* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anxiety Disorders
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Kleptomania wikipedia , lookup
Selective mutism wikipedia , lookup
Reactive attachment disorder wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Schizoid personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
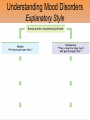
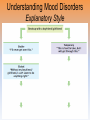
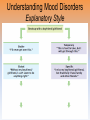
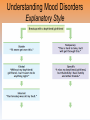
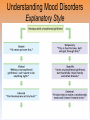
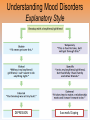
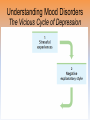
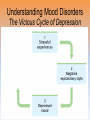
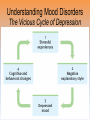
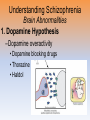
Unit 12: Abnormal Psychology Perspectives on Psychological Disorders Questions… • How should we define psychological disorders? • How should we understand disorders? • How should we classify psychological disorders? • • • • • • • • • • • Intellectual Disability Learning Disorder Tourette’s Disorder Pica Rumination Binge Eating Enuresis Encopresis Nightmare Disorder Erectile Disorder Female Orgasmic Disorder • Gender Dysphoria • Oppositional Defiant Disorder • Kleptomania • Pyromania • Gambling Disorder • Voyeuristic Disorder • Exhibitionist Disorder • Frotteuristic Disorder Caffeine Use Disorder Non-suicidal Self-Injury Internet Addiction Disorder Disorders We Need To Know… • Anxiety Disorders – – – – Anxiety Generalized Anxiety Panic Phobias • OCD • PTSD • Dissociative Disorders – Dissociative Identity Disorder – Dissociative Disorders • Mood Disorders – Major depressive disorder – Mania – Bipolar Disorder • Somatic Symptom Disorders• Schizophrenia – Somatoform – Conversion – Illness anxiety disorder (hypochandriasis) • Personality – Personality disorders – Antisocial Defining Psychological Disorders • Psychological disorders – clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior – Dysfunctional: maladaptive – interfere with day-today life Japan: hissing is polite way to show respect for superiors – Distressful Among the Karaki of New Guinea a man is considered abnormal if he has not engaged in sex with a man before marriage Thailand: PDA between men & women unacceptable; but men holding hands is a sign of friendship…& use of straws is considered vulgar – Deviant (different) behavior (from one’s culture) Understanding Psychological Disorders The Medical Model Demon …led topossession harsh and • Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) – reform inhumane conditions of mentally ill patients as ineffective cause for mental remedial illness treatment • Medical model psychopathology – Idea that mental illness has physical causes that can be diagnosed based on symptoms & sometimes cured through therapy in a hospital. Contrast this with the biopsychosocial approach to disordered behavior. Perspectives – Causes of Disordered Behavior Psychoanalytic unconscious conflict / childhood Humanistic no UPR /people putting CW on you Cognitive faulty thinking Behavioral faulty environment Biopsychosocial eclectic approach Understanding Psychological Disorders The Biopsychosocial Approach Mind & body are inseparable; negative emotions contribute to physical illness, and physical abnormalities contribute to negative emotions. self-focused rumination psycho rejection from others social low serotonin bio levels Why would it be difficult to explain anorexia nervosa occurring mostly in Western cultures in terms of the medical model? Classifying Psychological Disorders • DSM-IV-TR DSM-5 – Diagnostic & Statistical Manual (5th Revision) • What does it do? Why have it? *DESCRIBES DISORDER / DOES NOT EXPLAIN* – reliability of diagnoses by different psychologists (83%) – focuses treatment – common language – preconception & stereotypes can stigmatize – self-fulfilling prophecy + - Rosenhan Study • Use link on calendar to skim through or do your own internet search to find the answers to the following: – What was the purpose of the Rosenhan study? – What was the methodology? – What were the results? – Criticism of study? Labeling Psychological Disorders • Rosenhan’s study Do the characteristics that lead to psychological diagnoses reside in the patients themselves or in the environments in which observers find them? “pseudopatients” “empty” “hollow” “thud” Schizophrenia Up to them to gain their release “note taking behavior” Average stay = 19 days (52) Pseudopatient: “Pardon me Dr.___, when will I be allowed ground priveileges? Dr.: Good morning Dave. How are you today? Potential dangers and benefits of using diagnostic labels. Anxiety Disorders Read pages 569576 Anxiety Disorders • Anxiety disorders – distressing persistent worry / maladaptive behaviors that reduce the worry –Generalized anxiety disorder –Panic disorder –Phobia –Obsessive-compulsive disorder –Post-traumatic stress disorder Generalized Anxiety Disorder • Generalized anxiety disorder – Continual worry – No physical problem but can manifest itself physically or lead to physical problem • jittery; agitated; sleep issues – Women 2xs likely – Often accompanied by depression 300.02 3 of 6 need to be present Panic Disorder 300.01 Panic Disorder • Panic disorder –Panic attacks (1 in 75) • Strikes suddenly, minutes long, intense dread • Heart palpitations, shortness of breath, choking sensations, trembling or dizzy smokers have double risk panic disorder • Phobias Phobias – Irrational fear causes person to avoid some object, activity or situation –Specific phobia • Focus on animals, insects, heights, small spaces – specific trigger –Social Anxiety Disorder (social phobia) Go to lengths to –Agoraphobia avoid situation • Fear of situations where escape may be impossible or where panic attack happened before Understanding Anxiety Disorders The Learning Perspective • Fear conditioning Two ways to understand anxiety disorders: – Anxious people are hyperaware to possible threats Learning Perspective –Stimulus generalization –Reinforcement (negative) Perspective •Biological Observational learning – Parents communicate fear to children Understanding Anxiety Disorders The Biological Perspective • Natural selection – phobias focus on fears faced by our ancestors/compulsive acts exaggerate behaviors that helped survival • Genes – Runs in families / identical twins – anxiety gene – Glutamate & Serotonin • The Brain – Over-arousal in brain areas – impulse control & habitual behaviors – Anterior cingulate cortex (frontal lobe) / (amygdala) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • Obsessive-Compulsive disorder –Consistently interfere with everyday –An obsession vs a compulsion – Hoarders – Checkers – Counters – Cleaners https://youtu.be/LON36Xh pdDs DBS 5 min https://youtu.be/3lvbcShuz14 Pediatric OCD 4 min http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dSZNnz9SM4g https://youtu.be/OXjxbFQraL4 Afraid of Mom 1 min Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder • PTSD • Numbed social withdrawal, anxiety, insomnia • “shellshock” or “battle fatigue” – Not just due to a war situation – 10%-32% of those who experience trauma will develop – Greater one’s stress during event – Sensitive limbic system (stress hormones) – 1/10 women & 1/20 men • Post-traumatic growth https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7frOWBiU8D4 PTSD “benefit finding” Somatoform Disorders Somatic Symptom Disorder • mental illnesses that cause bodily symptoms, including pain. • may/may not be traced back to any physical cause. • not result of substance abuse or another mental illness. • not faking their symptoms. • Doctors need to perform many tests to rule out other possible causes before they diagnosis https://youtu.be/6xhypWbI0bk Conversion disorder – Weakness or paralysis – – – – – Conversion Disorder http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T9R Ps_ysYgE Conversion Disorder Today Show Abnormal movement, such as tremors or difficulty walking Loss of balance Cause: stressful Difficulty swallowing or "a lump in the throat" event triggers Seizures or convulsions At Risk: females; trauma; genetic Episode of unresponsiveness – anxiety converted into physical symptoms – Illness Anxiety Disorder Hypochondriasis • preoccupation with and fear of having or acquiring a serious disorder. • move from doctor to doctor (reinforcing) –factitious disorders » Munchasuen (Munchasuen by Proxy) Cause Somatic Symptom Disorder • Psychoanalytic: manifestation of unresolved conflict • Behaviorist: reinforced for behavior Dissociative Disorders http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=0tITzDjPf4g Intro to DID – Inside (5:05) https://youtu.be/n2atzoaA2NI 20 personalites (5 min) DID • Dissociative disorders – 2+ distinct identities or personality states are present, each w/ own relatively enduring pattern relating to the environment and self. – Amnesia must occur, defined as gaps in the recall of everyday events, important personal information and/or traumatic events. (dissociative fugue) – The disturbance is not part of normal cultural or religious practices. • This DID criterion is to eliminate diagnosis in cultures or situations where multiplicity is appropriate. Understanding Dissociative Identity Disorder Genuine disorder or not? losing oneself in a role? hypnotizable DID rates 1930s-60s = 2 per decade 1980s = 20,000 Therapist’s creation? Handedness & Shifting visual acuity Brain activity is different Result of trauma (PTSD/Freud) or reinforcing b/c reduces anxiety? Mood Disorders http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2rxeFgK IS9s Brain Imaging http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=InNhDfD fl5c Synapse Review • Mood disorders – emotional extremes –Major depressive disorder (unipolar depression) • 2+ weeks of – – – – – – – depressed mood sleep disturbance appetite disturbance lack of energy feelings of worthlessness loss of interest in family and friends loss of interest in activities w/o clear reason –women 2xs as likely Dysthymic Disorder – depressive state lasting more than 2 yrs. Major Depressive Disorder Women more likely to attempt, men more likely to succeed Bipolar Disorder • Bipolar Disorder • Alternate between hopelessness & lethargy of depression & overexcited mania Diagnosis of young boys has skyrocketed Afflicts men & women equally in adults. –Over-talkative, overactive, elated, little need for sleep, etc. (agitated/restless) • Bipolar disorder and creativity Understanding Mood Disorders • Trapped in depressed mood = inactive & unmotivated; when mood lifts, these behavior & cognitive accompaniments disappear • Very common = causes are probably common too • Women are more vulnerable to disorders involving internalized state (men tend to have external disorders = alcohol, antisocial conduct, impulse control) Gender gap starts in adolescence • Therapy speeds recovery but many return to “normal” w/o professional help. Permanent if 1st episode strikes later in life. • Risk of depression less than 1% w/o stressful life event • Increase is probably authentic = more come forward Mood Disorders Genetic: • Runs in families (twin studies) • 35-40% heritable Brain • Hippocampus vulnerable to stress • Less activity in frontal lobe (left) Biochemical • Serotonin • Norepinephrine • Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil / exercise The Social-Cognitive Perspective – Self-defeating beliefs & negative explanatory style –Susan Nolan-Hoekseme says women over-think– “ruminate” –Aaron Beck says that there is a “cognitive triad” – negative view of self, circumstance, future learned helplessness –Martin Seligman says depressed patients have a negative explanatory style Stable, global, internal explanations Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style Understanding Mood Disorders Explanatory Style DEPRESSION Successful Coping Understanding Mood Disorders The Vicious Cycle of Depression Understanding Mood Disorders The Vicious Cycle of Depression Understanding Mood Disorders The Vicious Cycle of Depression Understanding Mood Disorders The Vicious Cycle of Depression Schizophrenia http://www.youtube .com/watch?v=nL_O TM7I3C0 Childhood Schizophrenia (4:59) Symptoms of Schizophrenia • Schizophrenia (split mind) – Group of disorders characterized by disorganized & delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, & inappropriate emotions & actions 1 in 100 – Not multiple personalities 24 million world wide David Berkowitz John Hinkley Mark David Chapman Symptoms of Schizophrenia • Disorganized thinking • The sheep languished –Delusions • Delusions of persecution paranoid • Delusions of grandeur –“Word Salad” – Breakdown in selective attention • • • • blue trains suffer Run desk making dinner sunglasses menu Dogs sleep chicken pencil trees Garbage pink composition solely bags speak deodorant Horse paper handbags skipping forests play together Symptoms of Schizophrenia • Disturbed perceptions –Hallucinations • Sensory experience w/o sensory stimulation –hearing voices most common http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4LScZZOkeIs Virtual Reality Hallucination (3:40 – start at :34 Positive Schizophrenia • symptoms that are in ADDITION to normal behavior • delusions • hallucinations • erratic emotions • Acute (reactive) schizophrenia – increasingly odd behavior over short period of time Negative Schizophrenia • Symptoms that are TAKEN AWAY from normal behavior • Catatonia – flat affect • Emotionless state – psychomotor (waxy flexibility) • Chronic (process) schizophrenia – longer term / slow to develop characterized by lack of drive, underactivity, social withdrawal Understanding Schizophrenia Brain Abnormalities 1. Dopamine Hypothesis –Dopamine overactivity • Dopamine blocking drugs • Thorazine • Haldol Understanding Schizophrenia Brain Abnormalities 2. Abnormal Brain Activity & Anatomy – Frontal lobe & core brain activity lessened – Fluid filled areas of the brain • Surrounding cerebral tissue is smaller (thalamus) Understanding Schizophrenia Brain Abnormalities 3. Maternal Virus During Pregnancy – Influence of the flu during pregnancy 4. Genetic predisposition – 1 in 100 odds – 1 in 10 w/sibling or parent w/ disorder – 1 in 2 if identical twin has schiz. (even when reared apart) Personality Disorders http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=clw_97mqpM Charles Manson http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=ErB0R4wl B64 Jeffery Dahmer http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PuB_ng5 uVaI Anxiety Disorders Case Studies Answers 1. GAD 2. Panic Attacks w/ Agoraphobia 3. Specific Phobia 4. OCD 5. PTSD 6. Specific Phobia 7. OCD 8. Agoraphobia 9. GAD 10. Social Phobia 11. PTSD 12. GAD 13. PTSD Personality Disorders • Personality disorders – Maladaptive thought and behavior patterns that are troublesome to others, harmful, or illegal. Feels no anxiety, depression or delusion – Borderline • Emotionally unstable; impulsive; unpredictable; irritable; prone to boredom – Histrionic • Excessively dramatic – Narcissistic • Unrealistically self-important; manipulative; lack empathy – Antisocial Antisocial Personality Disorder • Antisocial personality disorder – – – – – – – – – Violate others’ rights w/ guilt or remorse manipulative & exploitive self-indulgent & irresponsible can be charming(con-artist) “sociopath” or “psychopath” typically male before 15 lower reaction to stress Unconcerned w/ social rewards http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=0qyCR9tP DgM https://youtu.be/_Cz7CjeVmKI frontal lobe Rates of Disorder Rates of Disorder • Mental health statistics • Influence of poverty • Other factors 01. OCD 02. Conversion Disorder 03. Phobia 04. Dissociative Fugue 05. OCD 06. Panic Disorder 07. Phobia 08. Dissociative Amnesia 09. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder 10. Conversion Disorder 11. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder 12. Generalized Anxiety Disorder 13. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder 14. Dissociative Amnesia 15. Conversion Disorder 16. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Major Depression Paranoid Schiz. Disorganized Schiz. Bipolar Paranoid Schiz. Catatonic Schiz. Paranoid Schiz. Paranoid Schiz. The End • Types of Files Teacher Information – This presentation has been saved as a “basic” Powerpoint file. While this file format placed a few limitations on the presentation, it insured the file would be compatible with the many versions of Powerpoint teachers use. To add functionality to the presentation, teachers may want to save the file for their specific version of Powerpoint. • Animation – Once again, to insure compatibility with all versions of Powerpoint, none of the slides are animated. To increase student interest, it is suggested teachers animate the slides wherever possible. • Adding slides to this presentation – Teachers are encouraged to adapt this presentation to their personal teaching style. To help keep a sense of continuity, blank slides which can be copied and pasted to a specific location in the presentation follow this “Teacher Information” section. Teacher Information • Hyperlink Slides - This presentation contain two types of hyperlinks. Hyperlinks can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take the user directly to the beginning of that subsection. This allows teachers quick access to each subsection. – Bold print term hyperlinks: Every bold print term from the unit is included in this presentation as a hyperlink. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of the hyperlinks will take the user to a slide containing the formal definition of the term. Clicking on the “arrow” in the bottom left corner of the definition slide will take the user back to the original point in the presentation. These hyperlinks were included for teachers who want students to see or copy down the exact definition as stated in the text. Most teachers prefer the definitions not be included to prevent students from only “copying down what is on the screen” and not actively listening to the presentation. For teachers who continually use the Bold Print Term Hyperlinks option, please contact the author using the email address on the next slide to learn a technique to expedite the returning to the original point in the presentation. Teacher Information • Continuity slides – Throughout this presentation there are slides, usually of graphics or tables, that build on one another. These are included for three purposes. • By presenting information in small chunks, students will find it easier to process and remember the concepts. • By continually changing slides, students will stay interested in the presentation. • To facilitate class discussion and critical thinking. Students should be encouraged to think about “what might come next” in the series of slides. • Please feel free to contact me at [email protected] with any questions, concerns, suggestions, etc. regarding these presentations. Kent Korek Germantown High School Germantown, WI 53022 262-253-3400 [email protected] Division title (green print) subdivision title (blue print) • xxx –xxx –xxx Division title (green print) subdivision title (blue print) Use this slide to add a table, chart, clip art, picture, diagram, or video clip. Delete this box when finished Definition Slide = add definition here Definition Slides Psychological Disorder = deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional patterns of thoughts, feelings, or behaviors. Attention-deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) = a psychological disorder marked by the appearance by age 7 of one or more of three key symptoms; extreme inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Medical Model = the concept that diseases, in this case psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and, in most cases, cured often through treatment in a hospital. DSM-IV-TR = the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, updated as of 2000 “text revision”; a widely used system for classifying psychological disorders. Anxiety Disorders = psychological disorders characterized by distressing, persistent anxiety or maladaptive behaviors that reduce anxiety. Generalized Anxiety Disorder = an anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal. Panic Disorder = an anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable minutes-long episodes of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. Phobia = an anxiety disorder marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object, activity, or situation. Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (OCD) = an anxiety disorder characterized by unwanted repetitive thoughts (obsessions) and/or actions (compulsions). Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) = an anxiety disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience. Post-traumatic Growth = positive psychological changes as a result of struggling with extremely challenging circumstances and life crises. Somatoform Disorder = psychological disorder in which the symptoms take a somatic (bodily) form without apparent physical cause. Conversion Disorder = a rare somatoform disorder in which a person experiences very specific genuine physical symptoms for which no psychological basis can be found. Hypochondriasis = a somatoform disorder in which a person interprets normal physical sensations as symptoms of the disease. Dissociative Disorders = disorders in which conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings. Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) = a rare dissociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities. Formerly called multiple personality disorder. Mood Disorders = psychological disorders characterized by emotional extremes. Major Depressive Disorder = a mood disorder in which a person experiences, in the absence of drugs or a medical condition, two or more weeks of significantly depressed moods, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished interest or pleasure in most activities. Mania = a mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Bipolar Disorder = a mood disorder in which the person alternates between the hopelessness and lethargy of depression and the overexcited state of mania. (formerly called manicdepressive disorder.) Schizophrenia = a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, and inappropriate emotions and actions. Delusions = false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur, that may accompany psychotic disorders. Personality Disorders = psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. Antisocial Personality Disorder = a personality disorder in which the person (usually a man) exhibits a lack of conscience for wrongdoing, even toward friends and family members. May be aggressive and ruthless or a clever con artist.