* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit C Lesson 6 Carboxylic Acids And Esters
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
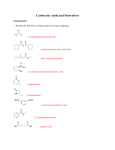
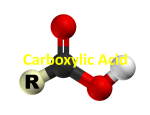
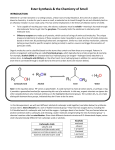
Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are weak acids that contain the carboxyl group (-COOH) Carboxyl group C=O | OH The hydrogen attached to the carboxyl group is released when these molecules ionize in water. R-COOH(aq) + H2O(l) R-COO-(aq) + H3O+(aq) Naming and Drawing Carboxylic Acids: Identify the root Locate the longest chain that includes the carboxyl group. Name the parent alkane. Identify the suffix Drop the –e at the end of the name of the parent alkane and replace it with –oic acid. Identify the prefix Name and number any alkyl side groups on the main chain. The carbon atom of the carboxyl group is always number one. EX. Name the following compound EX. Name the following compound EX. Name the following compound EX. Name the following compound EX. Draw the structure of butanoic acid EX. Draw the structure of 4-bromo-2-methylpentanoic acid EX. Draw the structure of 2,3-difluoropropanoic acid EX. Draw the structure of 3-phenylbutanoic acid Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids The carboxyl group is very polar, allowing the molecules to form hydrogen bonds with one another. The result is much higher boiling points than for other hydrocarbons and derivatives with the same number of carbon atoms. Compound butane butan-1-ol butanoic acid Boiling Point (oC) - 0.5 117.2 165.5 Short-chain molecules are liquids at standard temperature while longer-chain molecules are waxy solids. The polarity of the carboxyl group makes the short-chain (1 to 4 C atoms) molecules to be very soluble in water. As the hydrocarbon chain becomes longer, the non-polar characteristics of the chain cause the larger carboxylic acids to be less soluble in water. Molecules of 5 to 9 C atoms are less soluble Chains of 10+ C atoms are insoluble in water Carboxylic acids are weak acids they turn litmus paper red and conduct electricity. Esters An ester is a hydrocarbon derivative that contains the following functional group: O R C O R’ Esters are formed by a reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. To name an ester, the name of the carboxylic acid and alcohol is used as a combination. O O + R C O H carboxylic acid + H O alcohol R’ R C ester O R’ H O H water Naming and Drawing Esters: Identify the root Identify the part of the ester that contains the C = O group. The root of the name of the ester is based on the name of the acid. Determine the name of the parent acid. Identify the suffix Remove the –oic acid from the name of the parent acid and replace it with –oate. Identify the prefix The name of the alkyl group originating from the alcohol is the prefix for the name of the ester. There is always a space between the name of the alkyl group and the root. EX. Name the following compound EX. Name the following compound EX. Name the following compound EX. Name the following compound EX. Draw the structure of ethyl butanoate EX. Draw the structure of methyl propanoate EX. Draw the structure of butyl 2-methylpropanoate Physical Properties of Esters The C=O group makes esters somewhat polar but without the –OH group, ester molecules cannot form hydrogen bonds with one another. Therefore, their boiling points are much lower than similar sized alcohols and carboxylic acids. The most noticeable characteristic of esters is their volatility which allows them to generate aromas. Ex. ethyl octanoate (found in oranges) and pentyl ethanoate (found in bananas) Chem 30 Carboxylic Acids and Esters 1. Name each of the following molecules: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) 2. Draw a condensed structural diagram for each of the following: (a) propyl butanoate (b) propanoic acid (c) hexanoic acid (d) ethyl octanoate (e) 2-methylpropyl methanoate (f) 3,4-diethyl-2,3,5-trimethylheptanoic acid 3. Draw a line structural diagram for compound in question 2.