* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download monosaccharides
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Cryobiology wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
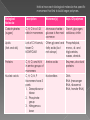
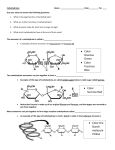
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids all are built from C, H, and O atoms are in different ratios 2. Each biological molecule is a polymer made of repeating subunits called monomers 3. These subunits link in dehydration synthesis reactions a.k.a. condensation 4. The other product is always water The next slide is not in your notes. It is an overview of the four biological molecules that we will be discussing. Read through the information. Notice how each biological molecule has specific monomers that link to build larger polymers. Biological Molecule Description Monomer(s) Exps. Of polymers Carbohydrates (sugars) C, H, O in a 1:2:1 ratio in monomers Monosaccharide – Starch, glycogen, glucose is the most cellulose, chitin common Lipids (fats and oils) Lots of C-H bonds, fewer O; NONPOLAR Often glycerol and Phospholipids, fatty acids (but mono-, di- and not always) triglycerides, waxes, steroids Proteins C, H, O, and N; N in amino groups of monomers Amino acids Enzymes, structural proteins Nucleic acids C, H, O, N, P Monomers have 3 parts: 1. Deoxyribose or ribose 2. Phosphate group 3. Nitrogenous base Nucleotides DNA RNA (messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA) Elements C, H, O Ratio of elements 1C : 2H: 1O Monomers Monosaccharides Polymers Polysaccharides Also disaccharides Bonds joining monomers are called… Glycosidic Main functions Quick energy, energy storage, structure Important fact(s) •Names often end in –ose •Ratio of H:O is same as in water so carbohydrate refers to carbon and “water” meaning 2:1 H:O ratio monomers of carbohydrates = monosaccharides or simple sugars contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 There are different type of monosaccharides. They join to form disaccharides or polysaccharides. common monosaccharides: › glucose › fructose › galactose › deoxyribose › ribose We’ll go through each of these in your notes. Glucose › Quick energy source for cells Cells use glucose 1st to make ATP! › made in plants during photosynthesis › most common monomer (links to form carb polymers) Fructose › sugar found in plants › sweet Ribose › C5H10O5 › found in ribonucleic acid (RNA) Deoxyribose › same as ribose See the difference? It’s right here! except missing an oxygen › found in DNA Galactose › Structurally similar to glucose Gives the simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound For monosaccharides: › (CH2O)n where n can vary › Exp. (CH2O)6 can also be written as C6H12O6 compounds with a single chemical formula but different structures Exps: glucose, fructose, and galactose are isomers! Why? › all have the same formula C6H12O6 › all have different structures that determine properties Same chemical formula (number and type of atoms) Different structural formulas (arrangement of atoms in space) DISACCHARIDES (double sugars) are made when 2 monosaccharides are joined together by a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis reaction. The disaccharide is a product of this reaction along with H2O – always! Water is considered the secondary product. › Sucrose table sugar glucose + fructose › Lactose milk sugar glucose + galactose › Maltose malt (grain) sugar glucose + glucose POLYSACCHARIDES are complex carbs made of many monosaccharides that are joined in condensation reactions or dehydration synthesis. The second product in these reactions is always H2O. The most common monomer = glucose. Examples of polysaccharides: › Glycogen, Chitin (animals) › Starch, Cellulose (plants Hundreds of highly branched chains of glucose monomers Intermediate energy source for animals Stored in liver and muscles Liver converts it to glucose through hydrolysis when quick energy is needed 2 forms: › Amylose – spiral chain of glucoses › Amylopectin branching chain of glucose monomers – not as branched as glycogen! Plant storage molecule--energy reserve Starch is stored in plant roots › Potatoes are “starchy” veggies! Thousands of glucose monomers in long straight chains Chains laid side by side and connected to each other by hydrogen bonds Structural carbohydrate-does not provide energy › gives cells strength and rigidity Also called “fiber” Most abundant carb on Earth! difficult to break down found in cotton and linen animals cannot digest it! H bonding occurs between hydroxyls on adjacent chains Second most abundant polysaccharide Chemically similar to cellulose but has N Structural carb - found in shells of insects › Very firm › Helps protect against harm and pressure › Must be shed for insect to grow Subject of medical research – accelerates skin healing; used to treat burns