* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria and Viruses
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
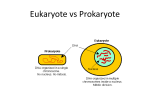
The Cell Theory Bacteria and Viruses Two Types of Cells • Prokaryotes (pro = before, karyote = nucleus) cells lack internal membrane structures Do not have a membrane bound nucleus Just bacteria • Eukaryotes (eu = true, karyote = nucleus) cells have internal membrane structures Do have a membrane bound nucleus Fungus, protists, plants and animals Kingdom Monera • All bacteria are prokaryotic • Unicellular organisms • Heterotrophs, Autotrophs or Chemotrophs (or a combination) • Two Kingdoms Archeabacteria - Live in extreme conditions (extreme hot/cold, very acidic/basic, very salty conditions). Eubacteria - Live generally in conditions that we are exposed to every day 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. Cell is basic unit of organization 3. Cells come from preexisting cells How Cells Acquire Energy • Autotrophs - Make their own food through Plants, algae and photosynthesis Cyanobacteria and Nitrogen Fixation • Heterotrophs - Obtain food through other organisms Animals eat • Chemotrophs - Obtain food through chemicals such as sulphur Create energy • Saprophytes - Obtain food through dead matter by decay Bacteria • Decomposers - Obtain food through break down of dead and decaying matter Bacteria Structure • Capsule Keep from drying out Protect from phagocytosis Disease-causing bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae Non-encapsulated mutants are a-virulent (don't cause disease) 1 Bacterial Structure Bacterial Structure • Cell Membrane • Barrier that lets some things and keeps others out • Made of a double lipid (fat) layer. Cell Wall Enclosed by rigid cell wall composed of peptidoglycan • a protein-sugar (polysaccharide) molecule Gives cell shape and surrounds cell membrane, protecting it from environment Two Types - Gram Positive and Gram Negative PEPTIDOGLYCAN Bacterial Structure • Cytoplasm - fluid filled inside of all cells • Plasmids - extra cellular DNA help bacteria to communicate to each other • Flagella - whip like tail helps bacteria move • Cilia - hair like structures help bacteria move • DNA - double circular strand • Ribosome - made from DNA and help make proteins for cell structure and function Plasmids • A circular piece of replicating DNA not of the genome of bacteria • Originally evolved by bacteria • May express antibiotic resistance or be modified to express proteins of interest What is transformation? • Uptake of foreign DNA, often a circular plasmid Plasmid Cell wall Bacterial chromosomal DNA 2 Bacterial Reproduction • Binary Fission - asexual reproduction One copies DNA Buds off making identical copy of itself • Pilus - structure help transfer DNA or plasmids to another bacteria Diversification • Endospores - copies made by binary fission and stored in parent cells Bacterial Arrangements • Strepto - More than two in a chain Streptococcus pyogenes Streptobacillus acidaphyllus • Staphylo - More than two in a cluster Staphylococcus aureus • Diplo - Two grouped together Diplococcus pneumonia • Tetra - Four group together Escherichia coliform How we fight the off? • Antibiotics - biologically made chemicals Penicillin - fights gram positive bacteria by preventing them from making a cell wall. Streptomycin - fights gram negative bacteria by preventing them from making proteins Sulpha Drugs - fight a broad spectrum of bacteria by inhibiting their metabolism. Bacterial Shapes • Cocci - are circular shaped bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes • Bacillus - are rod shaped bacteria Bacillus anthrasis • Spirillum (spiralchetes) Spirillum minus (rat bite fever) Identification Techniques • Streaking - uses petri dishes to spread bacteria on a growth media • Incubation - a type of oven used to grow bacteria streaked plates over time • Smear - uses a slide to smear bacterial sample for indetification • Fix -heat used to adhere bacteria to slide • Wet Mount - water used to suspend onto a slide • Simple Stain - uses one stain to see shapes and arrangements • Compound Stain -uses two or more stains to see what type of bacteria (grams stain) Types of Infections • Epidemic - a localized infection • Pandemic - a world wide infection 3 Viral Reproduction • Lysogenic Cycle - Retroviruses Work their way into cell and force their DNA into DNA of host cell Called provirus stage - host makes copies of it’s DNA, but also virus DNA Can convert to lytic cycle • Lytic Cycle All viruses must Lyse cells to get copies to external environment to further reproduction Microscopes as Tools • Enable to see objects too small to examine with just our eyes • Microscopes magnify, contrast and resolve images of an object Magnification - ability to make image look larger Contrast - ability to distinguish between light and dark parts of an image Resolution - ability to distinguish between two points of an image Types of Microscopes 1. Compound Light 2. Scanning Light (stereo) 3. Transmission Electron 4. Scanning Electron 5. Scanning-Tunneling Electron Microscopes • Light Microscopes Magnify cells 1000 time original size View live specimens See large things inside cells • Electron Microscopes Magnify cells 100,000x original size View only dead cells View things smaller than cells 4