* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BI 112 Instructor: Waite Exam #4 Study Guide Cell Membrane
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
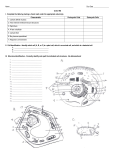
BI 112 Instructor: Waite Exam #4 Study Guide Cell Membrane • Know the 4 critical functions of cell membranes • Understand the primary structural component of the membrane is the phospholipid, and understand the unique properties of the phospholipid that make it perfectly suited to the plasma membrane • Know the other components of the cell membrane and their functions • Know that the cell membrane is fundamentally non-polar • Be able to label the components of the cell membrane on the diagrams on pages 4-5 and 4-7 of your study guide • Know the 5 functions of membrane proteins • Know the functions of cholesterol in the membrane • Know the functions of carbohydrates in the membrane Cytoplasm • Know the two components of the cytoplasm (cytosol and organelles) • Know the specific benefit of membrane-bound organelles that allows eukaryotic cells to be larger than prokaryotic cells • Be able to explain the relationship between surface area and volume, and why overall cells stay small • Know which organelles are membrane-bound and which are not • Know that a cell’s primary function is the production and management of protein • Know the path of protein production, and the role of each organelle in that process • Know what determines whether a protein will be produced by a free ribosome or by a ribosome on the rER • Know the function of the sER • Know what happens to proteins in the Golgi, and where vesicles from the Golgi end up • Know what the following vesicles are, and their functions: lysosome, peroxisome, phagosome, endosome • Know the structure and function of the mitochondria; know its role in the use of oxygen and in the generation of CO2 and ATP • Know the 4 primary components of the cytoskeleton (microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments, thick filaments), and the principal functions of each component • Know the 3 cellular extensions (cilia, flagella, and microvilli); know that all of them are derived from the cytoskeleton and are based on microtubules; know the differences between them, and principal functions of each • Know that the nucleus is membrane-bound, what it contains, and why this material is so important BI 112 Instructor: Waite Exam #4 Study Guide Crossing Cell Membranes • Know the definition of diffusion • Know how to determine the direction that a dissolved solute will flow through a semipermeable membrane • Know how solute concentration changes when the solute is an electrolyte vs a nonelectrolyte • Know that all types of diffusion are passive, and what that term means • Know the difference between simple diffusion, channel-mediated diffusion, and carriermediated diffusion • Know what type of solutes are able to pass through a cell membrane by simple diffusion and which must pass through by facilitated diffusion • Know the factors that influence the rate of diffusion • Know the difference between diffusion and osmosis; know when osmosis occurs compared to diffusion • Know how to determine the direction of osmotic water flow between two different solutions • Know the difference between a penetrating or diffusible solute and a non-penetrating or non-diffusible solute • Know the definition of tonicity and how to determine whether a given solution is hypertonic, isotonic, or hypotonic • Know the effect that tonicity has on a living cell (shrinks, swells) and why • Know the different types of energy-dependent membrane transport (primary active transport, secondary active transport, filtration, endocytosis, exocytosis) • Know the type of energy that drives each type of energy-dependent transport (ATP, solute gradient, pressure gradient) • Know the difference between symport and antiport • Know what clathrin is, and the process of clathrin-mediated endocytosis; know what happens to the clathrin once the vesicle has entered the cell • Know the difference between receptor-mediated endocytosis, phagocytosis, and pinocytosis; know what each process brings into the cell and how the vesicles differ in size • Know the process of exocytosis Membrane Potential • Be able to define membrane potential • Know that ions of like charge are repelled by each other; ions of opposite charge are attracted to each other • Be able to describe how membrane potential develops • Know some of the ways that cells use membrane potential BI 112 Instructor: Waite Exam #4 Study Guide DNA • Know that only DNA is required for genetic information storage and transfer; protein is not involved • Know that most DNA is located in the nucleus • Know that the DNA molecule is large and delicate and must be protected • Know that DNA is highly organized and wrapped around proteins called histones; the DNAhistone complex is known as chromatin • Know that DNA is subdivided into chromosomes of varying size • Know the definition of a gene and a locus • Know that the locus of a specific gene will be the same for every member of a species • Know that DNA codes for individual amino acids with a DNA triplet • Know the difference between the template strand and the coding strand of DNA • Know that genetic information is transferred to the cytoplasm in the form of a temporary copy known as mRNA • Know that the process of the information encoding by DNA being copied into mRNA is called transcription; know the steps of transcription and what happens at each step; know the enzyme complex involved in transcription is called RNA polymerase • Know that the DNA triplet emerges in mRNA as a codon • Know the different bases used in DNA vs RNA and how they pair • Understand how RNA is processed after transcription before it is translated; know the difference between introns and exons, which one codes for protein, and the 2 main advantages of storing coding information in this way • Know what alternative splice products or splice isoforms are • Know the definition of translation • Be able to describe how all 3 forms of RNA work together to translate genetic code into protein • Know the structure of a tRNA molecule (what an anticodon is and what it does; that a tRNA is attached to a specific amino acid) • Be able to describe the basic process of translation • Be able to translate a given set of codons when provided with the universal genetic code • Know the definition of a mutation and some possible sources of mutation • Know the 4 different types of mutation discussed in class, including a frameshift (which is really a possible consequence of one of the other types of mutation) • Be able to describe potential consequences for the cell of any one of these mutations