What is learning? On the nature and merits of a... definition of learning THEORETICAL REVIEW
... As was noted by Lachman (1997), most textbook definitions of learning refer to learning as a change in behavior that is due to experience. This is essentially a very basic functional definition of learning in that learning is seen as a function that maps experience onto behavior. In other words, lea ...
... As was noted by Lachman (1997), most textbook definitions of learning refer to learning as a change in behavior that is due to experience. This is essentially a very basic functional definition of learning in that learning is seen as a function that maps experience onto behavior. In other words, lea ...
TRADITIONAL LEARNING THEORIES
... affective as well as cognitive dimensions of learning was informed in part by Freud's psychoanalytic approach to human behavior. Although most would not label Freud a learning theorist, aspects of his psychology, such as the influence of the subconscious mind on behavior, as well as the concepts of ...
... affective as well as cognitive dimensions of learning was informed in part by Freud's psychoanalytic approach to human behavior. Although most would not label Freud a learning theorist, aspects of his psychology, such as the influence of the subconscious mind on behavior, as well as the concepts of ...
traditional learning theories
... theory, Bandura's social-cognitive theory, and Weiner's theory of motivation. However, three of these (Piaget, Vygotsky, and Weiner) "technically are not categorized as learning theories" but "have important implications for classroom practice" (p. 12). Since there is little consensus on how many le ...
... theory, Bandura's social-cognitive theory, and Weiner's theory of motivation. However, three of these (Piaget, Vygotsky, and Weiner) "technically are not categorized as learning theories" but "have important implications for classroom practice" (p. 12). Since there is little consensus on how many le ...
A Comparative-Ecological Approach to the Study of Learning
... conditioning, but the neutral stimulus is associated with a manipulandum (Brown & Jenkins, 1968). For example, in most autoshaping experiments with birds, the netural stimulus has been a lit pecking key. Even though no response is required for food to be delivered, the birds soon come to peck the ke ...
... conditioning, but the neutral stimulus is associated with a manipulandum (Brown & Jenkins, 1968). For example, in most autoshaping experiments with birds, the netural stimulus has been a lit pecking key. Even though no response is required for food to be delivered, the birds soon come to peck the ke ...
continued
... • Health care worker also relates more effectively with coworkers and other individuals ...
... • Health care worker also relates more effectively with coworkers and other individuals ...
Technology
... Relates to individual sensory dominance Auditory learners learn best by listening Visual learners learn best by seeing Kinesthetic/Tactile learners learn best by doing and touching ...
... Relates to individual sensory dominance Auditory learners learn best by listening Visual learners learn best by seeing Kinesthetic/Tactile learners learn best by doing and touching ...
Coaching Presentation - Doncaster Hockey Club, Melbourne
... How much playing experience do they have? How well do the players know each other? How well do they accept responsibilities? Are they accustomed to being told what to ...
... How much playing experience do they have? How well do the players know each other? How well do they accept responsibilities? Are they accustomed to being told what to ...
Other Recommendations for Using Multiple Intelligences
... dictates that adult learners benefit greatly when allowed to draw from their personal experiences in order to enhance their learning. Knowles (2005) states, “The richest resources for learning reside in adult learners themselves”. This aspect of Knowles theory connects directly with intrapersonal in ...
... dictates that adult learners benefit greatly when allowed to draw from their personal experiences in order to enhance their learning. Knowles (2005) states, “The richest resources for learning reside in adult learners themselves”. This aspect of Knowles theory connects directly with intrapersonal in ...
learners
... learning environment, which in turn helps to encourage prolific reciprocal tutoring. ...
... learning environment, which in turn helps to encourage prolific reciprocal tutoring. ...
Motivation - Studies
... • Gives more emphasis to the internal processes that occur when training content is learned and retained. • Information can come from another person or the learner’s own observation of the results of his action. • If the evaluation of the response is positive, this provides reinforcement that the be ...
... • Gives more emphasis to the internal processes that occur when training content is learned and retained. • Information can come from another person or the learner’s own observation of the results of his action. • If the evaluation of the response is positive, this provides reinforcement that the be ...
Learning and Memory PP
... Unwanted events that decrease the frequency of the behavior they follow when they are applied. Some effects: doesn’t teach alternatives Must be consistent to work Can create anger/hostility Can create the opposite effect Can confuse ...
... Unwanted events that decrease the frequency of the behavior they follow when they are applied. Some effects: doesn’t teach alternatives Must be consistent to work Can create anger/hostility Can create the opposite effect Can confuse ...
Cognitive Learning Theories
... • Behavioral Learning Theories – focuses on observable changes in outward behavior & on the impact of external stimuli to effect change. • Cognitive Learning Theories – focuses on the internal mental processes, how they change, and how they affect external behavior changes. ...
... • Behavioral Learning Theories – focuses on observable changes in outward behavior & on the impact of external stimuli to effect change. • Cognitive Learning Theories – focuses on the internal mental processes, how they change, and how they affect external behavior changes. ...
Adult Learning Theory
... Orientation to learning aspects: this provided me with the understating that adults can be utilized in the production of learning experiences by integration them into resources for learning. Often times, people do not utilize this reservoir of experiences and talents. At the same time, relating lear ...
... Orientation to learning aspects: this provided me with the understating that adults can be utilized in the production of learning experiences by integration them into resources for learning. Often times, people do not utilize this reservoir of experiences and talents. At the same time, relating lear ...
What is Development
... Vygotsky’s theories of cognitive development. What implications do these theories have for your teaching your future students? How does the information processing theory help you to understand the learning process in which students engage during class? ...
... Vygotsky’s theories of cognitive development. What implications do these theories have for your teaching your future students? How does the information processing theory help you to understand the learning process in which students engage during class? ...
LEARNER CENTERED APPROACH
... Acquisition of complex knowledge and skills requires extended learner effort and guided practice. Without learners' motivation to learn, the willingness to exert this effort is unlikely without force. ...
... Acquisition of complex knowledge and skills requires extended learner effort and guided practice. Without learners' motivation to learn, the willingness to exert this effort is unlikely without force. ...
Introduction to Behaviorism Introduction Basic Assumptions of
... Learning has occurred only when behavior change is observed. Behavior is conditioned by environmental events. The things we learn – the results of experience – are often beyond our control. ...
... Learning has occurred only when behavior change is observed. Behavior is conditioned by environmental events. The things we learn – the results of experience – are often beyond our control. ...
CD ch1-2 - Fairfield Public Schools
... how to nurture and educate children. • They have found that child development follows five general rules. ...
... how to nurture and educate children. • They have found that child development follows five general rules. ...
Innovative Models
... Learning Alison Leigh Brown Associate Vice President of Academic Affairs Northern Arizona University Extended Campuses Personalized Learning pl/nau.edu ...
... Learning Alison Leigh Brown Associate Vice President of Academic Affairs Northern Arizona University Extended Campuses Personalized Learning pl/nau.edu ...
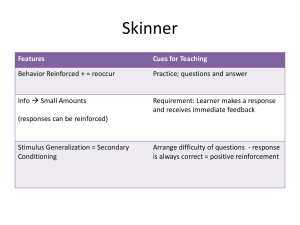
behaviorism learning theory
... • The behavioral learning theory is represented as an S-R paradigm. The organism is treated as a “black box.” We only know what is going on inside the box by the organism’s overt behavior. ...
... • The behavioral learning theory is represented as an S-R paradigm. The organism is treated as a “black box.” We only know what is going on inside the box by the organism’s overt behavior. ...
Secondary Instruction with Multisensory Algebra
... with peers and teachers. • Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances. • A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression. • A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems. Emotional disturbance includes schizophrenia. Th ...
... with peers and teachers. • Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances. • A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression. • A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems. Emotional disturbance includes schizophrenia. Th ...