* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
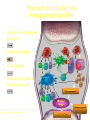
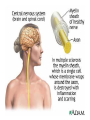
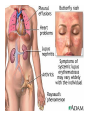
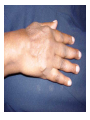
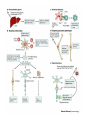
AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES DR IDA DZIFA KUWORNOO PHYSICIAN SPECIALIST KBTH • Greek word ‘auto’ meaning self. • Due to failure of an organism to recognize its own constituent parts as self leading to an immune response against its own cells and tissues. • Body’s own immune system begins to attack normal tissues cells and organs within the body. Potential Roles of B Cells in the Immunopathogenesis of RA • Secretion of proinflammatory cytokines • Antigen presentation • T-cell activation B cell Dendritic cell IL-6 • Autoantibody production and self-perpetuation TNF- Plasma cell IL-10 T cell RF TNF- Macrophage RF RF RF RF Fix complement IL-1 IL-6 (Dörner & Burmester, 2003; Edwards et al, 1999; Gause & Berek, 2001; Shaw et al, 2003; Takemura et al, 2001; Zhang & Bridges, 1986) B cell B cell TNF- IL-10 Inflamed synovia Cartilage loss Predisposing factors • Genetics eg.HLADR2-SLE and M. Sclerosis • HLADR3 SLE, Sjogrens, Myasthenia ,DM type 1 • HLADR4 R. Arthritis, Pemphigus vulgaris • Environmental • Sex :They tend to have female preponderance 75%. • Usually pubertal or childbearing age group • Hormonal • Infections :Bacterial or viral e.g. Klebsiella pneumoniae, Chlamydia, Coxsackie virus B. • Parasitic infections may be protective • Drugs • Toxins ,pesticides. Classification • Local eg Diabetes mellitus type 1,Graves disease, Addisons disease • Systemic eg. SLE, Rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis etc • GIT:e.g Crohns ,PBC,Autoimmune hepatitis • ENDOCRINE:e.g Type 1 diabetes,Graves disease,Hashimotos thyroiditis • SKIN e.g.pemphigus vulgaris • NERVOUS SYSTEM e.g.multiple sclerosis,CIDP • HAEMATOLOGIC e.g.autoimmune hemolytic anaemias,pernicious anaemia • RESPIRATORY e.g.COPD ,sarcoidosis Symptoms and signs • • • • • • • • Malaise Fatigue Rashes Hair loss Febrile illness Recurrent miscarriages Visual impairment Joint swellings or pain • Memory loss • Limb weakness • Strokes DIAGNOSIS • Accurate history of the illness • Physical examination • High index of suspicion LABORATORY TESTS • Varied probable depends on system involved. • Blood counts ,kidney function tests etc Serological assays for diagnosis, expensive • MRI’S • Biopsies for local involvement Treatment Non medical • • • • Multidisciplinary Counselors Physiotherapists Occupational therapists Treatment • Non immune therapy e.g. hormone replacement in thyroid disease, type 1 diabetes • Immune modulatory drugs e.g. Steroids, TNF inhibitors etc. • Anti inflammatory e.g. NSAIDS • Palliative • Together fourth largest cause of death among women. • Affects more people than heart disease in the USA • Poorly understood poorly recognised • Need for more awareness