* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animation
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
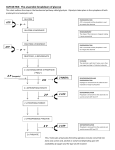
outline glycolysis to pyruvate with the yield of ATP and reduced NAD+ 1 10 steps in Glycolysis ADP phosphorylation ATP hexokinase 1 Glucose receives a phosphate group from ATP to form glucose-6phosphate. Process: phosphorylation Enzyme: hexokinase Next Review 2 2 isomerization Glucose-6phosphate converted to its isomer, fructose-6phosphate. Process: Isomerization Next Review 3 3 ADP phosphorylation ATP Phosphofructokinase Another ATP is invested to molecule, forming fructose1,6-bisphosphate. Process: Phosphorylation Enzyme: Phosphofructokinase Next Review 4 4 GlyceraldehydeDihydroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP) 3-phosphate (G3P) Fructose-1,6bisphosphate is then split into two 3carbon sugars, glyceraldehyde-3phosphate (G3P) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP). Process: Lysis / Cleavage Next Review 5 5 isomerization Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP) Glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate (G3P) Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is converted to its isomer, glyceraldehyde-3phosphate (G3P) a.k.a phosphoglycerate (PGAL) Process: Isomerization Next Review 6 6 G3P/ G3P/ 2NADH + 2H+ oxidation 2NAD+ G3P undergoes dehydrogenation with NAD+ as hydrogen acceptor. Product of this very exergonic reaction G3P reacts with inorganic phosphate present in cytosol to yield 1,3bisphosphoglycerate (BPG). Process: Oxidation / Dehydrogenation Next Review 7 7 BPG/ BPG/ ATP Substrate-level phosphorylation ADP (3PG) (3PG) One of phosphates of BPG reacts with ADP to form ATP resulting in 3phosphoglycerate (3PG). Process: Substratelevel phosphorylation Next Review 8 8 (3PG) (3PG) isomerization (2PG) 3PG is rearranged to 2phosphoglycerate (2PG) Process: Isomerization. (2PG) Next Review 9 9 (2PG) (2PG) dehydration H20 ONE molecule of water is removed, which results in formation of double bond. The product, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Process: Dehydration (removal of water) Next Review 10 10 ATP Substrate-level phosphorylation ADP Phosphate group of PEP molecules is transferred to ADP to yield ATP and pyruvate. Process: Substratelevel phosphorylation. Next Review 11 Review: Glycolysis 12 Watch the animation and answer the following questions 1 2 3 Animation 4 5 Energy investing phase Energy yielding phase Where reduced NAD+ is produced Name of enzymes at 1 & 3 6 7 8 9 10 13 14