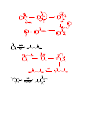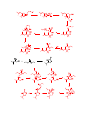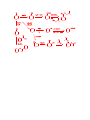* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer keys
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
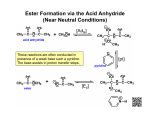
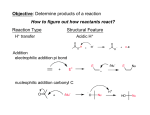
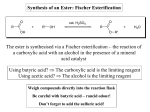
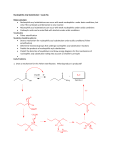
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Nomenclature 1. Provide the IUPAC or common names for each compound. 2,2-dimethylpropanoyl chloride cyclohexanecarboxylic anhydride ethyl 3-methylhexanoate cis-2-bromocyclohexanecarboxylic acid -caprolactone -valerolactam 1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid N,N-dimethylbenzamide glutaric acid 2. Give the structure corresponding to each name. (a) propanoic anhydride (b) -chlorobutyryl chloride (c) cyclohexyl propanate (e) isopropyl formate (f) 4-methylheptanenitrile (g) N,N-dibenzylformamide (h) diethyl oxalate (i) -valerolactone (h) phthalic acid Properties and Reactivity 3. Rank the compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution. Answer: 4. Explain why ester A is more reactive than ester B in nucleophilic acyl substitution. Answer: 5. Explain why acetamide is a weaker base than ethylamine. Answer: 6. Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. Mechanisms 7. Draw a stepwise mechanism for each of the following reactions. Synthesis 8. What carboxylic acid and alcohol are needed to prepare each ester by Fischer esterification? 9. Devise a synthesis of each compound using 1-bromobutane as the only organic starting material. You may use any other inorganic reagents. Answers: 10. Devise a synthesis of each compound from bromocyclohexane and any other organic or inorganic reagents. Answers: