QUANTUM COMPUTING
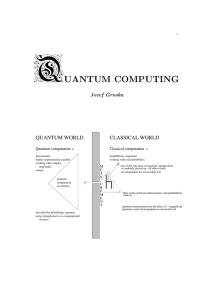
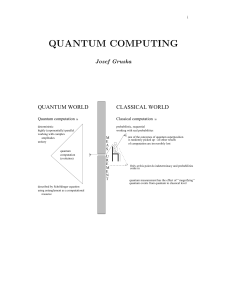
... Quantum computing is a potential. There are already results convincingly demonstrating that for some important practical problems quantum computers are theoretically exponentially more powerful than classical computers. Such results, as Shor's factorization algorithm, can be seen as apt killers for ...
... Quantum computing is a potential. There are already results convincingly demonstrating that for some important practical problems quantum computers are theoretically exponentially more powerful than classical computers. Such results, as Shor's factorization algorithm, can be seen as apt killers for ...
agostino pr´astaro
... PDE’s, formulated by Prástaro, is applied to some interesting PDE’s. In particular, in the first part a new general theory is developed that recognizes natural webs structures on PDE’s. These structures are important to solve (generalized) Cauchy problems. Some applications interesting PDE’s of the ...
... PDE’s, formulated by Prástaro, is applied to some interesting PDE’s. In particular, in the first part a new general theory is developed that recognizes natural webs structures on PDE’s. These structures are important to solve (generalized) Cauchy problems. Some applications interesting PDE’s of the ...
Lecture Notes for Physics 229: Quantum Information and Computation
... The moral we draw is that \information is physical." and it is instructive to consider what physics has to tell us about information. But fundamentally, the universe is quantum mechanical. How does quantum theory shed light on the nature of information? It must have been clear already in the early d ...
... The moral we draw is that \information is physical." and it is instructive to consider what physics has to tell us about information. But fundamentally, the universe is quantum mechanical. How does quantum theory shed light on the nature of information? It must have been clear already in the early d ...