* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Inside Cancer
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
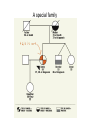
How to be a Breast Cancer Detective What is cancer? The common elements of many types of cancer are: 1) Cancer cells grow without external stimulation of growth factors. 2) Cancer cells resist growth suppression signals from within and without. 3) Cancer cells become immortal and override the features that normally lead to cell death. 4) Cancer cells do not respect tissue boundaries, so they become invasive and metastasize. www.breastdoc.com/.../Genetic-2.jpg Only 5-10 % of breast and ovarian cancer is inherited. If either one of your parents carry the gene, there is a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation regardless of the child's sex www.breastdoc.com/.../Genetic-2.jpg When studying human genetic diseases, geneticists often use pedigree charts to represent the inheritance of traits. How many individuals have died or are affected by this disease? F1 F2 F F 1 F3 A special family View film clip • Mary Claire king: Finding brca1 and 2 by pedigreehttp://www.dnai.org/media/a/king29604.swf Draw your own pedigree chart 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Go back 3 generations in a family Let circles = females Let squares = males Half shaded = has unexpressed trait Shaded area = has disease Shaded area with line drawn through=died from disease Finding the Genes What are genes? www.breastdoc.com/.../Genetic-2.jpg We all have the BRCA 1 and 2 genes, which are located on chromosome 13 and 17, respectively. A mutation in the form of extra DNA or loss of DNA that occurs in the gene is a problem. If a person inherits one of the mutations associated with cancer, he or she will have a higher risk of developing that cancer than people who have a healthy version of that gene. Mark Skolnick: Finding the breast cancer gene brca1: www.dnai.org/media/a/skolnick298_06.swf View film clip Why use Bioinformatics? Bioinformatics and combinatorial chemistry allow scientists to sort through molecules (both natural and synthetic) that interfere with cancer’s progress in a variety of ways. In addition, the ability to measure many different constituents (such as the DNA, RNA, and proteins) in both normal cells and cancer cells, will enable a more systemic genetic classification of cancer. Bioinformatics can discern patterns in those measurements to help better understand how cancer cells behave and how they react to different treatments. Bioinformatics is based on the actual genetic code of an organisms which has been sequenced using Biotechnology. Uses of Biotechnology and Bioinformatics • the ability to create vaccines • identification of protein markers for detecting and diagnosing cancers • purification of interleukin and other immunesystem enhancers • the preparation of bone marrow cells for transplants • the manipulation of natural products like taxol (from the Pacific yew tree) to make improved compounds that interfere with cell division Let’s do Bioinformatics-finding the breast cancer gene 1. Google “NBCI”. 2. Choose first hit. 3. Type in Brca 1 in Search Box 4. Choose a nucleotide in left box. 5. Click “Go” 6. You will now be presented with a long page of gene choices. See if you can identify some of them by their Latin names. 7. Click on a Brca 1 sequence and open it. There is a lot of information here. Step 1 –Google NCBI • NCBI HomePage • The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) provides an integrated approach to the use of gene and protein sequence information, the scientific literature (MEDLINE ... • www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov Step 2 Examine a breast cancer variant genome: LOCUS NM_007305 3759 bp mRNA linear PRI 28-JUL-2008 DEFINITION Homo sapiens breast cancer 1, early onset (BRCA1), transcript variant BRCA1-delta910-11b, mRNA. Questions 1. What is a “locus”? 2. How many “bp” base pairs are found in this locus? 3. Where is the gene found? 4. What does the gene encode for? Finding the coding sequence CDS • The CDS codes for a functional protein. • Find the CDS of this gene by scrolling down to CDS. Next to this you will find a locus: 201…..2360. • Carefully highlight, cut, and paste the nucleotides from 201 to 2360 onto a word document. • Save it under “CDS-breast cancer gene”. Finding similar Coding Sequences for functional genes • Its fun and interesting to find the same CDS in other animals, especially ones which are available to researchers. • One such animal is the C. Elegans, a nematode worm about 1 mm in length. • How can we find organisms with similar sequences? BLAST • One way is to use a bioinformatics program called BLAST. • It takes a sequence and searches for similar ones in its database. Directions for a Nucleotide BLAST • • • • Go back to the NCBI homepage Click Blast Mark “nucleotide” BLAST Copy and paste your nucleotide CDS into BLAST • Next to database : click others • Optimize for somewhat similar sequences • Click BLAST button What are your results? Find the % similarity of the gene in the: • Chimpanzee ________% • Gorilla ________% • Mouse ________% • Rat ________% Summary 1. Cancer is a disease caused by…….. 2. What percentage of breast cancers are caused by mutations? 3. What is the name of the gene responsible? 4. If one of your parents have the gene, what are your chances for having the gene? 5. How do scientists study family inheritance? 6. How has Biotechnology helped us solve the cancer problem? 7. Why does Biotechnology rely on Bioinformatics? 8. What type of information can a Biotechnology website give us? 9. How can we apply what we have found it today to a future research project? Final Video Clip Mary Claire king: Can women be tested for breast cancer? http://www.dnaiorg/media/a/king295_08.swf