* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20 - people.vcu.edu
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
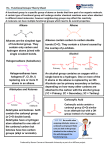
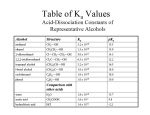
Chapter 20 – Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature o IUPAC This is our highest priority group Find the longest chain, drop the “e” and add “oic acid” Decane → decanoic acid Structure and physical properties o Extended hydrogen bonding leads to high boiling points. Acidity o pKa’s are around 4-5 o If electron withdrawing groups are near the carboxyl group, then the pK a is lowered. This is because the electron withdrawing group can stabilize the negatively charged conjugate base. Salts of carboxylic acids o Nomenclature – remove the “ic acid” and add “ate” - OH 3-methylbutanoic acid 3-methylbutanoate o The carboxylate ions are now much more water-soluble Synthesis of carboxylic acids o Oxidation of primary alcohols with chromic acid or KMnO4 See Chapter 11 for review o Cleavage of alkenes with vigorous KMnO4 This gives ketones or carboxylic acids, depending on the specific alkene. See Chapter 8 for review o Cleavage of alkynes with O3 or vigorous KMnO4 See Chapter 9 for review o Carboxylation of Grignards 1) 2) H+ CH3--MgBr o Hydrolysis of acid derivatives Any acid derivative H20 acid or base carboxylic acid or carboxylate + other piece Fischer Esterification o This is a big one to know! Even if you don’t know this mechanism for this class, your prehealth standardized tests will expect you to know it. o Overall: Carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water o Step 1: protonation of carbonyl to “activate” it for attack. H+ o Step 2: Alcohol attacks carbonyl carbon of the acid o Step 3: Deprotonation of the oxygen from the alcohol o Step 4: Protonation of one of the oxygens from the acid H+ o Step 5: Loss of water, forming a resonance-stabilized carbocation o Step 6: Deprotonation of carbonyl Hydrolysis of esters o Can be acid catalyzed. o When it’s base-catalyzed, it’s called saponification. When you hydrolyze triglycerides with base, you get carboxylates with long fatty chains. These chains form micelles. Water-soluble with lipophilic interiors. nonpolar dirt Direct formation of amides o What would happen if you put the following reagents into a vessel? Just acid-base chemistry. o In order to make the amide, you have to heat it up. heat H2O o Polymerization When you put molecules with dual functional groups in together, you get long chains heat ( ) n Reaction with alkyl lithiums o This is the only time we see alkyl lithiums behaving differently from Grignards o The alkyl lithium first deprotonates the carboxyl group, giving the carboxylate o A second alkyl lithium then adds to the carbonyl o After protonation, you have the hydrate, which forms the ketone. CH3-Li CH3-Li - - Reduction of carboxylic acids o COOH to 1° alcohol You’ve already seen this – add LiAlH4 o Conversion to the ketone o Reduction to the aldehyde. Convert to acid chloride, then use LiAl(OtBu)3H H+