* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chpt. 9 Endocrine System Review
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
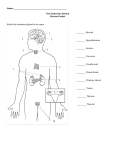
Chpt. 9 Endocrine System Review Part I. Short Answer 1. How are hormone concentrations are usually regulate? 2. Hypersecretions of growth hormone in adulthood leads to: 3. The ___ gland is located in the sella turcia in the brain. 4. What major body processes are controlled by hormones? 5. Hyposecretions of ADH leads to what disease? 6. The thyroid gland is located where? 7. The antagonist to calcitonin is what? 8. Name the mixed gland(s) in the body. 9. The gland referred to as the “Master Gland” is the ___. 10. Which gland is associated with the maturation of mature T-lymphocytes? 11. List the hormones that regulate mineral (salt) levels in the body. 12. True or false: the major endocrine organs of the body tend to lie near the midline of the body. 13. True or false: Epinephrine is a drug given to reduce inflammation. 14. Hypertension may result from the hypersecretion of what 4 hormones? 15. What 2 hormones are secreted by neurons? 16. True or false: Hormones travel throughout the body in the blood. 17. ANP, the hormone secreted by the heart, has exactly the opposite function to this hormone which is secreted by the outermost zone of the adrenal cortex. Name this hormone. 18. Define negative feedback & explain how it regulates blood levels of various hormones. 19. Define hormone. 20. Name 3 ways in which endocrine glands are stimulated to release their hormones & give one example of each way. 21. Hat are tropic hormones? 22. Name 3 hormone antagonists of insulin & 1 of PTH. 23. What causes a simple goiter? 24. The posterior pituitary is not really an endocrine gland. Why not? Why is it? 25. In general, the endocrine system becomes less efficient as we age. List 3 examples of problems that elderly individuals have as a result of decreasing hormone production. 26. Acromegaly is caused by hypersecretions of what hormone? 27. What system regulates metabolism & energy balance? 28. Does ADH prevent urine formation or increase heart rate? 29. Is it Diabetes I or Diabetes II that a person would be called insulin dependent? 30. Which gland is associated with Diabetes? Part II. Label the glands Part III. Fill in the Chart Gland Pineal Hormone Released Melatonin Target Tissue / Organ Chief Function of Hormone Involved in daily rhythms; possibly involved in maturation of sex organs Hypothalamus Hypothalamic-releasing & release-inhibiting hormones Anterior Pituitary Growth hormone (GH) Soft tissues, bones ______________________ Mammary glnds Stimulates protein synth. & bone growth Stimulates milk production & secretion Reg. Oogenesis & spermatogenesis Luteininzing Hormone; ______________________ ________________________________________________ Regulate anterior pituitary hormones Posterior Pituitary Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH); Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Thyroid stimulating (TSH) _______________________ ______________________ Uterus,mammary glands Kidneys, sweat glands Stimulate secretion of gluco-corticoids Stimulate secretion of ______________________________________ _______________________ _______________________ Uterine contractions, release of milk Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH); Thyroid ______________________________ Increases metabolic rate; helps to reglt. growth & development ______________________________________________ ____________________ All tissues _____________________ Bones, kidneys, intestine _______________________ Increases rate of cellular metabolism Triiodothyronine (T3) Parathyroid Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Bones, kidneys, intestine __________________________________________________ Thymus Thymosin _________________ Stimulates maturation of T lymphocytes Adrenal Gland Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine & Norepinephrine Cardiac & other muscles Stimulate ____________________ reaction; raise blood _______________________________________________ Adrenal Cortex Glucocorticoids ex. Cortisol ________________ ______________________________ Mineralcorticoids ex. Aldosterone Androgens ex. DHEA ________________ Increase reabsorption of ______ & to excrete __________ Stimulate onset of ___________, female sex drive _____________________ Liver, muscles, adipose tissues _______________ Pancreas ________________ ___________blood glucose levels Glucagon Gonads Ovaries Testes Lowers blood ________________ ____________________ Uterus _____________________ _____________________ ______________________ Uterus _____________________ Testes Inhibin _______________ Pelvis, cervix Ant. Pituitary Regulates menstrual cycle, secondary sex characteristics. Reg.menstrual cycle, pregnancy Dilates cervix & birth canal Inhibits ____________________ Regult. spermatogenesis, secondary sex characteristics inhibits FSH release Part IV. Matching Answer Statement 11. hormone that stimulates spermatogenesis & oogenesis Choices a. Relaxin 12. hormone that prevents urine formation b. Pineal Gland 13. hormone that regulates metabolism c. Luteininzing Hormone (LH) 14. hormone that raises blood glucose levels d. Insulin 15. hormone that lowers blood glucose levels e. Inhibin 16. hormone that dilates the cervix & birth canal f. Glucagon 17. hormone that inhibits FSH g. Epinephrine 18. regulates sleep & wake cycles h. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) 19. also known as adrenalin i. (T3 & T4 ) Triiodothyronine & Thyroxin