* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam Name___________________________________
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
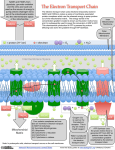
Exam Name___________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In the mitochondria NADH and QH2 are essentially oxidized by ________ since it is the terminal electron acceptor. B) ozone A) carbon dioxide C) hydrogen peroxide D) oxygen 1) 2) The ________ is between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondria. B) intermembrane space A) ATP synthase complex C) matrix D) intracellular fluid 2) 3) Oxidative phosphorylation requires all of the items listed below except A) the flow of electrons from NADH and QH2 in the membrane. B) a matrix more positively charged than the intermembrane space. C) a terminal electron acceptor which is H2 O in mitochondria. D) ATP synthase in the correct position in the membrane. E) enzyme complexes embedded in a membrane. 3) 4) ATP synthase is located in the ________ of the mitochondrion. A) intermembrane space B) outer membrane C) matrix D) inner membrane 4) 5) The inner mitochondrial membrane contributes to the formation of a proton gradient mainly because it A) is rich in proteins. B) is not rich in proteins. C) is the location of specific transporter proteins. D) contains ATP synthase complex. E) is a barrier to protons. 5) 6) The chemiosmotic theory is a concept that ________. A) the transport of Na+ and K+ across cell membranes is by active transport B) explains how transport by facilitated diffusion reaches a saturation limit C) a proton gradient that drives the formation of ATP D) explains the blood-brain barrier 6) 7) The protonmotive force is a result of ________. A) the flow of protons within the inner mitochondrial membrane B) a combination of an electrical potential and a chemical potential C) the flow of electrons from the matrix to the inner membrane space D) All of the above 7) 1 8) At one time the uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol was used as a weight reducing drug. Its side-effects, including death, resulted in its discontinued use. How could this drug cause weight loss? A) The uncoupler is an allosteric activator of ATP synthase. This increases the rate of translocation of H+ and the oxidation of fuels, including fats. B) The uncoupler allows the oxidation of fats from adipose tissue without the production of ATP. This allows the oxidation to proceed continuously and use up the fats. C) The uncoupler inhibits the transport of pyruvate into the matrix of the mitochondria. Fats are then degraded to glycerol and subsequently to pyruvate to provide the necessary energy. Thereby depleting fat stores. D) The uncoupler causes ATP to be produced at a much higher rate than normal and this causes weight loss. 8) 9) What feature of cytochromes makes them valuable in electron transport systems? B) the multiple α-helices A) aspartate residues in the active site C) the porphyrin ring D) the iron ion 9) 10) 10) Which has the highest reduction potential? B) O2 A) complex I C) complex II D) NADH 11) To reduce one molecule of O2 , ________ electron(s) must be passed through the electron transport chain and ________ molecule(s) of NADH is(are) oxidized. B) 4; 4 C) 1; 2 A) 1; 1 12) Which is a component of complex I? A) FMN B) FAD D) 4; 2 E) 2; 1 12) C) TPP D) Q 13) How many protons are translocated across the membrane by complex I for every pair of electrons that are passed from NADH to QH2 ? A) 1 B) 2 11) C) 3 D) 4 13) E) 5 14) Which complex in the electron transport chain does not contribute to the proton gradient? A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V 14) 15) The terminal electron acceptor for complex III of the electron transport chain is ________. A) Fe-S B) Q C) FAD D) cytochrome c 15) 16) Superoxide dismutase protects cells from damage caused by ________. A) H3 O+ B) ·O2 C) H2 O2 16) 2 D) O3 2- Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 1) D 2) B 3) B 4) D 5) E 6) C 7) B 8) B 9) D 10) B 11) D 12) A 13) D 14) B 15) D 16) B 3