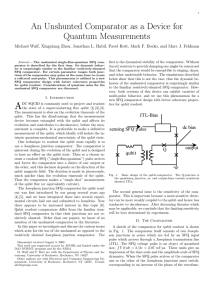
Chapter 3: Quantum Computing
... entangled states can be compressed to fewer qubits. This quantum compression could have important applications in practice, where the number of usable qubits is very limited. Schumacher [101] considered compression and decompression of a noiseless source of n quantum bits (qubits), each sampled inde ...
... entangled states can be compressed to fewer qubits. This quantum compression could have important applications in practice, where the number of usable qubits is very limited. Schumacher [101] considered compression and decompression of a noiseless source of n quantum bits (qubits), each sampled inde ...
Quantum Information Processing: Algorithms, Technologies and
... for transmission of classical information, still in certain cases entangled states can be compressed to fewer qubits. This quantum compression could have important applications in practice, where the number of usable qubits is very limited. Schumacher [101] considered compression and decompression o ...
... for transmission of classical information, still in certain cases entangled states can be compressed to fewer qubits. This quantum compression could have important applications in practice, where the number of usable qubits is very limited. Schumacher [101] considered compression and decompression o ...
Lecture Notes for Physics 229: Quantum Information and Computation
... Furthermore, in quantum theory, noncommuting observables cannot simultaneously have precisely de ned values (the uncertainty principle), and in fact performing a measurement of one observable A will necessarily in uence the outcome of a subsequent measurement of an observable B , if A and B do not c ...
... Furthermore, in quantum theory, noncommuting observables cannot simultaneously have precisely de ned values (the uncertainty principle), and in fact performing a measurement of one observable A will necessarily in uence the outcome of a subsequent measurement of an observable B , if A and B do not c ...
quant-ph/0608013 PDF
... From the seminal ideas of Feynman [1] and until now, quantum information and computation [2] has been a rapidly evolving field. While at the beginning, physicists looked at quantum mechanics as a theoretical framework to describe the fundamental processes that take place in Nature, it was during the ...
... From the seminal ideas of Feynman [1] and until now, quantum information and computation [2] has been a rapidly evolving field. While at the beginning, physicists looked at quantum mechanics as a theoretical framework to describe the fundamental processes that take place in Nature, it was during the ...