* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download here - Dalibor Hrg
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Basil Hiley wikipedia , lookup
Bell test experiments wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Algorithmic cooling wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Density matrix wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Quantum decoherence wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Quantum cognition wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum and classical computing
EECS
FER 16.9.2003.
Dalibor HRG
How to think?
Review / Classical computing
Classical computing:
Turing machine (A.Turing,1937.), computability (functions and
predicates), Computational Complexity – theory of classical
computation.
Bool’s algebra and circuits, today computers, (logic).
Algorithms and complexity classes (P, P/poly, PSPACE, NP, NPcomplete, BPP,…) – measuring how efficient is algorithm, can it be
useful?
Review / Classical computing
Famous mathematical questions today:
P PSPACE ?
P NP ?
P – predicates which are decidable in polynomial
time (head moves of Turing machine)
PSPACE – predicates decidable in polynomial
space (cells on Turing machine’s track)
Review / Classical computing
NP – we can check some solution in polynomial time, but finding it, is a
difficult problem.
Predicate: F : B* B, B {0,1}
SAT , HC (hamiltonian cycle),TSP (travelling salesman problem), 3SAT,…
Karp’s reducebility:
NP – complete: each predicate from NP is reducible to 3– SAT predicate.
SAT 3 SAT , HC TSP
Review / Classical computing
Review / Classical computing
NANOTECHNOLOGY
Review / Quantum computing
(R. Feynman,Caltech,1982.) – impossibility to simulate
quantum system!
(D. Deutsch, Oxford, CQC, 1985.) – definition of Quantum
Turing machine, quantum class (BQP) and first quantum
algorithm (Deutsch-Jozsa).
Postulates of quantum mechanics, superposition of states,
interference, unitary operators on Hilbert space, tensorial
calculation,…
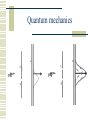
Quantum mechanics
Fundamentals: dual picture of wave and
particle.
Electron: wave or particle?
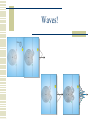
Quantum mechanics
Waves!
Secret of the electron
Does electron interfere with itself?
Quantum mechanics
Discrete values of energy and momentum.
State represent object (electron’s spin, foton’s
polarization, electron’s path,…) and its square
amplitude is probability for outcome when
measured.
Superposition of states, nothing similar in our
life.
Interference of states.
Qubit and classical bit
Bit: in a discrete moment is either “0” (0V) or
“1” (5V).
Qubit: vector in two dimensional complex space,
infinite possibilities and values.
Physically, what is the qubit?
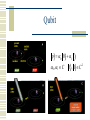
Qubit
0 0 1 1
0 , 1 C
0 , 1 C2
System of N qubits
x x
x{0,1}n
x 1
2
x{0,1}n
Unitary operators: legal operations on qubit.
†
†
U U UU I
Unitary operators: holding the lengths of the states.
Important!!
Tensors
For representing the state in a quantum register.
Example, system with two qubits:
0 ,
0 1
2
State in this systems is:
0 1 1
0
0 0 0 1
2
2
Quantum gates
Quantum circuits (one qubit): Pauli-X (UNOT), Hadamard (USRN).
(two qubits): CNOT (UCN).
U
U
NOT
NOT
10
0 1
U
SRN
2
U
NOT
U
1 1 1 0
SRN
2
U
0 1 - 1 0
SRN
2
Quantum parallelism
All possible values of the n bits argument is encoded in the
same time in the n qubits! This is a reason why the quantum
algorithms have efficiency!
n 1 1 . . . 1 11. . .1
n U U U 11 1
SRN
SRN
SRN
n1 1 0 1 0 ... 1 0
2 2
n1 11...1 11...0 ... 00...0
2 2
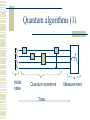
Quantum algorithms (1)
0
0
0
0
Initial
state
Quantum operators
Time
Measurement
Quantum algorithms (2)
Idea:
1. Make superposition of initial state, all values of argument
are in n qubits.
2. Calculate the function in these arguments so we have all
results in n qubits.
2 n 1
2 n 1
α
i 0
x
x
f
α
i 0
x
f ( x)
3. Interference ( Walsh-Hadamard operator on the state of n
qubits or register) of all values in the register. We obtain a
result.
(No-cloning theorem) Wooters & Zurek 1982
Unknown quantum state can not be cloned.
0 1
ψ 0 ψ ψ
Basis for quantum cryptology (or quantum key
distribution).
Quantum cryptology (1)
Alice
Quantum bits
Eve
Bob
Quantum cryptology (2)
Public channel for
authentication
Quantum teleportation Bennett 1982
It is possible to send qubit without sending it,
with two classical bits as a help.
Classical bits.
Alice
EPR
Alice & Bob share EPR (Einstein,Podolsky,Rosen) pair.
Bob
Present algorithms?
Deutsch-Josza
3
Shor - Factoring 1994., O n
Kitaev - Factoring
Grover - Database searching 1996., O
Grover - Estimating median
N
Who is trying?
• Aarhus
• Berkeley
• Caltech
• Cambridge
• College Park
• Delft
• DERA (U.K.)
• École normale supérieure
• Geneva
• HP Labs (Palo Alto and Bristol)
• Hitachi
• IBM Research (Yorktown Heights and
Palo Alto)
• Innsbruck
• Los Alamos National Labs
• McMaster
• Max Planck Institute-Munich
• Melbourne
• MIT
• NEC
• New South Wales
• NIST
• NRC
• Orsay
• Oxford
• Paris
• Queensland
• Santa Barbara
• Stanford
• Toronto
• Vienna
• Waterloo
• Yale
• many others…
Corporations?
Corporations?