* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate change
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
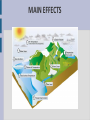
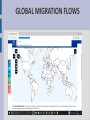
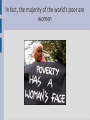
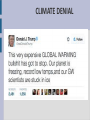
Climate change Climate change is become the main environmental issue of the XXI century INCREASING CO2 LEVEL Humanity's rapid industrial evolution over the last few centuries has substantially increased the CO2 content in the atmosphere due predominantly to three sources: the burning of fossil fuels such as oil, coal, peat and natural gas cement production large scale land use changes (grabbing) CARBON CICLE GREENHOUSE EFFECT If a planet's atmosphere contains greenhouse gases the atmosphere will radiate energy in all directions. Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, warming it. GREENHOUSE EFFECT GLOBAL WARMING The decadal average temperature over European land areas increased by approximately 1.3°C between pre-industrial times and the decade 2002-2011. GLOBAL WARMING MAIN EFFECTS Rising sea level as water gets warmer it takes up more space Melting glaciers glaciers continue to shrink almost worldwide Increased ocean acidity CO2 reacts with sea water Shrinking sea ice in 30 years summer sea ice has reduced the half MAIN EFFECTS CLIMATE ANOMALIES WHAT CAN WE DO? MITIGATION avoid the unmanageable ADAPTATION manage the unavoidable MITIGATION ADAPTATION prevention make dramatic changes to energy use civil protection actions and production changes in: promote renewable energy and innovative technologies stop deforestation building farming irrigation IN THE FUTURE ... The Mediterranean region has been identified as the main risk region in Europe for climate change, due to impacts on several sectors as tourism, agriculture (for example, decrease of grains production), forestry activities, infrastructures, energy and population health. THE CASE OF KIRIBATI ISLANDS Pacific islands are among the most vulnerable regions in the world to the impact of climate change. Remote and surrounded by the ocean, with small surface areas and low altitudes, these islands are at risk from both rapid-onset natural hazards, such as tsunamis, cyclones, typhoons and flooding, and slow-onset, such as soil erosion, droughts, coral bleaching, and salinization of soil and water. THE CASE OK KIRIBATI Kiribati comprehendes 3 main island groups with 33 scattered atolls and reef islands and one raised coral island. The islands of Kiribati could disappear within the next 30-60 years Ioane Teitiota, a Kiribati man, and his family arrived in New Zealand from Kiribati in 2007. After the expiration of their permits, they remained in the country illegally. After being arrested, they applied for refugee or protected person status. The New Zealand High Court rejected Teitiota’s claim. In 2013 Teitiota claimed the status of "climate change refugee" under the Convention of Geneva, referring to the part that regulates the Status of Refugees. ENVIRONMENTAL REFUGEES describes people who move due to the degradation of their environment, which can be linked to climate change. There are resemblances with people escaping war and persecution, except for the following distinctions: war refugees can at least hope to return home someday, environmental refugees can never return home; while the war refugees are protected by the Geneva Convention, the environmental refugees enjoy no such legal protection. man as a species has always been very mobile; we might as well refer to homo sapiens as homo migrans throughout history migration has been a survival tactic and adaptation strategy used in response to various environmental stresses we could go as far as to say that all of us originally migrated from Africa! GLOBAL MIGRATION FLOWS Climate change is affecting all countries, in all parts of the globe. But its impacts are distributed differently among: - regions - age classes - occupations - generations - income groups - genders Women in particular are most affected by Climate Change, since they lack the tools to adapt, mitigate and react to environmental changes. In fact, the majority of the world's poor are women TWO POSITIVE EXAMPLES: Ecuador “La naturaleza o Pacha Mama, donde se reproduce y realiza la vida, tiene derecho a que se respete integralmente su existencia y el mantenimiento y regeneración de sus ciclos vitales, estructura, funciones y procesos evolutivos. Toda persona, comunidad, pueblo o nacionalidad podrá exigir a la autoridad pública el cumplimiento de los derechos de la naturaleza.” Art. 71, Cap. 7, Derechos de la Naturaleza, Constitución de Ecuador, 2008 TWO POSITIVE EXAMPLES: Bolivia The government of Bolivia sets out key elements for Buen Vivir as part of Saving Planet Earth to Save Humanity: Denounce and end wars A world without imperialism or colonialism Basic services, such as water, education, health, communication, and collective transportation are human rights Consume what is necessary, put an end to consumerism, waste and luxury Promote diversity of cultures and economies Live well in harmony with Mother Earth CLIMATE DENIAL