Structure and Function of Thymosin β4
... In order to determine the structure and binding motif of the actin binding site in thymosin β4, mutational analysis was performed. The binding motif observed in virtually all of the β thymosins is 17LKKTET22 and, furthermore, the first three residues are also found in many other actin binding protei ...
... In order to determine the structure and binding motif of the actin binding site in thymosin β4, mutational analysis was performed. The binding motif observed in virtually all of the β thymosins is 17LKKTET22 and, furthermore, the first three residues are also found in many other actin binding protei ...
Sequence and Structure Classification of Kinases
... similarity of fold alone does not necessarily indicate a common ancestor. Furthermore, structural information is much less readily available than sequence information. Thus, the most effective route to the identification of homologs and the prediction of protein function is provided by the integrati ...
... similarity of fold alone does not necessarily indicate a common ancestor. Furthermore, structural information is much less readily available than sequence information. Thus, the most effective route to the identification of homologs and the prediction of protein function is provided by the integrati ...
Single-Amino Acid Substitutions Alter the Specificity and Affinity of
... A ConserVed Lys or Arg Residue in PDZ Domains of PSD95 Is a Key Determinant for Interaction with nNOS. PSD95 contains three tandem PDZ domains that have distinct binding specificities. The second PDZ domain, which has been shown to interact with the PDZ domain of nNOS (11, 12), has a Lys residue in ...
... A ConserVed Lys or Arg Residue in PDZ Domains of PSD95 Is a Key Determinant for Interaction with nNOS. PSD95 contains three tandem PDZ domains that have distinct binding specificities. The second PDZ domain, which has been shown to interact with the PDZ domain of nNOS (11, 12), has a Lys residue in ...
Life Inside a Microtubule
... a direct relationship between a given kinase and actin phosphorylation1. For example, Ser and Tyr residues on actin are phosphorylated in response to insulin via unknown kinases, leading to reduced DNAse I binding1 (Fig. 1). Likewise, activation of the p21-activated kinase PAK1 leads to actin phosph ...
... a direct relationship between a given kinase and actin phosphorylation1. For example, Ser and Tyr residues on actin are phosphorylated in response to insulin via unknown kinases, leading to reduced DNAse I binding1 (Fig. 1). Likewise, activation of the p21-activated kinase PAK1 leads to actin phosph ...
ELM Database Entry Data Collection - Eukaryotic Linear Motif
... http://elm.eu.org/elms/elmPages/DEG_SCF_TIR1_1.html#abstract). It should be a biological abstract that reviews cellular systems in which the ELM(s) belonging to this functional site work and includes appropriate references (literature, PDB structures, related motifs in ELM,…). Free form text of at l ...
... http://elm.eu.org/elms/elmPages/DEG_SCF_TIR1_1.html#abstract). It should be a biological abstract that reviews cellular systems in which the ELM(s) belonging to this functional site work and includes appropriate references (literature, PDB structures, related motifs in ELM,…). Free form text of at l ...
Mechanistic Studies Of Drug Resistance Conferred By An ABC
... important modules in the C-terminal domain of DrrA that might be essential for conformational interplay between DrrA and DrrB during the catalytic cycle. One module present at the extreme C terminus of DrrA consists of two separate motifs, DEF and CREEM. CREEM motif together with its upstream region ...
... important modules in the C-terminal domain of DrrA that might be essential for conformational interplay between DrrA and DrrB during the catalytic cycle. One module present at the extreme C terminus of DrrA consists of two separate motifs, DEF and CREEM. CREEM motif together with its upstream region ...
Plakoglobin domains that define its association with the
... plakoglobin is required for its interactions with N-cadherin (Sacco et al., 1995). In this report we extend our studies to show that a domain near the N terminus is also necessary for plakoglobin to associate with classical cadherins. In addition, we show that a domain near the C terminus plays a ro ...
... plakoglobin is required for its interactions with N-cadherin (Sacco et al., 1995). In this report we extend our studies to show that a domain near the N terminus is also necessary for plakoglobin to associate with classical cadherins. In addition, we show that a domain near the C terminus plays a ro ...
The regulation of receptor protein tyrosine
... dimerization of the D2 domain can inhibit the phosphatase activity of PTPRs. A few models have been proposed to explain how phosphatase activity is inhibited by dimerization, but the precise mechanism is still not established. In this review, we discuss the regulatory mechanism of the phosphatase ac ...
... dimerization of the D2 domain can inhibit the phosphatase activity of PTPRs. A few models have been proposed to explain how phosphatase activity is inhibited by dimerization, but the precise mechanism is still not established. In this review, we discuss the regulatory mechanism of the phosphatase ac ...
Maternal control of the zebrafish organizer
... and F2 males of family no. 33. In 7 of 33 families, we were able to recover F2 females that transmitted the ichabod phenotype to their progeny (F3 embryos). Ratios of ichabod-transmitting females in four of the families generated from crosses of F1 siblings are presented. The number of F2 females ob ...
... and F2 males of family no. 33. In 7 of 33 families, we were able to recover F2 females that transmitted the ichabod phenotype to their progeny (F3 embryos). Ratios of ichabod-transmitting females in four of the families generated from crosses of F1 siblings are presented. The number of F2 females ob ...
uncorrected proof
... domains is 1.70 Å. This parameter compares best with the corresponding parameter found in permanent heterocomplexes, which form together with enzyme–inhibitor complexes the most complementary interfaces.21 In a-actinin-3, an eight-residue linker connects the two CH domains in a stable hairpin confo ...
... domains is 1.70 Å. This parameter compares best with the corresponding parameter found in permanent heterocomplexes, which form together with enzyme–inhibitor complexes the most complementary interfaces.21 In a-actinin-3, an eight-residue linker connects the two CH domains in a stable hairpin confo ...
Introduction Wnt signaling in development
... Furthermore, the strong amino- and carboxy-terminal transactivation domains of β-catenin transform TCF/LEF-1 into an active bipartite transcription factor. The conversion of a transcriptional repressor into an activator ensures that Wnt target gene expression is highly specific. It is clear from the ...
... Furthermore, the strong amino- and carboxy-terminal transactivation domains of β-catenin transform TCF/LEF-1 into an active bipartite transcription factor. The conversion of a transcriptional repressor into an activator ensures that Wnt target gene expression is highly specific. It is clear from the ...
The intercalated disc-associated Xin family of proteins in cardiac
... addition, a direct interaction between mXinα and the adherens junction protein β-catenin facilitates mXinα’s interaction with the actin filaments. Based on this in vitro characterization of mXinα, we proposed that mXinα may act as a direct link between the adherens junctions and actin cytoskeleton, ...
... addition, a direct interaction between mXinα and the adherens junction protein β-catenin facilitates mXinα’s interaction with the actin filaments. Based on this in vitro characterization of mXinα, we proposed that mXinα may act as a direct link between the adherens junctions and actin cytoskeleton, ...
Recombinant N-terminal Nucleotide
... halves, each containing up to six putative membrane-spanning a-helices and one cytoplasmically sided nucleotide-binding domain with characteristic Walker motifs A and B (7). P-glycoprotein structural organization is typical of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC)1 superfamily including yeast (8) and proto ...
... halves, each containing up to six putative membrane-spanning a-helices and one cytoplasmically sided nucleotide-binding domain with characteristic Walker motifs A and B (7). P-glycoprotein structural organization is typical of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC)1 superfamily including yeast (8) and proto ...
McClay et al.
... to bring development completely to the pluteus stage. It is the ‘priority region’ where differentiation begins. And when differentiation has begun, ‘from this center all other regions are determined in their role by a regulatory action” (cited in ...
... to bring development completely to the pluteus stage. It is the ‘priority region’ where differentiation begins. And when differentiation has begun, ‘from this center all other regions are determined in their role by a regulatory action” (cited in ...
The Wnt signaling pathway mechanisms
... homozygous functional disruption of Dvl2 includes double outlet right ventricle or ...
... homozygous functional disruption of Dvl2 includes double outlet right ventricle or ...
E-cadherin controls β-catenin and NF
... E-cadherin controls mesenchymal gene transcription siRNA and ΔTCF4 were affecting the transcriptional activity of this complex. We checked the requirement of β-catenin and TCF4 activity for the transcription of fibronectin and LEF1. In cells with expression of these genes, downregulation of β-cateni ...
... E-cadherin controls mesenchymal gene transcription siRNA and ΔTCF4 were affecting the transcriptional activity of this complex. We checked the requirement of β-catenin and TCF4 activity for the transcription of fibronectin and LEF1. In cells with expression of these genes, downregulation of β-cateni ...
β-catenin controls differentiation of the retinal pigment epithelium in
... the choroid. The RPE is vital for growth and function of the vertebrate eye and improper development results in congenital defects, such as microphthalmia or anophthalmia, or a change of cell fate into neural retina called transdifferentiation. The transcription factors microphthalmia-associated tra ...
... the choroid. The RPE is vital for growth and function of the vertebrate eye and improper development results in congenital defects, such as microphthalmia or anophthalmia, or a change of cell fate into neural retina called transdifferentiation. The transcription factors microphthalmia-associated tra ...
PDF
... Thus, Wnt signaling is required for the induction of posterior structures. β-Catenin-dependent Wnt signal transduction is a multi-step process that consists of several molecular components. It is initiated by secreted Wnt glycoproteins that bind to transmembrane Frizzled receptors (Angers and Moon, ...
... Thus, Wnt signaling is required for the induction of posterior structures. β-Catenin-dependent Wnt signal transduction is a multi-step process that consists of several molecular components. It is initiated by secreted Wnt glycoproteins that bind to transmembrane Frizzled receptors (Angers and Moon, ...
In the prevailing view Conducitn is usually considered to act as a
... head interaction surface of the axin DIX domain preventing its homopolymerisation, but leaves the tail interaction surface intact for interaction with Dvl2 (Fiedler et al., 2011). We propose that this results in blunting of Dvl2 polymers leading to smaller complexes no longer visible as puncta (see ...
... head interaction surface of the axin DIX domain preventing its homopolymerisation, but leaves the tail interaction surface intact for interaction with Dvl2 (Fiedler et al., 2011). We propose that this results in blunting of Dvl2 polymers leading to smaller complexes no longer visible as puncta (see ...
Tcf7l1 protects the anterior neural fold from adopting the neural crest
... Tcf7l1 and Tcf7l2 (alias Tcf3 and Tcf4) (Castrop et al., 1992). Tcf/ Lefs share several characteristic protein features, such as the Nterminal β-catenin-binding motif, GRG motifs for binding of Groucho/TLE co-repressors, and the HMG box containing the DNA-binding domain. Tcf7 and Tcf7l2 also contain ...
... Tcf7l1 and Tcf7l2 (alias Tcf3 and Tcf4) (Castrop et al., 1992). Tcf/ Lefs share several characteristic protein features, such as the Nterminal β-catenin-binding motif, GRG motifs for binding of Groucho/TLE co-repressors, and the HMG box containing the DNA-binding domain. Tcf7 and Tcf7l2 also contain ...
Binding
... EBA-175, BAEBL, and JSEBL all can bind sialic acid residues, but each recognises different erythrocyte sialoglycoproteins; receptor for EBA175 is human RBC receptor glycophorin A. Redundant pathways means that EBA-175 is not essential. X-ray structure of EBA-175 was solved with sialic acid derivativ ...
... EBA-175, BAEBL, and JSEBL all can bind sialic acid residues, but each recognises different erythrocyte sialoglycoproteins; receptor for EBA175 is human RBC receptor glycophorin A. Redundant pathways means that EBA-175 is not essential. X-ray structure of EBA-175 was solved with sialic acid derivativ ...
Two classic cadherin-related molecules with no cadherin
... of known classic cadherin family members (Oda et al., 2002). Instead, its extracellular region consists of two laminin globular domains (LGs) and one cysteine-rich EGF-like domain (CE) that partially matches with the sequence of the primitive classic cadherin domain (PCCD) complex that occurs in all ...
... of known classic cadherin family members (Oda et al., 2002). Instead, its extracellular region consists of two laminin globular domains (LGs) and one cysteine-rich EGF-like domain (CE) that partially matches with the sequence of the primitive classic cadherin domain (PCCD) complex that occurs in all ...
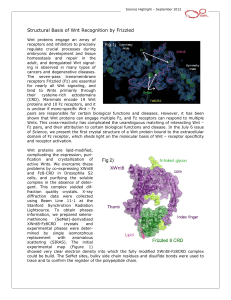
Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
Slide 1
... repeats (EC) and an intracellular catenin-binding domain (CBD). Only type I cadherins contain a conserved His-Ala-Val (HAV) cell adhesion recognition sequence in their first EC domain. Desmosomal cadherins contain in part an extended cytoplasmic domain (dotted box), and their CBD differs from type I ...
... repeats (EC) and an intracellular catenin-binding domain (CBD). Only type I cadherins contain a conserved His-Ala-Val (HAV) cell adhesion recognition sequence in their first EC domain. Desmosomal cadherins contain in part an extended cytoplasmic domain (dotted box), and their CBD differs from type I ...
Relation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
... follistatin (7-9). If the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway continues under control, biologic processes like proliferation, differentiation, and regulation of target genes’ transcription occur normally, but these target genes’ aberrant activation causes cancer and other serious diseases. In addition, ...
... follistatin (7-9). If the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway continues under control, biologic processes like proliferation, differentiation, and regulation of target genes’ transcription occur normally, but these target genes’ aberrant activation causes cancer and other serious diseases. In addition, ...