* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DeconstructionforEnzymeUnit
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
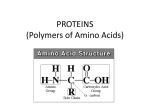
Program of Studies: SC-H-UD-U-2 Students will understand that within every cell are specialized parts for the transport of materials, energy transfer, protein building, waste disposal, information feedback and even movement. In addition, most cells in multi-cellular organisms perform specialized functions that others do not. SC-H-UD-S-7 Students will describe and classify a variety of chemical reactions required for cell functions. SC-H-UD-S-8 Students will describe the processes by which cells maintain their internal environments within acceptable limits. Core Content: SC-HS-3.4.3 Students will: describe cell regulation (enzyme function, diffusion, osmosis, homeostasis); predict consequences of internal/external environmental change on cell function/regulation. Cell functions are regulated. Regulation occurs both through changes in the activity of the functions performed by proteins and through selective expression of individual genes. This regulation allows cells to respond to their internal and external environments and to control and coordinate cell growth and division. DOK 2 Knowledge -Chemical reactions occur in the cell, and some are regulated by enzymes. -Cell functions are regulated. -Regulation occurs through changes in the activity of the functions performed by proteins and through selective expression of individual genes. - Regulation occurs through many processes such as: diffusion osmosis enzyme function active transport endocytosis exocytosis feedback loops such as the lac operon - Regulation through these processes leads to a state of homeostasis which is the maintenance of a state of Reasoning Skills • analyze the parts within a cell responsible for particular processes and create analogous models for those processes pos• identify a variety of specialized cell types and describe how these differentiated cells contribute to the function of an individual organism as a whole -predict consequences of internal/external environmental changes on cell function/regulation Explain the importance of homeostasis in life’s chemical reactions. DOK1 Explain the role of transport processes across the membrane in maintaining cell homeostasis. DOK2 Classify organic compounds based upon structure and Process Skills Products appropriate internal conditions. -Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. -Osmosis is a special type of diffusion involving water molecules. -Enzymes are proteins that regulate chemical reactions by lowing the activation energy needed to get the reaction started. - Enzymes operate in a narrow range of temperature and pH. Conditions out of this range can cause the threedimensional shape of the enzyme to change thus changing its function. This is called denaturation. -Enzymes have an area called the active site to which the substrate binds. The enzyme then causes a change in the substrate but is itself unchanged. If denaturation occurs, the active site is changed resulting in the substrate being unable to bind. -Inhibitors are molecules other than the substrate that bind to the active site of an enzyme. They prevent the substrate from binding thus stopping the enzyme from working. -Coenzymes -Enzymes are responsible for facilitating many reactions in the cell. This includes cell growth and division through the process of mitosis. function. DOK1 Compare and contrast osmosis and diffusion. DOK2 Compare and contrast active vs. passive transport. DOK2 Design an experiment and predict the type and direction of transport that will occur in a variety of conditions. DOK3 Describe and explain the reasons for the limits on cell size. DOK2 Describe and classify a variety of chemical reactions required for cell functions. DOK2 Describe the processes by which cells maintain their internal environments within acceptable limits. DOK2 Given a mitotic anomaly, students will predict the consequences to the daughter cells. DOK2 Describe and explain the role proteins/enzymes play in the movement of materials across the plasma membrane. DOK2 Design an experiment and predict the effects of various factors on enzyme activity. DOK3 Apply knowledge of enzyme activity to authentic situations such as fevers, hot tub use, snake and insect bites, etc. Identify a variety of specialized cell types and describe how these differentiated cells contribute to the function of - within every cell are specialized parts for the transport of materials, energy transfer, protein building, waste disposal, information feedback and even movement. In addition, most cells in multi-cellular organisms perform specialized functions that others do not. - the many body cells in an individual can be very different from one another even though they are all descended from a single cell and thus have essentially identical genetic instructions. Different parts of the instructions are used in different types of cells. an individual organism as a whole. DOK2