* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Translation (Protein Synthesis)
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
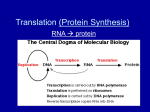
Translation (Protein Synthesis) Using the Cell’s Machinery to Make a protein The Central Dogma Characteristics of Proteins • Proteins are made by joining _______ _____ into long ___________ chains. – Polypeptides contain a combination of ____ different amino acids. – __________ of proteins: determined by ______ of amino acids. • What determines the order of amino acids in a protein? Genetic Code • The ________ of _____. – Uses the __ different bases (__, __, __, & __). – How can a code of four bases be used to make 20 different amino acids? • Genetic code read ______ letters at a time. – Each _______-letter combination in mRNA create a ______. • 3 consecutive nucleotides that specify an amino acid. • ___________ = _______:: _______ = ______ Examples UCGCGACCU This would be broken down to ____ ____ ____ This means it makes _______ ________ _______ Genetic Code • How many possible codons are there? – (____ Bases)3 = ___ • __ x __ x __ = ___ • Amino acids can be specified by ____ _____ ____ codon. – Only ___ codon = “____” • ___ = Methionine – Three codons = “_____” * Found on page 303 in your text book • ___ ____ code for aa. • Signal ___ of polypeptide. Translation • The decoding of an ____ into a ___________ chain (also known as a _________) • This takes place on which organelle?? – ________ (Protein factory) How Does Translation Occur in Your Cells? • Transcription of ___ to ____ in the _______. – mRNA transported ____ of the _______ to the _________. • Translation ______ when an _____ molecule reaches a ________. – _______ of mRNA move through, “coding” for _______ AAs to be attached to the ___________. – Ribosome ______ _____ know which amino acid to ______ each codon. • Who matches correct AA to correct codon? How Does Translation Occur in Your Cells? ! • Job of ________ RNA (__RNA). – Has ______ _____ attached to one end. – Region of _____ _________ _____ to the other. • Called __________. • _____________ to one of the mRNA _______. How Does Translation Occur in Your Cells? ! • Ribosome forms _______ bond between ___ & ___ AA. • Also, breaks ____ that held ____ to its ______ ____. – Releases tRNA. • Polypeptide chain grows until ribosome reaches _____ codon. – __________ & _____ released. Translation has 3 steps • __________ • __________ • __________ Terminology • _____: single stranded RNA takes message from nucleus to cytoplasm • ______: 3 letter base code that codes for an amino acid • _____: transfers amino acid to the ribosome to make the protein • __________: 3 letter code on the tRNA that allows it to match up with the corresponding mRNA codon • ______ _____: monomer of a protein • ____________: chain of amino acids that makes up a protein How Does Translation Occur in Your Cells? • Use vocab to label and describe what is happening mRNA Codon tRNA Anticodon Amino acid Polypeptide (Protein) Be tRNA and Put Together a Polypeptide! • Use your mRNA sequence and determine the amino acid sequence: ! CAG ACC AUG AUC CGC CAU CGU GUA UAC UAA AUC UUG ! * Remember to start translating at the first start codon and stop at the stop codon! Put these steps in order ____mRNA attaches to the ribosome ____Amino acids are connected together to form a polypeptide or protein ____ tRNA molecules line up by matching their anticodons to the mRNA codon sequence ____ tRNA pick up amino acids and bring them to the ribosome ____ mRNA detaches from ribosomes, proteins are modified and folded for use ! The above process is called ___________________ What Happens When There are Mistakes in Translation? • Cells make mistakes!!! – Anything from copying DNA to inserting an incorrect base to skipping a base • Mistakes are called _________. – Changes in the ____ sequence that affect ________ information. – Come in many shapes and sizes. • Can be ____ or ____________. • Not necessarily _____ or ____…just different! Changes in DNA = Mutations • _____ mutations affect only ___nucleotide. – _______: Results in a ______ that codes for the _____ amino acid. • Does not cause a _____ in the amino acid _________. • No ___________ _______ in protein. • Evolutionarily ________. ➢ Nucleotide cytosine is replaced by uracil, resulting in no change. Changes in DNA = Mutations • Point mutations affect only ONE nucleotide. – __________: Results in a ______ that codes for a __________ amino acid. • May lead to a ______________ protein. ➢ Nucleotide adenine is replaced by cytosine, introducing an incorrect amino acid. Changes in DNA = Mutations • Point mutations affect only ONE nucleotide. – _________: Results in a ______ that _____ ____ code for an amino acid. • Leads to protein product that is ____________ early. ➢ Nucleotide cytosine is replaced by thymine, introducing a STOP codon. Changes in DNA = Mutations • _________ mutations disrupt the “_______ ______” of the genetic message. – Affects _____ amino acid that _______ the point of the mutation. • Usually involves the _________ or ________ of a nucleotide in which the number of deleted base pairs is not divisible by ______. Point vs Frameshift Mutation THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT (normal) ! THE FAT HAT ATE THE RAT What happened? ! ! TEF ATC ATA TET HER AT What happened? Effects of Mutations ________ Mutation: occur in ___ of the cells of the body except the germ cells (_____ and ___). These are ___ ______ on to children. ! ________ Mutation: gene change in the body's _____________ cells (egg or sperm) that becomes incorporated in the ___ of ______ cell in the body. These ___ __ ______ on to further ____________. Effects of Mutations Somatic Mutation: occur in any of the cells of the body except the germ cells (sperm and egg). These are not passed on to children. ! Germline Mutation: gene change in the body's reproductive cells (egg or sperm) that becomes incorporated in the DNA of every cell in the body. These can be passed on to further generations. _____ Mutations in DNA of skin cells of sunbathing senior citizen ! _____ Mutation in DNA of brain cells in developing embryo ! _____ Mutations in DNA of sperm cells of X-ray recipient ! _____ Mutations in RNA made during transcription of lactase gene