* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4_Carbonyl and carboxylic acid questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
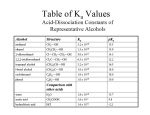
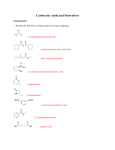
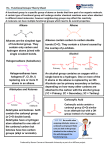
Carbonyl and carboxylic acid questions Carbonyls Answer all questions. 1. For each of the following tests complete the following: a. For which functional group should it give a positive reaction? b. What observation should be made for a positive reaction? c. Write down the equation (or half equation) that explains the observations made. Reactions: 2,4-DNPH; Ammoniacal silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent); Fehling’s solution; Acidified potassium dichromate. [12] 2. Give full mechanisms for the following reactions. a. Addition of HCN to propanone b. Reduction using lithium aluminium hydride [6] 3. Explain the bonding in carbonyls based on hybridisation of s and p orbitals and use it to explain its typical reactivity. [4] 4. Explain in terms of bonding why carbonyls have higher b.ps than corresponding alkanes but lower b.ps than corresponding alcohols. [2] Carbonyl and carboxylic acids: Knowing your reactions: Answer all questions. 5. Consider the reaction scheme shown below a. State the reagent(s) that could be used for: i. step 1 ii. step 2. [2] b. Compound B has optical isomers. What structural feature in compound B results in optical isomerism? [1] c. Draw the structure of compound C. [1] d. Compound C can be reduced to propane-1,2-diol. Using [H] to represent the reducing agent, construct a balanced equation for this reduction. [2] Unit 4_Organic_Carbonyl_Carboxylic acid questions_June 09 6. The oxidation of an alkene with trioxygen (ozone), followed by hydrolysis (process is called ozonolysis) gives 2 carbonyl compounds: In such an experiment an alkene C6H12 gave an aldehyde K and a ketone L, both of molecular formula C3H60. a. Describe a test, giving the result in each case, which would: i. Show that both K and L contain a carbonyl group. ii. Distinguish K from L iii. Show that L contains the CH3-CO unit [3] b. Draw the structures of the products formed when K and L are reduced with sodium tetrahydridoborate (III) (NaBH4). [2] c. Aldehydes can be prepared by the controlled oxidation of alcohols. i. State the reagents and conditions required to bring about this oxidation. [2] ii. How might you carry out the oxidation in the laboratory to maximise the yield of aldehyde. [2] Properties and reactivity of carboxylic acids. Answer all questions. 7. Carboxylic acids have the following properties: a. higher melting and boiling points than comparable alkanes (Mr) b. solubility in water Account for these properties in terms of the specific properties of the COOH group. [3] 8. Carboxylic acids react as typical acids. Use this information to predict the products of the following: [6] a. CH3COOH + NaOH b. 2CH3COOH + CaCO3 9. Write down the structural formula of: a. propanoic acid b. the propanoate ion Applying knowledge challenge Unit 4_Organic_Carbonyl_Carboxylic acid questions_June 09 c. 2CH3COOH + Mg [1] [1] This is an extension section requiring application of knowledge from AS and unit 4 of A2. 10. Two isomeric compounds, A and B, each have a relative molecular mass of 58 and the following percentage composition by mass: C = 62.1%; H = 10.3%; O = 27.6%. a. Calculate the molecular formula of A and B. [2] b. Draw the structural formula of A and B. [2] c. Name a reagent that reacts with only one of A and B. Identify which isomer reacts and state the observation. [2] 11. Devise a reaction sequence that results in the production of pentanoic acid, having been provided with pentanoyl chloride, water and ammonia as possible starting reagents. Give reagents and conditions for each step required and name every compound used/produced in the reaction sequence. 12. Answer Q6 attached (June 08 unit paper). Try to answer as much as you can if attempting this question, it requires application of chemistry knowledge and potentially a little research! Unit 4_Organic_Carbonyl_Carboxylic acid questions_June 09