* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10.2 Neurones
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
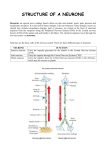
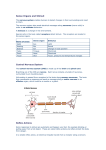
10.2 Neurones AQA A2 2011 ad Learning objectives: Name and give location of the three types of neurones. Relate the structure of the neurone to its function. Structure of neurone Cells specialised for rapid transmission of electrical impulses. Consist of Cell body: contains large nucleus, large amount RER for protein and neurotransmitter production Dendrons: extensions of the cell body subdivided into dendrites carrying impulses to the cell body Axon:long fibre carries nerve impulses away from cell body Schwann cells: wrap round axon with many layers of membrane, providing electrical insulation. Phagocytic removing cell debris and involved in nerve regeneration. Myelin sheath: axon covering made of the membranes of Schwann cells. Membranes rich in lipid myelin. Myelinated axons transmit impulses faster than non-myelinated axons. Nodes of Ranvier: 2-3µm gaps every 1-3mm between Schwann cells where there is no myelinated sheath Neurones Motor neurone Sensory neurone Intermediate neurone Summary Neurones are adapted to carry electrochemical changes called (1). Each neurone comprises a cell body that contains a (2) and large amounts of (3), which is used in the production of proteins and neurotransmitters. Extending from the cell body is a single long fibre called an axon and smaller branched fibres called (4). Axons are surrounded by (5) cells, which protect and provide (6) because their membranes are rich in a lipid called (7). There are three types of neurone. Those that carry nerve impulses to the effectors are called (8) neurones. Those that carry impulses from a receptor are called (9) neurones and those that link the other two types are called (10) neurones. 1. Nerve impulse/action potential 2. Nucleus 3. RER 4. Dendrites 5. Schwann cells 6. Insulation 7. Myelin 8. Motor 9. Sensory 10. Intermediate