* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ribosomal MLST - The Maiden Lab
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
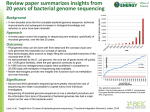
Ribosomal MLST: Universal Bacterial Typing using Whole Genome Sequences James E. Bray, Keith A. Jolley, Martin C.J. Maiden Department of Zoology, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, OX1 3PS, UK. Contact: [email protected] Introduction Overview of the Bacterial Domain using Protein-encoding Ribosomal Genes The Ribosomal Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (rMLST) database hosted on the PubMLST website provides allelic sequence definitions for more than 3,000 different bacterial species and can be used for rapid speciation and sequence typing across the bacterial domain [1]. The rMLST approach indexes the variation of the 53 ribosomal protein subunit (rps) genes. These genes are present in all bacterial species and therefore this approach can provide a universal bacterial typing nomenclature for the biomedical community. rMLST Website pubmlst.org/rmlst Schematic diagram of the ribosomal subunits. RNA is shown in yellow and orange, protein domains are shown in blue. Image courtesy of RCSB Protein Data Bank Speciation by rMLST is concordant with 16S rRNA but is able to resolve individual species that, in many cases, 16S rRNA cannot. Currently, more than 100,000 bacterial genomes have been collected from public repositories and the rMLST allelic variation has been catalogued using the BIGSdb platform [2]. BIGSdb is opensource software that includes a database for storing isolate sequences, meta-data and allelic definitions for defined loci. The platform includes advanced functionality for interrogating genomic data using a gene-by gene approach at different levels of resolution from traditional 7-locus MLST, 53 gene rMLST, through to core genome MLST and whole genome analyses. Neighbor-joining tree reconstructed from concatenated rMLST alleles from 1565 bacterial isolates. Compare Genomes at Different Taxonomic Levels A) Species within a Genus NeighborNet diagram of Campylobacter isolates from 12 different species. Ribosomal Sequence Typing Nomenclature The Genome Comparator module of the BIGSdb platform allows genomic data from hundreds of isolates to be compared using gene-by-gene analysis at any taxonomic level. As rMLST uses 53 loci it is able to resolve down to the level of strain type, comparable, and often better, than conventional MLST For example, Campylobacter isolates can be analysed at genus, species, or individual clonal complex level. NeighborNet diagrams were calculated by SplitsTree [3] using nucleotide variation of concatenated rMLST alleles. C) Isolates within a Single Clonal Complex B) Isolates within a Species NCBI Genomes (Assembled) Velvet Assembly Pipeline [4] Isolates Identify alleles for all ribosomal genes Scan Ribosomal sequence types (rSTs) are defined based on the unique combination References of alleles at the 53 rps loci. Ribosomal sequence types have been defined for 14 bacterial genera including many human pathogenic species including Campylobacter jejuni, Neisseria meningitidis and Staphylococcus aureus and work is on-going to scale-up the process to encompass all bacterial species. Designate NeighborNet diagram of 186 Campylobacter jejuni isolates from within the ST-21 complex NeighborNet diagram of 36 Campylobacter jejuni isolates (one representative of each clonal complex and C. jejuni subsp. doylei) Public Genomes (Raw Reads) Define Alleles Define unique combinations of alleles Analyse all alleles for each gene for a whole genus Profiles Using Ribosomal Alleles and Sequence Types to Identify Species Genomic Sequence File Library of ribosomal allele sequences The library of ribosomal allele sequences can be searched with any bacterial genome sequence. The BIGSdb Species Finder program will identify all the exact allelic matches within the sequence. The program reports the number of isolates and associated species annotations for each allelic match and the ribosomal sequence type (rST) if there is a complete profile match. 53 loci 300,000+ sequences Streptococcus 3,987 Staphylococcus 3,709 Campylobacter 1,964 Escherichia 1,825 Neisseria 1,423 Salmonella 1,101 Mycobacterium 840 Acinetobacter 603 Vibrio 304 Shigella 251 Bacillus 249 Listeria 215 Yersinia 149 Bordetella 60 Total 16,680 Conclusions • We have developed a universal bacterial sequence typing method for analysing bacterial genomes using the 53 protein encoding ribosomal genes (rps). • Genomes can be compared at all taxonomic levels using the BIGSdb Genome Comparator module. • We have defined more than 16,000 ribosomal sequence types (rSTs) for 154 bacterial species including many human pathogens of clinical importance. References Identify exact allelic matches 1. Jolley, K.A., et al., Ribosomal multilocus sequence typing: universal characterization of bacteria from domain to strain. Microbiology, 2012. 158(Pt 4): p. 1005-15. 2. Jolley, K.A. and M.C. Maiden, BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinformatics, 2010. 11: p. 595. 3. D.H. Huson and D. Bryant, Application of Phylogenetic Networks in Evolutionary Studies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2006, 23(2):254-267. 4. Zerbino, D.R. and E. Birney, Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res, 2008. 18(5): p. 821-9. Look up allele indexes in profile database to find Ribosomal Sequence Type (rST) Processes involved for species identification using BIGSdb Species Finder program Genus Number of Ribosomal Sequence Types Defined Web interface for the BIGSdb Species Finder program This project is funded by the Wellcome Trust.