* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLULAR TRANSpoRT PRACTICE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
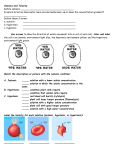
Name _____________________ Cellular Transport Practice 1. For each environment, draw an arrow to show the direction of water movement into or out of each cell. 2. Complete the following chart: Molecule Method of Transport Passive or Active? Direction of Movement Osmosis _________a concentration gradient Facilitated Diffusion _________a concentration gradient Diffusion _________a concentration gradient Endocytosis _________a concentration gradient Exocytosis _________a concentration gradient Description Match the direction of net movement to its description. The direction of net movement choices may be used more than once. ____ 3. diffusion ____ 4. facilitated diffusion ____ 5. osmosis ____ 6. endocytosis ____ 7. exocytosis a. movement from high to low concentration b. movement from low to high concentration 1 Name _____________________ A. B. C. D. For each environment, complete the following: Determine the solute and solvent for the solution outside the cell (environment) and for the inside of the cell. Tell whether the solution outside of the cell is hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic. Tell what will happen to the cell (shrink or swell). Give the direction of the net movement of water (into cell, out of cell, or into & out of cell at equal rates). 20% solute ____% solvent 80% solute ____% solvent ____% solute 10% solvent ____% solute 90% solvent solvent B. _______________________ B. _______________________ C. _______________________ C. _______________________ D. _______________________ D. _______________________ 40% solute ____% solvent 30% solute ____% solvent 50% solute ____% solvent solvent 50% solute ____% solvent solvent B. _______________________ B. _______________________ C. _______________________ C. _______________________ D. _______________________ D. _______________________ 80% solute ____% solvent ____% solute 70% solvent ____% solute 10% solvent 30% solute ____% solvent B. _______________________ B. _______________________ C. _______________________ C. _______________________ D. _______________________ 2 D. _______________________ Name _____________________ _______ 14. a. b. c. d. During diffusion molecules move _____________________. up the concentration gradient down the concentration gradient from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration in a direction that doesn’t depend on concentration _______ 15. When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system, the system has reached __________________. a. maximum concentration b. homeostasis c. osmotic pressure d. equilibrium _______ 16. a. b. c. d. The substance that is dissolved to make a solution is called the __________. diffuser solvent solute concentrate a. b. c. d. The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called _____. active transport facilitated diffusion osmosis phagocytosis _______ 17. _______ 18. Endocytosis and exocytosis are forms of _______________ transport. a. active b. passive _______ 19. a. b. c. d. Energy for active transport comes from the cell’s _____________. Golgi complex nucleus mitochondria lysosomes a. b. c. d. e. A cell must expend energy to transport substances using ______________. diffusion facilitated diffusion protein channels osmosis endocytosis _______ 20. _______ 21. White blood cells engulf, digest, and destroy invading bacteria using __________________. a. facilitated diffusion b. protein channels c. endocytosis d. osmosis 3 Name _____________________ _______ 22. a. b. c. d. e. All of the following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT _________ . diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis exocytosis protein channels _______ 23. If you soak your hands in water, your skin absorbs water and swells into distinct wrinkles. This is because your skin cells are ________ to the ________ water. a. hypotonic, hypertonic b. hypertonic, hypotonic c. hypotonic, hypotonic d. isotonic, hypotonic e. hypertonic, isotonic _______ 24. You buy a new fish for your freshwater aquarium. When you introduce the fish to its new tank, the fish swells up and dies. You later learn that it was a fish from the ocean. Based on what you know about osmosis, the most likely explanation is that the unfortunate fish went from a(n) ________ solution into a(n) ________ solution. a. isotonic, hypotonic b. hypertonic, isotonic c. hypotonic, hypertonic d. hypotonic, isotonic _______ 25. In osmosis, water moves toward the ___________ solution, and this is the solution with the _________ solute concentration. a. isotonic, greater b. hypertonic, greater c. hypertonic, lesser d. hypotonic, greater e. hypotonic, lesser _______ 26. a. b. c. d. You know that a cell is in a(n) _____ solution when it _____. hypotonic, becomes turgid hypotonic, gets smaller hypertonic solution, becomes turgid hypertonic, gains water _______ 27. The concentration of solutes in a red blood cell is about 2%. Sucrose cannot pass through the membrane, but water and urea can. Osmosis would cause red blood cells to shrink the most when placed in which of the following solutions? a. hypertonic sucrose solution b. hypotonic sucrose solution c. hypertonic urea solution d. hypotonic urea solution e. pure water 4 Name _____________________ _______ 28. Sea water is dangerous to drink because a. one cup of sea water contains enough sodium to poison you b. sea water is hypertonic to your body tissues and drinking it will cause you to lose water by osmosis c. sea water is isotonic to your body fluids and you will absorb too much water, causing your cells to burst d. the salt causes hypertension and you will promptly die of a stroke e. it contains toxic levels of iodine _______ 29. If the volume of a cell increases when it is placed in a solution, that solution is said to be __________ to the cell. a. hypertonic b. subatomic c. isotonic d. hypotonic _______ 30. Placing a cell in a hypotonic solution will cause water to ________________. a. move into the cell b. move out of the cell 33. What will happen if a cell that has a water concentration of 87% is placed in a 5% saltwater solution? 34. What will happen a cell with an internal salt concentration of 0.8% if it was placed in a 20% salt solution? Reading: Passive Transport Read the passage below. Notice that the sentences are numbered. Then answer the questions that follow. The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Like other forms of diffusion, osmosis involves the movement of a substance—water—down its concentration gradient. Osmosis is a type of passive transport. If the solutions on either side of the cell membrane have different concentrations of dissolved particles, they will also have different concentrations of “free” water molecules. Osmosis will occur as water molecules diffuse into the solution with the lower concentration of free water molecules. 35. What key term is defined in this passage? What does this term mean? 36. How are diffusion and osmosis related? 37. What does the word water in Sentence 2 tell you about osmosis? 38. Osmosis is a type of a. passive transport. b. diffusion. c. active transport. d. Both (a) and (b) 5