* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unicellular Organisms
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
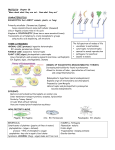
Unicellular Organisms Objective 7.L.1.1 Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life. Essential Question: What are the characteristics of the following single-celled organisms? Euglena Amoeba Paramecium Volvox All of the Organisms we talk about today will be eukaryotic. They are protists: eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants, or fungi. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bNTQL qWEpXU Vocabulary • unicellular organism: an organism made of one cell • prokaryotic cell: a cell that doesn’t have a nucleus • eukaryotic cell: a cell that does have a nucleus Definitions • locomotive structures: structures that help an organism move • flagellum: long tail like projection of cell membrane which is adapted as a locomotory organ • cilia: small hair like projections of cell membrane which are adapted as a locomotory organ Definitions • pseudopod: a temporary projection of the cytoplasm of certain cells, especially amoebas, that serves in locomotion and phagocytosis. Talk with a partner: What is a protist? FOLDABLE TIME Comparisons of Singlecelled Organisms • Please write down anything that is in RED in your own words. These are the important concepts. Euglena • Move by flagellum • Known for a unique feature—eye spot • Contain chloroplasts photosynthesis • Common in fresh water • Does not contain a cell wall Euglena • Found in calm fresh and salt water • Autotrophs and Heterotropshs– can make their own food and also eat other things. • Have features of both plants and animals. Euglena https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fI7nEWU jk3A Amoeba • Move by cytoplasmic streaming • Surrounds food and engulfs it using pseudopods, it is then enveloped, stored, and digested in vacuoles Amoeba • • • • • Can change shape Heterotrophic Eats bacteria, algae, and other protozoa Reproduce asexually Can survive forcible division Amoeba • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pvOz4 V699gk • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7pR7T NzJ_pA Tell me one characteristic of a euglena and one characteristic of an amoeba. Paramecium • Most complex and specialized of the protists • Moves by cilia (hairlike projections) Paramecium • Can move about 12 body lengths per second • Shape of a pill capsule • Heterotrophic • Relatively large • Common in pond scum and freshwater • Contain two nuclei (macro and micro) Paramecium • Uses cilia to sweep food into the oral groove • Feeds on micro-organisms like bacteria, algae, and yeasts • Stiff elastic membrane gives it shape and is covered in cilia that allow it to spiral through water Paramecium • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sn3M TYNe8mM What did one paramecium say to the other paramecium? You’re Cilia than me Volvox • A spherical colony of ciliates may include up to 50,000 cells • Contain chloroplasts •Move and act as one multi-cellular organism •Can survive independent of the colony Volvox • Type of green algae • Lives in lots of freshwater habitats – ponds, ditches, puddles, lagoons • Colonies use flagella to swim • Cells have eyespots • Make food via photosynthesis • Autotrophic VOLVOX • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d8xs8F 9gln0 RAFT Role – Paramecium Audience – Euglena Format – Letter Topic – Why I am better than you! Quiz Be sure you have these in your notes!!! Which single-celled organisms moves by flagellum? A. Euglena B. Amoeba C. Paramecium D. Volvox A. Euglena Which single-celled organism moves by cilia or hairlike projections? A. Euglena B. Amoeba C. Paramecium D. Volvox C. Paramecium Which single-celled organism uses pseudopods to surround and engulf their food? A. Euglena B. Amoeba C. Paramecium D. Volvox B. Amoeba Which single-celled organism is a colony of ciliates of which some contain chlorophyll? A. Euglena B. Amoeba C. Paramecium D. Volvox D. Volvox Which single-celled organism has a unique feature of an eye spot? A. Euglena B. Amoeba C. Paramecium D. Volvox A. Euglena Which single-celled organism moves by cytoplasmic streaming? A. Euglena B. Amoeba C. Paramecium D. Volvox B. Amoeba Which types of single-celled organisms can have chlorophyll? A. Euglena and Amoeba B. Amoeba and Paramecium C. Paramecium and Volvox D. Euglena and Volvox D. Euglena and Volvox Which organism appears in the photos? • paramecium Look at the picture. Be able to answer the questions on the following slide! What organelle engulfs food? A. cytoplasm B. pseudopods C. vacuoles D. nucleus What organelle digests the food? A. cytoplasm B. pseudopods C. vacuoles D. nucleus B. pseudopods C. vacuoles A. B. Name the organelles located at A. and B. A. nucleus B. cytoplasm