* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download behaviorism learning theory
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
B. F. Skinner wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Positive education wikipedia , lookup
Clark L. Hull wikipedia , lookup
Instructional simulation wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Reinforcement wikipedia , lookup
Professional practice of behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Classroom management wikipedia , lookup
Learning through play wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral economics wikipedia , lookup
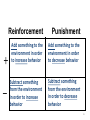
BEHAVIORISM LEARNING THEORY By : Habibi • According to the behaviorists, learning can be defined as “the relatively permanent change in behavior brought about as a result of experience or practice.” Behaviorists recognize that learning is an internal event. However, it is not recognized as learning until it is displayed by overt behavior. The focus of the behavioral approach is on how the environment impacts overt behavior. behavior environment behaviorism • The behavioral learning theory is represented as an S-R paradigm. The organism is treated as a “black box.” We only know what is going on inside the box by the organism’s overt behavior. Stimulus (S) Organism (O) Response (R) • Notice that the behaviorists are only interested in that aspect of feedback that connects directly to overt behavior. Behaviorists are not interested in the conscious decision of the individual to disrupt, modify, or go against the conditioning process. Classical Conditioning Theory Classical conditioning was the first type of learning to be discovered and studied within the behaviorist tradition (hence the name classical). The major theorist in the development of classical conditioning is Ivan Pavlov, a Russian scientist trained in biology and medicine Pavlov was studying the digestive system of dogs and became intrigued with his observation that dogs deprived of food began to salivate when one of his assistants walked into the room. He began to investigate this phenomena and established the laws of classical conditioning. Example: • Child is harassed at school • Child feels bad when harassed • Child associates being harassed and school • Child begins to feel bad when she thinks of school Operant Conditioning The response is made first, then reinforcement follows. + _ Reinforcement Punishment Add something to the environment in order to increase behavior Add something to the environment in order to decrease behavior Subtract something from the environment in order to increase behavior Subtract something from the environment in order to decrease behavior 16 Behaviorism in the Classroom • Rewards and punishments • Responsibility for student learning rests squarely with the teacher • Lecture-based, highly structured THANKS !