* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Micro Syndrome
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
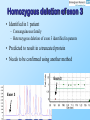
Identification of mutations in a novel gene for Micro syndrome in a cohort of international patients Frances Bond West Midlands Regional Genetics Laboratory 12/04/10 Overview • Micro syndrome • Aim of project & methods • Results • Conclusion Micro Syndrome • Rare autosomal recessive disorder Eyes Brain Small eyes Congenital cataracts Loss of optic nerve fibres Genital Microgenitalia Severe mental retardation Severe cortical visual impairment Novel Gene Discovery ~60% of cases • RAB3GAP is a key regulator of the Rab3 protein – Converts active Rab3-GTP to inactive Rab3-GDP – Involved in exocytosis of neurotransmitters and hormones • Autozygosity mapping studies – 5.5Mb region of homozygosity on chromosome 10 – Sequence analysis of candidate genes within this region identified variants in the ‘MICRO3’ gene Aim of Project • To screen 63 unrelated patients to identify mutations and copy number abnormalities in MICRO3 • Bi-directional sequencing – Plate-based high-throughput strategy – All the exons in the 4 alternative transcripts of MICRO3 • MLPA – Synthetic probes for exons 1_1, 1_2, 2, 3, 6, 8 and 9 Results • Variants were detected in 13 unrelated patients (21%) – 10 different novel variants – 6 patients had variants that are likely to be pathogenic (10%) c.88C>A 1_1 1_2 Deletion of exon 1_1 and 1_2 c.187-55T>A c.71T>A 2 3 Deletion of exon 3 4-1a 4_1b c.186+57G>A 4_1c 4_2 5 6 c.277_279delAGA 7 c.260-7dupA 8 c.619T>C 9 c.577G>A p.Leu24Gln • Identified in 4 patients – Consanguineous Pakistani families – Segregated with Micro syndrome • 2 codons downstream of a published variant – Results in an inactive GDP-bound protein • In silico analysis – Little effect on splicing – Predicted to affect protein function • Functional studies – Disrupted protein does not bind to GDP or GTP p.Arg93del, p.X207GlnextX21 & p.Gly193Ser • Identified in 1 patient – Non-consanguineous American Caucasian family – Segregated with Micro syndrome – p.X207GlnextX21 and p.Gly193Ser in cis • Suggests one is not pathogenic • p.X207GlnextX21: Extends protein – ?Abolish C-terminal post-translational modification and subsequent membrane targeting? p.Arg93del, p.X207GlnextX21 & p.Gly193Ser • In silico analysis – All: Little effect on splicing – P.Gly193Ser: Predicted to be tolerated • Functional studies – p.Arg93del – Disrupted protein does not bind to GDP or GTP – Pathogenic: p.Arg93del & p.X207GlnextX21 – Non-pathogenic: p.Gly193Ser Homozygous deletion of exon 3 • Identified in 1 patient – Consanguineous family – Heterozygous deletion of exon 3 identified in parents • Predicted to result in a truncated protein • Needs to be confirmed using another method Exon 3 Exon 3 Conclusion • 6 patients had likely pathogenic variants in MICRO3 (10%) – 5 of these had variants that affect exon 3 • Analysis of RAB3GAP should be the first-line test followed by MICRO3 testing – Screen exon 3 first in consanguineous Pakistani families • Dr Aligianis’ Research Group, MRC Human Genetics Unit, Edinburgh – RAB3GAP testing for any patient with a negative result – Functional studies to confirm pathogenicity of variants – Research into MICRO3 role in development Acknowledgments I would like to thank everyone who has contributed to this project: Dr Aligianis’ Research Group – Irene Aligianis – Danai Bem WMRGL – Fiona Macdonald – Carol Hardy – Sequencing and fragment analysis technical staff