* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ice Cream Sundae Gene Expression
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
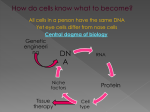
Primary Type: Lesson Plan Status: Published This is a resource from CPALMS (www.cpalms.org) where all educators go for bright ideas! Resource ID#: 75998 Ice Cream Sundae Gene Expression This lesson allows students to visualize how genes are expressed by completing the process of transcription and translation of 10 ice cream sundae genes. After students have completed the transcription and translation they will be using the expression of each gene to assemble an ice cream sundae with their coded ice cream type and toppings. The students will be able to make a connection between how genes are expressed in an ice cream sundae and relate it back to human gene expression. Subject(s): Science Grade Level(s): 9, 10, 11, 12 Intended Audience: Educators Suggested Technology: Internet Connection, Overhead Projector, Computer Media Player Instructional Time: 59 Minute(s) Resource supports reading in content area: Yes Freely Available: Yes Keywords: Codon, DNA, Genetic Code, Gene Expression, mRNA, Polypeptide Chain, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, Translation Resource Collection: FCR-STEMLearn Diversity and Ecology ATTACHMENTS Ice Cream Sundae Synthesis for cpalms.doc Amino acid code chart.docx Amino acid code wheel.docx LESSON CONTENT Lesson Plan Template: General Lesson Plan Learning Objectives: What should students know and be able to do as a result of this lesson? Student will be able to demonstrate understanding of gene expression by transcribing a DNA sequence and translating it to a protein. Prior Knowledge: What prior knowledge should students have for this lesson? This activity should be used after an initial introduction to transcription and translation as a means of understanding how genes are expressed. Students should have prior knowledge of: Base pairing rules for replication and transcription DNA replication process Students should have prior knowledge of the following benchmark from 7th grade life science SC.7.L.16.1 - Understand and explain that every organisms requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes located in the chromosomes of each cell, and that heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. Students should have prior knowledge of the following benchmarks from high school biology SC.912.L.16.3 - Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. page 1 of 5 SC.912.L.16.9 - Explain how and why the genetic code is universal and is common to almost all organisms Familiar Vocabulary: Codon, DNA, Gene, Genetic Code, mRNA, Polypeptide, rRNA, tRNA, Replication, Transcription, Translation Guiding Questions: What are the guiding questions for this lesson? How is the expression of genes displayed in individuals? (students should be able to give examples of human traits) Why is gene expression different from one individual to another? (students should be able to relate that DNA holds the codes for genes and those genes exhibit different traits) In this exercise/activity what are the types of genes to be expressed and what initiates the expression of that particular gene? (students should be able to relate that the different genes codes for different toppings of their ice cream sundae and it is initiated by the DNA sequence) Describe the process of transcription and translation. (students should be able to explain that transcription assembles a complement DNA thus creating an mRNA and translation is the process of building a protein from amino acids) Why will one person have a gene that expresses chocolate ice cream while another will have a gene that expresses vanilla? (students should be able to explain that the genes are different due to differences in the original DNA sequences) What role does base pairing play in transcription? (students should understand that A pairs with T in DNA, but there is no T in RNA - RNA contains a U: this is important to the replication process.) How does base pairing work in a cell? (students should be able to distinguish between A-T/C-G in DNA replication where RNA for Transcription and Translation A-U/CG) Teaching Phase: How will the teacher present the concept or skill to students? Students will be given a strip of DNA upon entrance into the classroom (print, copy and cut sequences into strips). Bellringer/Bellwork/Lesson Starter: Determine the number of genes their sequence contains (10) Verify that students get 10 gene sequences as their answer. Show the 7 minute video reviewing Transcription and Translation that explains gene expression. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h5mJbP23Buo The transcription and translation should draw upon students' prior knowledge of genetics and DNA structure. Explain to students that they will using the DNA code they received upon entering the class to show expression of genes in an ice cream sundae. They will be taking their code from DNA - transcribing it into mRNAs - translating it into polypeptide chains that will allow the expression of genes (topping for their ice cream sundae). Once they have completed their gene expressions they will be using it to build their own ice cream sundae based upon their expression. Guided Practice: What activities or exercises will the students complete with teacher guidance? Teacher will guide students in completion of a gene sequence. All ice cream sundaes must start with a bowl. On the board/overhead, etc write: (DNA) TACTTTCTAACT TAC TTT CTA ACT (4 codons) (mRNA)AUG AAA GAU UGA = Transcription (amino) Met- Lys- Asp- Stop (remind AUG = start) = Translation This gene codes for a bowl!!!! Inform students: for simplicity, the gene sequences given are much smaller than "real" gene sequences found in living organisms. Each gene has two versions that result in a different trait being expressed. page 2 of 5 Teacher needs to hand out the instructions and gene expression chart for students to continue with their independent practice (see attachment). Independent Practice: What activities or exercises will students complete to reinforce the concepts and skills developed in the lesson? Students will complete the transcription of their DNA code (see attachment with answer key). Teacher should walk around the room checking to make sure students are performing their transcription correctly. Students will complete the translation of their mRNA code using the genetic code chart (see attachments for sample of chart and answer key). Teacher should walk around the room checking to make sure students are performing their translations correctly. Students will determine the expression of their gene based upon the amino acid sequence they determined (see attachments for gene expression chart). Teacher should walk around the room checking to make sure students are using the chart correctly. Students will assemble their ice cream sundaes using given supplies based on the code their genes express. (It may be advantageous to recruit help/assistance from other teachers, aides, etc for cleanliness, quantity management, etc). Closure: How will the teacher assist students in organizing the knowledge gained in the lesson? Teacher will lead discussion regarding why some students have chocolate ice cream and others have vanilla as their initial gene 1 sequence. Closing questions and discussion: What in the cell is actually building a new RNA strand, and where does this take place? What in the cell is actually building the protein, and where does this take place? How could we change our ice cream activity to make it more realistic? Students will complete the activity by composing an essay with the explanation of why their ice cream sundae may/may not have looked similar to their classmates and then relate it to an explanation of why they may/may not have similar phenotypic characteristics as their parents (visable and non visable phenotypes). Note: Responses will vary based on combinations. Summative Assessment Students will construct an ice cream sundae expressing the correct genes as coded for by their given DNA strand. Essays will be read for accuracy of information and understanding of the concept of gene expression. Formative Assessment Students will be working through their DNA sequence, demonstrating an understanding of base pairing by making a mRNA strand (transcription) starting with AUG and ending with either UAA, UAG or UGA (stop codons). Students will take their mRNA code and correctly use a genetic code map to translate their codon into an amino acid. Students will take their amino acid chain (polypeptide, protein) to match the "gene" expressed for the building of their ice cream sundae. Correct coding of genes will result in an ice cream sundae with the correct components (gene expression). ** Students should be allowed to continue at their own pace while teacher answers questions and verifies correct responses for their particular code. Feedback to Students After students have completed their polypeptide sequences and before they build their Ice Cream Sundae check to verify the proteins/genes are correctly coded. Students that do not have the correct expression of their gene may go back and find their errors. ACCOMMODATIONS & RECOMMENDATIONS Accommodations: Assignment could be made into a paper activity by giving students pictures of each topping and they can build them at their desks/tables. Assignment could be made into a paper activity by having the student draw their ice cream sundae using colored pencils/crayons and blank paper. Assignment could be made where supplies are laid out, students build their own ice cream sundae and then work backwards to make a DNA code. Included are different levels of the activity to accommodate differentiation. Level 1 is mRNA code separated into codons and different gene sequences Level 2 is DNA code separated into the different gene sequences and students will need to separate into codons. Level 3 is DNA code that students will need to separate into codons. Level 4 is DNA code that students will need to separate into codons and remove "junk" DNA between each gene. Extensions: page 3 of 5 Students may do research on a human gene sequences and compare the lengths. Students may design their own lab to demonstrate gene expression. Have students make a mutation of a portion of their DNA and decipher what changes in the gene expression will occur. Have students change one of their toppings and track the mutation down to their DNA strand. Suggested Technology: Internet Connection, Overhead Projector, Computer Media Player Special Materials Needed: Copies of genetic code Copies of DNA sequences with gene chart To make ice cream sundaes: Bowls Spoons Ice Cream Chocolate Vanilla Swirl Neapolitan Various toppings (these can easily be changed out to another topping or have one gene code for an item and the other code for NOT having the item) M&M's Chocolate Chips Redi-whip Marshmallows Twix Kit Kat Chocolate Syrup Caramel Syrup Oreos Jelly Beans Snickers Bites Reeses Pieces Round Sprinkles Shaped Sprinkles Cherries Strawberries Further Recommendations: Students are good about bringing supplies if they know they get to eat :) It is advisable: to set up stations around the room for each gene expression (topping) to eliminate crowding. It has shown to work best when students begin building their sundae as they have completed their gene expression (all 10 complete), rather than waiting until all students finish. to recruit/receive aid during this activity for cleanliness and organization. Consider pulling in students from a study hall or recruit other teachers on their planning, by allowing them to build their own ice cream sundae as well. to have their closure assignment on the board/overhead before they begin assembly of the ice creams sundaes so those that finish first have something to work on while others are still finishing. SOURCE AND ACCESS INFORMATION Contributed by: Neely Calhoun Name of Author/Source: Neely Calhoun District/Organization of Contributor(s): Okaloosa Is this Resource freely Available? Yes Access Privileges: Public License: CPALMS License - no distribution - non commercial page 4 of 5 Related Standards Name SC.912.L.16.5: Description Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. page 5 of 5