* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download untitled file - Blue Earth Area Schools
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
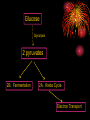
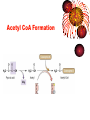
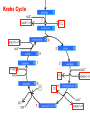
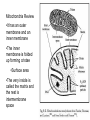
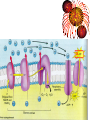
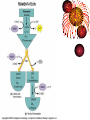
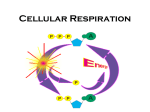
Chapter 5 Section 3 Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration • The conversion of organic matter into energy within the cell • Stored potential energy used to convert ADP into ATP • Happens in both environments • Anaerobic= No Oxygen • Aerobic= In the presence of Oxygen − More efficient!!!!!!! Stages of Cellular Respiration 1. Glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvate • Glycolysis 2a. Aerobic Respiration • In the presence of oxygen • anaerobic conditions 2b. Fermentation Equation C6H12O6 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 +6H2O Glucose ------------- Glycolysis 2 pyruvates 2B. Fermentation 2A. Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Glycolysis • Glucose (6 Carbons) split into 2 molecules of pyruvate (3 Carbons) • Small enough to cross the mitochondrial membrane • Takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell • All cells have cytoplasm • 2 ATP in 4 ATP out = net +2 ATP • 2 NAD+ converted to 2 NADH by stripping high energy e- from pyruvate • NADH must donate the H to other compounds to recycle NAD+ • NO O2 required!!!! (anaerobic) Glycolysis Diagram Aerobic Respiration • In the presence of oxygen pyruvate enters the mitochondria and is converted into a 2 carbon molecule. • This releases 1 CO2 and converts a NAD+ into a NADH • The 2 carbon molecule joins a coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA • The acetyl CoA enters the Krebs Cycle or citric acid cycle Krebs Cycle • First described by Sir Hans Krebs in 1937 • It is a series of chemical reactions in which high energy electrons are stripped from organic molecules and used to create NADH and FADH2 – Small amounts of ATP and CO2 are also generated Acetyl CoA Formation Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain • So far we have generated just ATP 4 • 2 from glycolysis and two from the Krebs Cycle • You use 1,000,000 ATP/cell/second which is equal to 100,000,000,000,000,000,000/ sec • But we have created many molecules that contain high energy electrons • NADH (10) and FADH2 (2) Mitochondria Review •It has an outer membrane and an inner membrane •The inner membrane is folded up forming cristae •Surface area •The very inside is called the matrix and the rest is intermembrane space ETC Continued • NADH and FADH2 enter into the ETC • ETC located in the inner mitochondrial membrane • High energy electrons enter and move down the chain NAD+ and FAD+ are recycled • H+ pumped out of the matrix to form a gradient • Protons (H+) are allowed back into the matrix, but through an enzyme that converts ADP -- into ATP • The final electron acceptor is O2 which pairs with H+ to form water • C6H12O6 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 +6H2O 34 Aerobic Net Gain • 2 ATP from Glycolysis • 2 ATP from Krebs cycle • Approx 34 ATP from ETC _____________________________________ 38 ATP/Molecule of Glucose in the presence of Oxygen Fermentation • Takes place in anaerobic conditions • NADH produced in glycolysis must release its high energy electron, but there is no O2 to be the final electron acceptor • NADH donates the high energy electron back to pyruvate to form either lactic acid or ethanol and CO2 • Then NAD+ is recycled and glycolysis can proceed Fermentation Cont. • No ATP produced after glycolysis so net gain of 2 ATP/molecule of glucose • As compared to 38 in aerobic conditions • Lactic acid can cause muscle fatigue, but it is better that the alternative = no ATP • Fermentation used in the production of some foods and beverages • Beer and wine • bread