* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conditioning Definitions - No Spaces Between
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
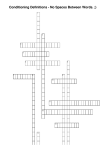
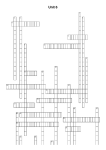
Conditioning Definitions - No Spaces Between Words. ;) 1 2 3 4 5 7 6 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Across Down 3. a response is rewarded after an unpredictable amount of time has passed. This schedule produces a slow, steady rate of response. Does your boss randomly drop by your office a few times throughout the day to check your progress? This is an example. 4. a decrease in response to a stimulus after repeated presentations. For example, a novel sound in your environment, such as a new ring tone, may initially draw your attention or even become distracting. After you become accustomed to this sound, you pay less 1. a schedule of reinforcement where a response is reinforced after an unpredictable number of responses. This schedule creates a steady, high rate of responding. Gambling and lottery games are good examples of a reward based on a variable ratio schedule. 2. a previously neutral stimulus that, after becoming associated with the unconditioned stimulus, eventually comes to trigger a response. 6. a response or behavior is strengthened by stopping, removing or avoiding a negative attention to the noise and your response to the sound will diminish. 5. a term used in both classical and operant conditioning. It involves the ability to distinguish between one stimulus and similar stimuli. 7. your teacher's last name. 10. refers to the gradual weakening of a conditioned response that results in the behavior decreasing or disappearing. In other words, conditioned behavior eventually stops. 11. involves the addition of a reinforcing stimulus following a behavior that makes it more likely that the behavior will occur again in the future. When a favorable outcome, event, or reward occurs after an action, that particular response or behavior will be strengthened. After you execute a turn during a skiing lesson, your instructor shouts out, "Great job!" 12. is one that unconditionally, naturally, and automatically triggers a response.Pollen from grass and flowers causes you to sneeze. The pollen from the grass and flowers is it. 13. a schedule of reinforcement where a response is reinforced only after a specified number of responses. 15. the learned response to the previously neutral stimulus. 16. a schedule of reinforcement where the first response and subsequent responses are rewarded only after a specified amount of time has elapsed. 17. the tendency for the conditioned stimulus to evoke similar responses after the response has been conditioned. For example, if a child has been conditioned to fear a stuffed white rabbit, it will exhibit fear of objects similar to the conditioned stimulus such as a white toy rat. (Starts with a G) outcome or aversive stimulus. You decide to clean up your mess in the kitchen (the behavior) to avoid getting into a fight with your roommate (removal of the aversive stimulus). 8. it involves taking something good or desirable away to reduce the occurrence of a particular behavior. A teenage girl stays out for an hour past her curfew, so her parents ground her for a week. 9. the unlearned response that occurs naturally in reaction to the unconditioned stimulus. For example, if the smell of food is the unconditioned stimulus, the feeling of hunger in response to the smell of food 14. it involves presenting an unfavorable outcome or event following an undesirable behavior. You wear your favorite baseball cap to class but are verbally reprimanded by your instructor for violating your school's dress code.