense of the diminution of the available energy reserves and an accumulation of entropic waste • All economic activity creates only temporary value, at the expense of the degradation of the resource base on which it depends • Along with capital and labor inputs, energy is the “missing factor,” accounting for the rest of the productivity and economic growth P202, 204 The Third Industrial Revolution From linear to cyclical modes of production and consumption The Value Chain Inbound Logistics Operations Outbound Logistics The Value Cycle Outbound Logistics Production & Reproduction Reverse Logistics Marketing Service Remarketing Marketing Service From the thermodynamic perspective, the most important lesson we an learn is how to budget our consumption patterns to conform with nature’s recycling schedules, so that we can live more sustainably on Earth* The New Capitalist Manifesto * The Third Industrial Revolution From Technical Productivity to SocioProductivity • Today’s challenge is achieving a better kind of efficiency altogether: Socio efficiency that minimizes both direct costs and full-spectrum losses, creating thicker value • To achieve gains to next-generation efficiency, all three— Walmart, Nike, and Interface—are innovating the cornerstone of industrial-age production itself: they are producing not in lines, but in circles • They are doing this not out of altruism, but because doing so unlocks radical new paths for strategy, competition, and ultimately a new source of advantage: Loss advantage • Simply, renewing resources for tomorrow is wiser than exploiting them today The New Capitalist Manifesto Food for Culture Food as total nourishment for the body, the senses, the mind and the earth • The entire food chain is reflected in what we eat, running from the soil to the plate Nature Food • It is beyond the modernist concept of nutritionism • Sharing food = creating community Culture Sustainism is the New Modernism Food for Culture • The disconnection between young people and the global food system is growing. - Most young people do not grow up wanting to be farmers. Consumers all over the world have forgotten basic cooking skills because of an overreliance on processed foods. • Agricultural diversity is declining: most diets in riche countries consist of just six foods, including maize, wheat, rice and potatoes. • Agriculture is looked down upon as a career and is often viewed as work for the poor or people who have no other options. • Farmers also lack access to markets, making it hard for them to earn an income from their work Danielle Nierenberg, Is Sustainability Still Possible? Transition Culture Reinstating the idea that food is something that grows near where you live, by someone you have some kind of a relationship with, and that you actually cook yourself Global Consumption Production Local Sustainism is the New Modernism Food Production and consumption occurred at the same place From food as a part of local experience and community to food as a global economic commodity Global Present: different places Consumption Production Past: the same place Local Sustainism is the New Modernism Marketplace wants “Less for More”* Quantities Lower Higher Fewer Diverse Products More selective about what to grow and what not *Chris Anderson, The Long Tail Sustainism is the New Modernism In valuing time and place, we value seasonal and local foods Option I: Shifting Global Consumption Option II: Balancing Production Local Sustainism is the New Modernism Every morning in Africa, a gazelle wakes up. It knows it must run faster than the fastest lion or it will be killed. Every morning a lion wakes up. It knows it must outrun the slowest gazelle or it will starve to death. It does not matter whether you are a lion or a gazelle. When the sun comes up, you better start running. African Proverb “If You want to go quickly, go alone; if you want to go far, go together.” African Proverb “It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to change.” Charles Darwin