* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid
Survey
Document related concepts
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
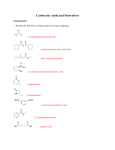
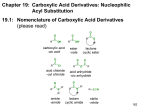
I. DEFINITION & NOMENCLATURE OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
A. CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
The organic compounds that are classified as carboxylic acid derivatives are all carbonyl-containing compounds (except
for nitriles) that can be converted to a carboxylic acid by hydrolysis, i.e., addition of water. This condition requires that the
carboxylic acid derivative has an electronegative atom bonded to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group. The functional
groups that belong to this class of compounds are:
O
O
O
R
O
R
R"
X
Acyl halide
Anhydride
O
O
O
R
OR'
(CH2)n
Ester
Lactone
O
O
O
O
NH
R
NH2
R
NHR'
R
NR'2
(CH2)n
Primary Amide
O
R
Secondary Amide
O
N
H
O
R"
Primary Imide
R
Tertiary Amide
O
O
N
R"
H
N
Lactam
O
R'
(CH2)n
Secondary Imide
Cyclic Imide
(Primary)
O
R'
N
O
(CH2)n
Cyclic Imide
(secondary)
O
R
C
Nitrile
N
H2N
NH2
Urea
B. NOMENCLATURE OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES (21.1)
1. Nomenclature of Acyl Halides
a. Acyl halides are named by replacing the "ic acid" ending of the corresponding carboxylic acid with "yl" followed
by the halide. It is represented as two words.
2. Nomenclature of Anhydrides
a. Symmetrical anhydrides (both carbonyl groups are the same) are named by replacing the "acid" suffix of the
corresponding carboxylic acid with "anhydride"
b. Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named by removing the "acid" suffix from each of the two acyl groups that make up
the anhydride, placing the names in alphabetical order and adding an "anhydride" suffix.
c. Cyclic anhydrides have common names.
3. Nomenclature of Esters
a. Esters have two carbon containing components; one bonded to the oxygen atom ("alkyl") and one bonded to the
carbonyl group ("alkanoate"). Esters are named by combining these two components.
4. Nomenclature of Amides
a. Primary amides are named by replacing the "oic acid" or "ic acid" ending of the corresponding carboxylic acid with
"amide".
b. Secondary and tertiary amides are named as "N-alkyl-" or "N,N-dialkyl-" amides. The parent is
determined as for primary amides.
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
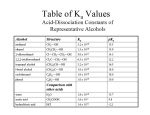
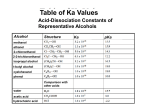
II. PROPERTIES OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
A Boiling points
Carboxylic acid derivatives that cannot H-bond tend to have lower boiling points than those that can H-bond.
Carboxylic acids and primary and secondary amides tend to have higher boiling points.
B. Leaving groups
The leaving groups associated with nucleophilic acyl addition reactions of carboxylic acid derivatives include:
chlorides, carboxylate and carboxylic acids, alkoxides and alcohols, hydroxides and water, and amines.
C. Primary imides are acidic
O
O
O
R
N
R
R
O
N
R
H
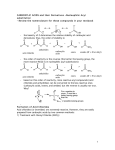
D. RELATIVE REACTIVITIES OF CARBOXYLIC DERIVATIVES WITH NUCLEOPHILES (21.2)
Inductive and resonance effects help to predict the relative reactivity of carboxylic acids and derivatives.
acyl halide
O
R
ester
acid anhydride
O
O
>
Cl
O
O
~
>
R
O
amide
O
δ+
R
carboxylic acid
R
very strong inductive effect
due to electronegative Cl
OR'
>
R
OH
R'
NR2
inductive effect due to electronegative
oxygen but less reactive than Cl
O
O
δ+
R
O
R
strong inductive effect
enhanced by resonance effect
IV. NUCLEOPHILIC ACYL SUBSTITUTIONS OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
(21.2)
A. MECHANISM OF THE NUCLEOPHILIC ACYL SUBSTITUTION REACTION
Carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives react with nucleophiles via the nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction either
under basic conditions or acidic conditions.
Base-Catalyzed Nu Acyl Substitution
O
Nu
Nu:
R
XR
X = halogen, oxygen, nitrogen
R
O
O
XR
R
Nu
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
Acid-Catalyzed Nu Acyl Substitution
H
H
H+
R
O
O
O
XR
R
R
XR
XR
Nu
X = halogen, oxygen, nitrogen
H
H
O
O
O
R
R
Nu
H+
Nu:
R
Nu
XR
Nu
H
V. PREPARATION OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
A. Preparation of Acyl halides
1. Acyl halides are usually prepared from carboxylic acids with SOCl2.
B. Preparation of Anhydrides
1. Anhydrides are usually prepared by reacting acyl chlorides with carboxylic acids in the presence of pyridine.
C. Preparation of Esters: Esters can be prepared in three ways.
1. Fisher Esterification: Reaction of alcohols with a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst.
2. Reaction of alcohols with acyl chlorides in the presence of pyridine.
3. Reaction of alcohols with anhydrides in the presence of pyridine.
D. Preparation of Amides
1. Primary amides are usually prepared by reaction of two moles of ammonia with acyl halides, anhydrides or esters.
2. Secondary and tertiary amides are usually prepared by reaction of two moles either a primary amine (to give a secondary
amide) or a secondary amine (to give a tertiary amide) with acyl halides, anhydrides or esters.
E. Preparation of Nitriles: Nitriles can be prepared in two ways.
1. Nucleophilic substitution of an alkyl halide
2. Nucleophilic addition of HCN with aldehydes & ketones
VI. REACTIONS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
A. REACTIONS WITH ACYL HALIDES (Catalyst usually not needed)
1. Acyl halide reactions with oxygen nucleophiles (carboxylates, alcohols/phenols, water) to generate anhydrides, esters
and carboxylic acids respectively.
Reaction with a Carboxylate
acyl halide
O
O
R
R
O
O
Cl
Cl
O
O
R
O
O
O
R'
anhydride product
R
carboxylate ion
R
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
Reaction with an Alcohol
acyl halide
O
O
O
R
R
Cl
Cl
R
O
O
O
H
H
ester product
alcohol
Reaction with a Phenol
acyl halide
O
O
O
H
R
R
Cl
Cl
R
O
O
H
O
ester product
phenol
2.
Acyl halides react with primary and secondary amines to generate amides.
acyl halide
O
O
O
H
R
R
Cl
Cl
R
N
N
NH
H
secondary amide
H
H
primary amine
B. REACTIONS OF ANHYDRIDES (Catalyst usually not needed)
1. Acid anhydride reactions with oxygen nucleophiles (alcohols/phenols, water) to generate esters and carboxylic acids
Reaction with Alcohol
acid anhydride
O
O
O
O
R
R
O
R'
R
O
O
O
H
alcohol
O
O
1
R
O
H
+
HO
R'
carboxylic acid
ester product
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
Reaction with Phenol
acid anhydride
O
O
O
O
R
R
O
R
R'
O
R
O
+
O
H
HO
R'
carboxylic acid
ester product
O
phenol
H
2.
O
O
1
Acid anhydrides react with primary and secondary amines to generate amides.
Reaction with Primary Amine
acid anhydride
O
O
O
O
R
R
O
R
R'
O
H
R
N
H
N
H
O
O
1
+
N
H
amine
C. Reactions of Esters
1. Ester reactions with oxygen nucleophiles (alcohols/phenols, water).
Acid Catalyzed Reaction with Alcohols (Transesterification)
ester
H+
O
R
OH
OR'
R
OH
OR'
R
OH
OR'
OH
OH
R"
R"
R
OR'
OR"
H+
H
O
O
HOR'
alcohol
+
R
OR"
new ester
R
R'
carboxylic acid
amide product
H
HO
OR'
OR" H
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
Acid Catalyzed Hydrolysis
ester
H+
O
R
OH
OR'
OH
R
OR'
R
OH
OR'
OH
OH
H
H
R
OR'
OH
H+
H
O
O
+
HOR'
alcohol
R
R
OH
OR'
OH
carboxylic acid
H
Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
ester
O
O
O
H+
R
R
OR'
OR'
R
OH
R'OH
alcohol
RO'
alkoxide
carboxylic acid
OH
2.
+
OH
Ester reactions with primary and secondary amines to generate amides.
Primary amines give secondary amides and secondary amines give tertiary amides.
Reaction of Esters with Amines
ester
O
O
O
R
R
OR"
H
R'N
NHR'
OR"
H
R
NHR'
amide
+
R'OH
alcohol
H
3.
Ester reactions with carbon nucleophiles and hydrides.
a. Esters react with Grignard reagents and primary or secondary alkyl lithiums to form alcohols
i. Two equivalents of reagent is needed to convert esters to alcohols.
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
Reaction of Esters with Organometallic Reagents
ester
"intermediate ketone"
O
O
O
R
R
OR"
H+
OR"
CH3
R
R"OH
R"O
+
CH3
alcohol
alkoxide
CH3
CH3
(from Grignard or alkyl lithium)
(second equivalent of reagent)
O
OH
H+
R
CH3
R
CH3
CH3
CH3
Tertiary alcohol
b.
Esters are reduced with hydrides to alcohols with LiAlH4 to alcohols or to an alcohol and aldehyde with DIBAL
i. Reaction with DIBAL gives an aldehyde and and alcohol.
ii. If LiAlH4 is used as hydride reagent, the aldehyde continues to undergo reduction to a primary alcohol. Two
alcohols (one primary, the other from the original ester) result as products of the reaction.
Reaction of Esters with Hydrides
aldehyde product if DIBAL
ester
O
O
O
R
R
OR"
H
+
R
H
R"OH
R"O
alcohol
alkoxide
H
H
DIBAL or LiAlH4
H+
OR"
"intermediate aldehyde" if LiAlH4
(second equivalent of hydride if LiAlH4)
O
OH
H+
R
H
H
R
H
H
Primary alcohol with LiAlH4
E. Reactions of Carboxylic Acids (Either activated or acid catalyzed)
1 Activation with SOCl2
Alcohols can be "activated" or converted to an acyl chloride with thionyl chloride prior to reaction with nucleophiles.
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
Reaction of Carboxylic Acid with Thionyl Chloride
LG
O
O
O
O
O
S
R
R
OH
Cl
O
Cl
S
O
R
O
Cl
Cl
Cl
S
Cl
LG
O
O
O
S
R
R
O
Cl
Cl
Cl
acid chloride
2.
Reaction with alcohols (acid catalyzed) (Fisher esterification)
Reaction of Carboxylic Acids with Alcohols (Acid-Catalyzed)
H+
O
R
OH
OH
OH
R
OH
R
OH
OH
OH
OR'
R'
H
R
OH
OR'
H+
alcohol
H
O
O
+
H2O
water
R
R
OR'
OH
ester
3.
OR'
H
Reaction with hydrides (1) LiAlH4 2) H+)
Reaction of Carboxylic Acid with Hydride
O
O
O
R
R
H
LiAlH4
OH
H+
OH
H
+
R
H
HO
H 2O
water
hydroxide
H
"intermediate aldehyde"
(second equivalent of hydride if LiAlH4)
O
OH
H+
R
H
H
R
H
H
Primary alcohol with LiAlH4
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
F. Reactions of Amides
1. Reaction with alcohols and water (acid- catalyzed)
Reaction of Amides with Alcohols (Acid-Catalyzed)
H+
O
R
OH
NHR"
R
OH
OH
OH
R
NHR"
OH
OR'
R'
H
R
NHR"
OR'
H+
alcohol
H
O
O
+
H2NR"
R
amine
R
OR'
ester
NHR"
H
OR'
Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Amides
H+
O
R
OH
NHR"
R
OH
OH
OH
R
NHR"
OH
OH
H
H
R
NHR"
OH
H+
water
H
O
O
H2NR"
amine
+
R
R
OH
NHR"
OH
carboxylic acid
H
Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Amides
O
O
O
R
R
NHR"
OH
2.
H+
NHR"
OH
R
OH
carboxylic acid
+
NHR"
R"NH2
amine
Reaction with hydrides
i. LiAlH4 can be used to reduce amides to amines
ii. Reduction of a primary amide gives a primary amines; reduction of a secondary amide gives a secondary amine and
reduction of a tertiary amide gives a tertiary amine.
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
Lecture Outline
Reaction of Amides with Hydrides
"H+"
O
O
OH
R
R
NR"
NHR"
H
R
H
NR"
H
H
H
LiAlH4
H-OH
intermediate imine
NR"
R
NR"
H
R
NR"
H
R
H
H
H
H
amine
G. Hydrolysis of Imides and Nitriles
1. Hydrolysis of Imides: Gabriel Synthesis
a. Imides can be used to synthesize amines through the Gabriel synthesis.
b. The Gabriel synthesis is a multi-step reaction involving acid/base chemistry, an SN2 reaction followed by basecatalyzed hydrolysis to synthesize primary amines.
Acid-Base Reaction
O
O
(alkyl halide)
OH
R-X
NH
N
O
O
phthalimide
phthalimide ion
O
O
OH
OH
SN2 Reaction
NR
NR
O
O
N-substituted phthalimide
Hydrolysis
O
OH
OH
OH
NHR
O
O
O
OH
NHR
OH
O
OH
O
+
H+
H2NR
primary amine
NHR
Organic Chemistry
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions
2.
Lecture Outline
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
Nitriles can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions to provide primary amides.
Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Nitriles
H+
H+
N
NH
NH
C
NH
H
C
C
R
C
O
R
O
R
R
H
H
OH
H
water
NH2
NH2
C
C
R
O
O
R
H
Primary amide
Base-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Nitriles
H+
N
NH
N
C
R
O
H
NH2
C
C
R
NH
O
O
H
R
O
O
R
R
H
Primary amide