* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 胆碱受体激动药
Survey
Document related concepts
CCR5 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of TRPV1 antagonists wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
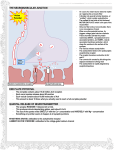
Cholinoceptoractivating drug Cholinoceptor-activating drug • Acetylcholine receptor stimulants • Cholinesterase inhibitors • Mimic acetylocholine Acetylcholine receptor stimulants • Classified by their spectrum of action depending on the receptor type • Activate muscarinic receptor • Activate nicotinic receptor Muscarinic receptor stimulants • Choline esters: acetylcholine, methacholine, carbachol, bethanechol • Alkaloid: pilocarpine, arecoline Acetylcholine • Cardiovascular system: – Vessel: dilation via EDRF – Negative chronotropic effect – Negative dromotropic effect – Negative inotropic effect Acetylcholine • Gastrointestinal tract: increase motility, stimulate secretion • Urinary bladder: detrusor contraction, trigone and sphincter relaxation • Glands: stimulate secretion • Eye: contract sphincter muscle of iris, contract ciliary muscle for near vision Acetylcholine • A large dose of Ach after administration of atropine can activate nicotinic receptor • N1: ganglion • N2: neuromuscular junction Activate NN receptor • All ganglion are activated • Sympathetic effects: increase in blood pressure • Parasympathetic effects: glands secret, contract smooth muscle • excite adrenal gland medulla • Overdose: excitement inhibition Activate Nm receptor • Neuromuscular end plate • Skeletal muscle Contraction methacholine • Selectively activate muscarinic receptor • Stronger effects on cardiovascular system • Clinical uses: sjogren’s syndrome • Asthma, ulcer, anoxemia others • Carbachol: pharmacodynamics is similar to Ach, uses for glaucoma • Bethanechol: more selective to M receptor Alkaloid Including pilocarpine, arecoline, muscarine, oxotremorine pilocarpine • Pharmacodynamics: – Eye: miosis, ocular pressure reduction, accommodation – Glands: secretion 阿托品阻断 毛果芸香碱激动 M受体 瞳孔括约肌 缩瞳 (动眼神经的胆碱能神经支配) 瞳孔开大肌 (去甲状腺素能神经支配) Α受体 扩瞳 虹膜(包括瞳孔括约肌和瞳孔开大肌 ) 毛果芸香碱的缩瞳作用 睫状体上皮 细胞分泌 狭窄时眼内 压增高,闭 角型青光眼 (急,慢型 充血性青光 眼) 房水 前房角间隙 间隙扩大,房 水入循环 变性或硬化 时眼内压增 高 开角性 青光眼(慢 性单纯性青 光眼) 血管 渗出 瞳孔 毛果芸香碱收 缩瞳孔括约肌 前房 缩瞳虹膜拉紧 虹膜根部变薄 降低眼内压 小梁网 毛果芸香碱 巩膜静脉窦 收缩睫状肌 扩张小血管 阿托品扩瞳,虹膜退向四周,前房角 血流 间隙变窄,房水回流受阻,眼内压升高 毛果芸香碱的降低眼内压作用 正常时晶体较扁平 受睫状肌控制 环状肌 (瞳孔括约肌) 辐射状肌 (瞳孔开大肌) 睫状肌起点 动眼神经兴奋 悬韧带 或毛果芸香碱 外 界 动眼神经胆 碱能神经 向瞳孔中心收缩悬韧 带,睫状小带放松 晶状体变凸 屈光度增加 只视近物(调节痉挛) 阿 托 品 去甲肾上腺素能 神经支配 对眼 调节无重要意义 睫状肌松弛而退向 外缘,悬韧带拉紧 晶状体变扁 屈光度降低 只视远物(调节麻痹) 毛果芸香碱的调节痉挛作用 Clinical uses • Glaucoma • Iritis Muscarine Direct acting muscarinic receptor: toxic reaction nicotine • Contributes to increased risk of vascular disease and sudden coronary death • Contributes to high incidence of ulcer recurrence with peptic ulcer Anticholinesterase agents Acetylcholinesterase Ach====AchE Ach- AchE choline+AcAchE Acetate+Ache The entire process takes place in 150ms AchE • Nerve terminal, synaptic cleft, effectors • Most chlinergic synapses are richly supplied with AchE, the half-life of Ach is very short Anticholinesterase agents • Binds to AchE complex • The covalent bond is resistance to the second process, and this step is prolonged classification • Hydration process is prolonged for 30 minutes to 6 hours • Hydration process is prolonged for hundreds of hours Anticholinesterase agents • Pharmacodynamics: – Eye: miosis, ocular pressure reduction, accommodation – Gastrointerase systems: contract, increase secretion Anticholinesterase agents • Neuromuscular junction: – Therapeutic concentration: prolong and intensify the actions of Ach; activate skeletal muscle directly – Higher concentration: fibrillation of muscle fibers Anticholinesterase agents • Respiratory, urinary tract: contract • Cardiovascular system: increase activation in ganglia and at acetylcholine receptors on neruoeffector cells( HR ,BP ) Anticholinesterase agents • Glands: secret • CNS – Low concentration: activation of EEG, subjective alerting response – High concentration: coma, respiratory arrest Clinical uses • • • • • • Myasthenia gravis Ileus, Glaucoma Detoxifcation Alzheimier’s disease cholinergic crisis Neostigmine • Inhibit AchE and thereby increase the concentration of endogenous Ach • Act at neuromuscular junction and smooth muscle Selectively • Myasthenia gravis • Ileus, Pyridostigmine • Pharmacodynamics is similar to Neostigmine • Take effect slowly • Myasthenia gravis • Ileus, physostigmine • Eye • CNS: toxic reaction • glaucoma • Edrophonium chloride: Use for diagnosis • Ambenonium chloride: • Galanthamine • Demecarium bromide Organophosphates • Binds to AchE complex • The covalent bond is stable and hydrolyzes in water at a very slow rate • Aging: more stable and more difficult to split Toxic symptom • Activate M receptor • Activate N receptor • CNS • Diagnosis • Prevention • Detoxifcation – Atropine – PAM