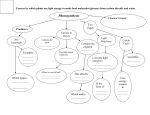
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SBI 4UI Test – Metabolic Processes: Cell Respiration
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
SBI 4UI Diagnostic Quiz: Metabolic Processes Name; Part A: Multiple Choice (answers go onto the answer sheet) 1. Which of the following does NOT occur during pyruvate oxidation? a. reduction c. decarboxylation b. hydration d. co-enzyme activity 2. When there is oxygen debt, the pyruvic acid will; a. be oxidized by NADH c. enter the mitochondria b. be converted to lactic acidd. d. all of the above are correct 3. Which of the following moves H+ ions into the intermembrane space? a. cytochrome Q c. glucose-6 phosphate b. cytochrome oxidase d. all the above are correct. 4. P680 is; a. a chlorophyll molecule b. used to reduce NADPH 5. The Calvin Cycle: a. occurs in the matrix b. releases O2 gas. c. d. D. part of photosystem I. all of the above are correct. c. fixes CO2 into glucose all of the above are correct. 6. Chemiosmosis: a. generates ATP molecules b. involves the proton channel c. d. occurs in cell respiration & photosynthesis all of the above are correct. 7. Glycolysis: a. occurs in the stroma b. produces 2 NADH c. d. uses 4 ATP for activation energy all of the above are correct. 8. Which process below does NOT occur in the mitochondria? a. The synthesis of BPG c. The use of Co-A as a carrier + b. The reduction of FAD d. The oxidation of Cytochrome Q 9. Photosynthetic reactions; a. are generally anabolic b. trap radiant energy c. d. occur in the chloroplast all of the above are correct 10. Antenna pigments; a. are in the Thylakoid b. transfer energy to P700 c. d. absorb different light frequency all of the above are correct. 11. The process to oxidize glucose into pyruvate is called; a. glycolysis c. chemiosmosis b. fermentation d. obligate respiration 12. Thylakoid is the inner membrane of the ; a. cytoplasm c. chloroplast b. mitochondria d. nucleus Part B; Circle TRUE or FALSE on the answer sheet. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Chemiosmosis moves H+ into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria. In the Kreb’s Cycle, malate is oxidized into fumarate. Aerobic cellular respiration harvests energy from organic compounds without O2. The total chemical potential energy in the reactants of photosynthesis is less than the total chemical potential energy in the products of photosynthesis. An overall goal of cellular respiration is to move hydrogen atom electrons from glucose to oxygen to form water. In C4 plants, the carbon fixation reduces photorespiration by pumping CO2 back into the Calvin Cycle. The Kreb’s Cycle generates ATP through substrate level phosphorylation The proton channel in the cristae moves protons from the matrix of the mitochondria to the intermembrane space. Spinach contains different pigamnets to maximize absorption of light frequencies,. Each Glucose eventually yields 2 ATP directly from the Kreb’s Cycle. The last acceptor of protons and electrons in the ETC is oxygen. The proton channel moves protons out of the intermembrane space. Part C: Identify the term described on the ANSWER SHEET on p. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. The name of the chemical fixed to CO2 in the Calvin Cycle? The name of the other oxidizing agent in the Krebs Cycle in addition to NAD+? The name of the enzyme that transfers the electron entering the mitochondrial ETC from NADH to Cytochrome Q AND pumps one H+? Which type of respiration is fermentation? It increases molecule to molecule in the ETC which explains why the electrons do not go back up the ETC. The location of the photosystem pigments inside the chloroplast? The name of the reducing agent transferred from the light dependent reactions to the light independent reactions? The name of the molecules combined in the calvin Cycle to yield 1 glucose? From the overall reaction of photosynthesis, how many water molecules were used as reactants? The name of the complex in the ETC that transfers electrons from PQ to Pc in chloroplasts? SBI 4UI Diagnostic Quiz: Metabolic Processes Answers Part A: Multiple Choice (answers go onto the answer sheet) Name; 1. Which of the following does NOT occur during pyruvate oxidation? a. reduction c. decarboxylation b. hydration d. co-enzyme activity 2. When there is oxygen debt, the pyruvic acid will; a. be oxidized by NADH c. enter the mitochondria b. be converted to lactic acid. d. all of the above are correct 3. Which of the following moves H+ ions into the intermembrane space? a. cytochrome Q c. glucose-6 phosphate b. cytochrome oxidase d. all the above are correct. 4. P680 is; a. a chlorophyll molecule b. used to reduce NADPH c. d. part of photosystem I. all of the above are correct. 5. The Calvin Cycle: a. occurs in the matrix b. releases O2 gas. c. d. fixes CO2 into glucose all of the above are correct. 6. Chemiosmosis: a. generates ATP molecules b. involves the proton channel c. d. occurs in cell respiration & photosynthesis all of the above are correct. 7. Glycolysis: a. occurs in the stroma b. produces 2 NADH c. d. uses 4 ATP for activation energy all of the above are correct. 8. Which process below does NOT occur in the mitochondria? a. The synthesis of BPG c. The use of Co-A as a carrier + b. The reduction of FAD d. The oxidation of Cytochrome Q 9. Photosynthetic reactions; a. are generally anabolic b. trap radiant energy c. d. occur in the chloroplast all of the above are correct 10. Antenna pigments; a. are in the Thylakoid b. transfer energy to P700 c. d. absorb different light frequency all of the above are correct. 11. The process to oxidize glucose into pyruvate is called; a. glycolysis c. chemiosmosis b. fermentation d. obligate respiration 12. Thylakoid is the inner membrane of the ; a. cytoplasm c. chloroplast b. mitochondria d. nucleus Part B; Circle TRUE or FALSE on the answer sheet. F1. Chemiosmosis moves H+ into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria. F2. In the Kreb’s Cycle, malate is oxidized into fumarate. F3. Aerobic cellular respiration harvests energy from organic compounds without O2. F4. The total chemical potential energy in the reactants of photosynthesis is less than the total chemical potential energy in the products of photosynthesis. T5. An overall goal of cellular respiration is to move hydrogen atom electrons from glucose to oxygen to form water. T6. In C4 plants, the carbon fixation reduces photorespiration by pumping CO2 back into the Calvin Cycle. T7. The Kreb’s Cycle generates ATP through substrate level phosphorylation F8. The proton channel in the cristae moves protons from the matrix of the mitochondria to the intermembrane space. T9. Spinach contains different pigments to maximize absorption of light frequencies,. T10. Each Glucose eventually yields 2 ATP directly from the Kreb’s Cycle. T11. The last acceptor of protons and electrons in the ETC is oxygen. T12. The proton channel moves protons out of the intermembrane space. Part C: Identify the term described on the ANSWER SHEET on p. 3. 1. The name of the chemical fixed to CO2 in the Calvin Cycle?pyruvate 2. The name of the other oxidizing agent in the Krebs Cycle in addition to NAD+? FAD 3. The name of the enzyme that transfers the electron entering the mitochondrial ETC from NADH to Cytochrome Q AND pumps one H+? NAD Dehydrogenase 4. Which type of respiration is fermentation? anaerobic 5. It increases molecule to molecule in the ETC which explains why the electrons do not go back up the ETC. electronegativity 6. The location of the photosystem pigments inside the chloroplast? thylakoid 7. The name of the reducing agent transferred from the light dependent reactions to the light independent reactions? NADPH 8. The name of the molecules combined in the Calvin Cycle to yield 1 glucose? G3P 9. From the overall reaction of photosynthesis, how many water molecules were used as reactants? 6 10. The name of the complex in the ETC that transfers electrons from PQ to Pc in chloroplasts? b6-f