* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ectoderm Germ Layer
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Beta-catenin wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
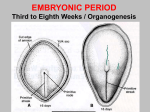
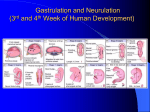
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin become localized to dorsal side? Beta-catenin evenly distributed before fertilization. Dsh and GBP translocated to dorsal side by kinesin • • • Rides on microtubule tracks laid down after fertilization during cortical rotation Dorsal surface enriched in Dsh and GBP Dsh and GBP inhibit GSK3 – Beta-catenin degrades on ventral side and is stabilized on dorsal side Beta-catenin activates other genes Turns on goosecoid gene in organizer Goosecoid mRNA can induce new axis Activates involution Determines dorsal mesoderm Represses Wnt8 Important in brain formation BMP Gradient Controls Dorsal/Ventral Axis VegT and Veg1 Present in vegetal cortical region Genes required for endoderm and mesoderm formation VegT antisence RNA causes epidermis only Xnr Gradient High Xnr – Organizer, goosecoid Med Xnr – Lateral mesoderm Low Xnr > high BMP4 + Xwnt8 – Ventral mesoderm Neural ectoderm induced by soluble factor? Controlled by goosecoid and beta-catenin? Neural structures default – epidermis induced by BMP's BMP – bone morphogenic protein Induce ectoderm to become epidermis Organizer secretes factors that block BMP from acting BMP inhibitors Noggin, Chordin and Follistatin Diffusable proteins Induced dorsal ectoderm to become neural Dorsalizes mesoderm cells Inhibits BMP's Found in dorsal lip then in the notochord Noggin mRNA rescues Dorsal Structures Localization of Noggin Localization of Chordin mRNA Expression of paraxial protocadherin Paraxial protocadherin expression Blue=paraxial protocadherin Red=chordin How is the ant/pos axis determined? During neurulation beta-catenin forms a gradient Greatest concentration at organizer • Becomes posterior end BMP Gradient Controls Dorsal/Ventral Axis Wnt Gradient Controls Anterior/Posterior Axis Gastrulation Induces Nervous System Chick Hensen's Node Can Induce Gene Expression in Frog Development of Neural Crest Establishing Neural Cells • Competence • • Specification • • Cell have been induced to be neuroblasts, but can develop into other cells if signals change Commitment (determination) • • Cell has the capacity to be induced to become neuroblasts Neuroblast has entered the neural differentiation pathway. Cannot be influenced by inhibitory signals. Differentiation • Neuroblast stop mitosis and express neuron specific genes. Wnt/b-catenin Stem cells from posterior neural plate form spinal chord Chick Neural Tube Closure Primary neurulation Directed by cells adjacent to neural plate Anterior Secondary neurulation Split in medullary chord Posterior Chick Neural Tube Closure Starts near anterior end Open at both ends until fully closed Anterior and posterior neuropore Primary Neurulation Divides ectoderm into three types of cells • Neural tube - brain and spinal chord • Epidermis – skin • Neural crest cells – peripheral nerves, pigment cells, glia etc... Primary Neurulation MHP Medial neural hinge point DLHP Dorsolateral hinge point Neural Tube Defects Spina bifida – failure to close posterior neuropore Anencephaly – failure to close anterior neuropore Folate Requirements During Pregnancy Folate-binding protein expressed on neural folds of mouse embryos. Causes of Folate Related Problems. Folate deficiency increases chance of neural tube closure defects in humans. Most women bearing children with neural tube defects have antibodies against folate-binding protein. Fungal contamination of corn produces fumonisin – alters function of folate-binding protein. • Teratogen – substance that alters development. Role of Cadherins in Neurulation Neural plate cells switch to N-cadherin expression just before neurulation. Injection of E-cadherin mRNA into neural plate cells or injection of N-cadherin to adjacent cells alters development Secondary Neurulation Medullary cord – condensed mesenchyme cells Splits to form neural tube Brain Development Nervous System • • Central Nervous System (CNS) • Brain and spinal cord. • Both contain fluid-filled spaces which contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). • The central canal of the spinal cord is continuous with the ventricles of the brain. • White matter is composed of bundles of myelinated axons • Gray matter consists of unmyelinated axons, nuclei, and dendrites. Peripheral nervous system. • Everything outside the CNS. • Spinal and cranial nerves Somite formation Derived from the paraxial mesoderm Laid down during Hensen's node regression Order of somite formation is predetermined FGF and Retinoic Acid Gradients Retinoic Acid Gradient • Posterior high => Anterior low • Retinoic acid production at posterior end – Retinoic acid degraded at anterior end Pre-somatic mesoderm has positional identity Cdx genes • Posterior end – Activated by retinoic acid • Drosophila caudal gene homologue • Cdx in conjunctions with other morphogenic factors activate Hox genes Hox Genes • Homeotic gene paralogues – Have same basic functions of Drosophila homeotic genes • Gene duplication caused multiple copies to form • Expressed along dorsal axis – – Neural tube, neural crest, paraxial mesoderm, surface ectoderm Anterior boundary of hindbrain to end of tail Control of Hox Genes Expression • Partially controlled by retinoic acid and Cdx genes – Transcriptional control Hom and Hox Gene Paralogues Segment Identity Which Hox gene are expresses in a particular segment determines segment identity. How was this determined? • Three types of experiments on Hox gene expression – Gene “knockout” (deletion) – Retinoic acid teratogenesis – Comparative anatomy Chick and Mouse Vertebral Pattern Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Mouse 4 13 6 4 Chick 14 7 12/13 5 Comparative Anatomy of Bird and Mouse Vertebrae Mice exposed to retinoic acid • • • • A,C Normal; B, D Retinoic acid Defects in facial and cranial skeleton Missing vertebrae Deformed pharyngeal arches Hox C-8 Deletion in Mouse • First lumbar vertebra transformed into thoracic