* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Abstract_Metabolomic_RFMF
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Cryobiology wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Natural product wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization wikipedia , lookup
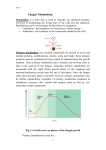
In situ Identification and Imaging of Metabolites using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Gregory Hamm, David Bonnel, Raphael Legouffe, Guillaume Hochart, Fabien Pamelard, Joachim Trouverie and Jonathan Stauber ImaBiotech, MALDI Imaging Department, Parc Eurasanté, Loos, France By definition, metabolites are intermediates and products from different metabolisms. More commonly, they are small compounds (between 100 and 1000 Da) found in organisms that have an important part in cells live and survival. They can be identified with different technics such as Nuclear Magnetic Resonance or Mass Spectrometry. Each of them is different at a biological level and can have a specific function. They can be nucleotides, amino acids or vitamins. The glucose-6-phosphate and the couple ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate)/ADP (Adenosine DiPhosphate) are examples of metabolites. Their identification permitted the decomposition of major biological pathways: the Glucose-6-Phosphate is implicated in glycolysis that converts glucose to pyruvate. This metabolism permits the synthesis of ATP, which one has a critical role in energy transfer and metabolism. ATP is also implicated in the Krebs Cycle (or Citrate Cycle), which is another example of important biological pathway. The purpose of this study was the identification and the localization of these metabolites using high resolution mass spectrometry. This study was done using two different organs (liver and brain) from rat. Slices of about 10µm thickness of each organ were put on ITO slides. For MALDI experiments, different matrixes were tested for best results and various polarities (2,5-dihydroxy benzoic acid, α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid or 9Aminoacridine). Matrixes were deposited using a SunCollect Automated Sprayer (SunChrome, Friedrichsdorf, Germany). For LESA experiments, slices were let without preparation. All the data were obtained using FTICR Solarix 7.0T (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). In order to perform at a higher spectral resolution, spectra were performed using Full Scan and CASI (Continuous Accumulation of Selected Ions) mode between 100 and 600 Da, each windows corresponding to 100 Da. After data treatments, a list of metabolites was obtained. In order to localize these compounds, MALDI Images were performed on the different organs at a special resolution of 100µm. These images show the distribution of different metabolites such as ATP of Glucose-6-Sulfate in specific histological regions of the tissue. These results are correlated with previous studies of metabolites such as the citrate cycle composition. Consequently, mass spectrometry imaging is successfully applied to study in-situ metabolism in tissue and to follow the process of biological pathways. www.imabiotech.com Contact : [email protected]