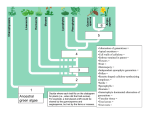
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes - Kawameeh Middle School
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Name: ____________________________ Class Notes Life Science Parts of Chapters 3, 4, 5, & 9 Seventh Grade Science Date: ________________ Period: _____ The Cell Cycle 1. What is the cell cycle? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Through the cell cycle, organisms ______________, _____________, replace _____ or ____________________ cells, and ___________________ new cells. 3. The three major steps in the cell cycle are _____________________, ________________, ____________________. Levels of Organization Unicellular Organisms 4. What is cell differentiation? _______________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 5. ________________ are groups of _______________ types of cells in a ___________________ organism that work together to carry out __________________ tasks. 6. The four main types of tissues in humans are: _____________________, ________________, ___________________, ________________ 7. What is an organ? ________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is an organ system? _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction 1. What is sexual reproduction? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. During a process called ___________________, an egg cell and a sperm cell join together to create a ________________________. 3. Organisms that reproduce sexually form ___________ cells and ________ cells. 4. What is a diploid cell? ____________________________________________________ 5. What is a haploid cell? ____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 6. How many chromosomes are in a human diploid cell? _____________________ 7. How many chromosomes are in a human haploid cell? ____________________ 8. What is asexual reproduction? ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 9. Because the ___________________ inherit all their DNA from ________ parent, they are ___________________ Type of Asexual Reproduction Fission Budding Regeneration Vegetative reproduction Cloning ________________ to each other and their parent. Explain Process Genetics 1.What is heredity? __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is genetics? _________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. a) A ________________ trait is a genetic factor that blocks another genetic factor. This type of trait is expressed using ____________________ _____________. b) A _________________trait is a genetic factor that is blocked by the presence of a dominant factor. This type of trait is expressed using __________ _________ _________________. 4. What is a gene? __________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is an allele? ________________________________________________________ 6. How a trait appears, or is expressed, is the trait’s _______________, and the two alleles that control the phenotype of a trait are called the trait’s ________________. 7. What does it mean if the alleles are homozygous? What does it mean if they are heterozygous? ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is a Punnett square? ________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. It will produce 100% red kernels because they are all heterogenous genotypes, meaning the dominant gene will block the recessive trait. Interactions Among Living Things 1. What is an ecosystem?____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________ factors are the nonliving parts of an ecosystem. 3. List some examples of abiotic factors: ______________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 4. ______________ factors are all of the living or once living things in an _______________. 5. What is a population? _____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. What is a community? ____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Symbiotic Relationships 7. What is a habitat? ________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is a symbiotic relationship? _________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 9. These relationships can be ________________to ________ organisms, beneficial to ________ and ____________to the other, or beneficial to one and ______________to the __________________. 10. Mutualism a. What is mutualism? _______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ b. Example: ___________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 11. Parasitism a. What is parasitism? _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b. Example - __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 12. Commensalism a. What is commensalism? _____________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b. Example - __________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Energy and Matter 1. Scientists classify organisms by the way they get the ______________that they need to ______________________. 2. Almost all energy on Earth comes from the _______________________. 3. What do producers do? ____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. ______________________ cannot make their own food and get _____________________ from eating other ________________________. 5. What is a food web? ______________________________________________________.