* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What you should know
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
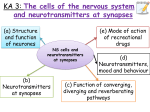
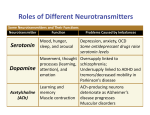
Unit 3, Key Area 3: What you should know 1. The nervous system is composed of sensory, inter and motor _______________ which transmit electrical signals, and ____________ cells. 2. Each neurone consists of a cell __________ and associated nerve fibres: one axon and several _______________. 3. An axon is surrounded by a __________________ sheath of insulating material whose presence greatly increases the _____________ at which nerve impulses can be transmitted through the fibre. 4. Glial cells _____________ neurones, maintain a stable environment around neurones and produce the myelin ________________. 5. _______________________ continues until adolescence. The myelin sheath is destroyed by certain _______________ causing loss of coordination. 6. A synaptic __________ is a tiny space between two neurones. Information is transmitted at a synapse by a chemical called a _________________________ being released from vesicles in the _____________________ neurone. The neurotransmitter combines with ____________ sites on the postsynaptic membrane. 7. The receptor determines whether the signal generated is ___________ or inhibitory. 8. To prevent continuous stimulation of __________________ neurones, neurotransmitters are ________________ from the synaptic cleft by ________ action or re-uptake. 9. The cumulative effect of a series of _____________ stimuli that together bring about an impulse is called _____________________. 10. In a _________________ neural pathway, nerve impulses from several sources meet at a common destination. 11. In a ________________ neural pathway, the route along which a nerve impulse travels divides, allowing information to pass to several destinations. 12. In a _______________ pathway, later neurones form synapses with earlier ones, allowing the nerve impulse to be sent _________ through the circuit. 13. The ability of brain cells to become ____________ as a result of new environmental experiences is called __________ of response. 14. ____________________ are chemicals that function like neurotransmitters and act as natural _________________. 15. ____________________ is a neurotransmitter secreted by neurones in the brain’s _________________ pathway which is activated by certain types of beneficial behaviour. 16. Chemicals that act like neurotransmitters are used in the treatment of some disorders. An _____________ is a chemical that stimulates specific receptors in postsynaptic neurones and ___________ the action of the naturally occurring neurotransmitter. An ____________ blocks receptors and prevent the neurotransmitter from acting on them. 17. Some drugs act by _________________ the enzyme that degrades the natural neurotransmitter or by inhibiting its _________________. 18. Many __________________ drugs bring about their effect by affecting the brain’s reward circuit thereby altering the person’s ___________, perception and _______________. The drugs may act as agonists, antagonists or inhibitors. 19. An increase in the number and sensitivity of neurotransmitter receptors following repeated exposure to a drug that is an antagonist is called ___________________ and leads to ______________. 20. A decrease in the number and sensitivity of neurotransmitter receptors following repeated exposure to a drug that is an agonist is called ___________________ and leads to drug _____________. addiction agonist altered antagonist back behaviour body cleft converging dendrites desensitisation diseases diverging dopamine endorphins enzyme excitatory glial inhibiting mimics mood myelin myelination neurones neurotransmitter painkillers plasticity postsynaptic presynaptic receptor recreational removed re-uptake reverberating reward sensitisation sheath speed summation support tolerance weak